Abstract
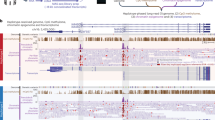
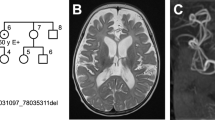
X-linked congenital cerebellar ataxia is a heterogeneous nonprogressive neurodevelopmental disorder with onset in early childhood. We searched for a genetic cause of this condition, previously reported in a Buryat pedigree of Mongolian ancestry from southeastern Russia. Using whole-genome sequencing on Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform, we found a missense mutation in the ABCB7 (ABC-binding cassette transporter B7) gene, encoding a mitochondrial transporter, involved in heme synthesis and previously associated with sideroblastic anemia and ataxia. The mutation resulting in a substitution of a highly conserved glycine to serine in position 682 is apparently a major causative factor of the cerebellar hypoplasia/atrophy found in affected individuals of a Buryat family who had no evidence of sideroblastic anemia. Moreover, in these affected men we also found the genetic defects in two other genes closely linked to ABCB7 on chromosome X: a deletion of a genomic region harboring the second exon of copper-transporter gene (ATP7A) and a complete deletion of PGAM4 (phosphoglycerate mutase family member 4) retrogene located in the intronic region of the ATP7A gene. Despite the deletion, eliminating the first of six metal-binding domains in ATP7A, no signs for Menkes disease or occipital horn syndrome associated with ATP7A mutations were found in male carriers. The role of the PGAM4 gene has been previously implicated in human reproduction, but our data indicate that its complete loss does not disrupt male fertility. Our finding links cerebellar pathology to the genetic defect in ABCB7 and ATP7A structural variant inherited as X-linked trait, and further reveals the genetic heterogeneity of X-linked cerebellar disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Bergmann C, Zerres K, Senderek J et al: Oligophrenin 1 (OPHN1 gene mutation causes syndromic X-linked mental retardation with epilepsy, rostral ventricular enlargement and cerebellar hypoplasia. Brain 2003; 126: 1537–1544.
Najm J, Horn D, Wimplinger I et al: Mutations of CASK cause an X-linked brain malformation phenotype with microcephaly and hypoplasia of the brainstem and cerebellum. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1065–1067.
Nadif Kasri N, Nakano-Kobayashi A, Malinow R, Li B, Van Aelst L : The Rho-linked mental retardation protein oligophrenin-1 controls synapse maturation and plasticity by stabilizing AMPA receptors. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 1289–1302.
Zanni G, Calì T, Kalscheuer VM et al: Mutation of plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase isoform 3 in a family with X-linked congenital cerebellar ataxia impairs Ca2+ homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 14514–14519.
Caramins M, Colebatch JG, Bainbridge MN et al: Exome sequencing identification of a GJB1 missense mutation in a kindred with X-linked spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA-X1). Hum Mol Genet 2013; 22: 4329–4338.
Illarioshkin SN, Tanaka H, Markova ED, Nikolskaya NN, Ivanova-Smolenskaya IA, Tsuji S : X-linked nonprogressive congenital cerebellar hypoplasia: clinical description and mapping to chromosome Xq. Ann Neurol 1996; 40: 75–83.
Van Oven M, Kayser M : Updated comprehensive phylogenetic tree of global human mitochondrial DNA variation. Hum Mutat 2009; 30: E386–E394.
Derenko M, Malyarchuk B, Grzybowski T et al: Origin and post-glacial dispersal of mitochondrial DNA haplogroups C and D in northern Asia. PLoS One 2010; 5: e15214.
Ruiz-Pesini E, Lott MT, Procaccio V et al: An enhanced MITOMAP with a global mtDNA mutational phylogeny. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: D823–D828.
Rootsi S, Zhivotovsky LA, Baldovic M et al: A counter-clockwise northern route of the Y-chromosome haplogroup N from Southeast Asia towards Europe. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 204–211.
International Society of Genetic Genealogy Y-DNA Haplogroup Tree 2014, Version: 9.117, 9 November 2014. Available at: http://www.isogg.org/tree/ (accessed 13 November 2014).
Kharkov VN, Khamina KV, Medvedeva OF, Simonova KV, Eremina ER, Stepanov VA : Gene pool of Buryats: clinal variability and territorial subdivision based on data of Y-chromosome markers. Russ J Genet 2014; 50: 180–190.
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E et al: The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 2010; 20: 1297–1303.
Ye K, Schulz MH, Long Q, Apweiler R, Ning Z : Pindel: a pattern growth approach to detect break points of large deletions and medium sized insertions from paired-end short reads. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 2865–2871.
1000 Genomes Project Consortium, Abecasis GR, Auton A et al: An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 2012; 491: 56–65.
Miller JA, Ding S-L, Sunkin SM et al: Transcriptional landscape of the prenatal human brain. Nature 2014; 508: 199–206.
Hawrylycz M, Ng L, Feng D, Sunkin S, Szafer A, Dang C The Allen Brain Atlas; in: Kasabov N (ed): Springer Handbook of Bio-/Neuroinformatics. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2014, pp 1111–1126.
Stamm S, Zhu J, Nakai K, Stoilov P, Stoss O, Zhang MQ : An alternative-exon database and its statistical analysis. DNA Cell Biol 2000; 19: 739–756.
Nurtdinov RN, Neverov AD, Mal’ko DB et al: EDAS, databases of alternatively spliced human genes. Biofizika 2006; 51: 589–592.
Allikmets R, Raskind WH, Hutchinson A et al: Mutation of a putative mitochondrial iron transporter gene (ABC7 in X-linked sideroblastic anemia and ataxia (XLSA/A). Hum Mol Genet 1999; 8: 743–749.
Kelley LA, Sternberg MJE : Protein structure prediction on the Web: a case study using the Phyre server. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 363–371.
Kumar P, Henikoff S, Ng PC : Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 1073–1081.
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P et al: A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 248–249.
Salamov AA, Nishikawa T, Swindells MB : Assessing protein coding region integrity in cDNA sequencing projects. Bioinformatics 1998; 14: 384–390.
UniProt Consortium: Activities at the Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: D191–D198.
Kapushesky M, Emam I, Holloway E et al: Gene expression atlas at the European bioinformatics institute. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38: D690–D698.
Shulha HP, Crisci JL, Reshetov D et al: Human-specific histone methylation signatures at transcription start sites in prefrontal neurons. PLoS Biol 2012; 10: e1001427.
Okuda H, Tsujimura A, Irie S et al: A single nucleotide polymorphism within the novel sex-linked testis-specific retrotransposed PGAM4 gene influences human male fertility. PLoS One 2012; 7: e35195.
Jin Q, Pan H, Wang B et al: The PGAM4 gene in non-obstructive azoospermia. Syst Biol Reprod Med 2013; 59: 179–183.
Zutz A, Gompf S, Schägger H, Tampé R : Mitochondrial ABC proteins in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1787: 681–690.
Hollenstein K, Dawson RJP, Locher KP : Structure and mechanism of ABC transporter proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2007; 17: 412–418.
Bekri S, Kispal G, Lange H et al: Human ABC7 transporter: gene structure and mutation causing X-linked sideroblastic anemia with ataxia with disruption of cytosolic iron-sulfur protein maturation. Blood 2000; 96: 3256–3264.
Maguire A, Hellier K, Hammans S, May A : X-linked cerebellar ataxia and sideroblastic anaemia associated with a missense mutation in the ABC7 gene predicting V411L. Br J Haematol 2001; 115: 910–917.
Hellier KD, Hatchwell E, Duncombe AS, Kew J, Hammans SR : X-linked sideroblastic anaemia with ataxia: another mitochondrial disease? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 2001; 70: 65–69.
Pagon RA, Bird TD, Detter JC, Pierce I : Hereditary sideroblastic anaemia and ataxia: an X linked recessive disorder. J Med Genet 1985; 22: 267–273.
D’Hooghe M, Selleslag D, Mortier G et al: X-linked sideroblastic anemia and ataxia: a new family with identification of a fourth ABCB7 gene mutation. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2012; 16: 730–735.
Tchan MC, Wilcken B, Christodoulou J : The mild form of Menkes disease: a 34 year progress report on the original case. JIMD Rep 2013; 9: 81–84.
Donsante A, Tang J, Godwin SC et al: Differences in ATP7A gene expression underlie intrafamilial variability in Menkes disease/occipital horn syndrome. J Med Genet 2007; 44: 492–497.
Tümer Z, Birk Møller L, Horn N : Screening of 383 unrelated patients affected with Menkes disease and finding of 57 gross deletions in ATP7A. Hum Mutat 2003; 22: 457–464.
Jiang L, Ranganathan P, Lu Y, Kim C, Collins JF : Exploration of the copper-related compensatory response in the Belgrade rat model of genetic iron deficiency. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2011; 301: G877–G886.
Monnot AD, Behl M, Ho S, Zheng W : Regulation of brain copper homeostasis by the brain barrier systems: effects of Fe-overload and Fe-deficiency. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2011; 256: 249–257.
Pyatskowit JW, Prohaska JR : Iron injection restores brain iron and hemoglobin deficits in perinatal copper-deficient rats. J Nutr 2008; 138: 1880–1886.
Reeves PG, DeMars LCS : Signs of iron deficiency in copper-deficient rats are not affected by iron supplements administered by diet or by injection. J Nutr Biochem 2006; 17: 635–642.
Pyatskowit JW, Prohaska JR : Copper deficient rats and mice both develop anemia but only rats have lower plasma and brain iron levels. Comp Biochem Physiol C 2008; 147: 316–323.
Collins JF, Prohaska JR, Knutson MD : Metabolic crossroads of iron and copper. Nutr Rev 2010; 68: 133–147.
Lizio M, Harshbarger J, Shimoji H et al: Gateways to the FANTOM5 promoter level mammalian expression atlas. Genome Biol 2015; 16: 22.
Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Oksvold P et al: Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteom 2014; 13: 397–406.
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS et al: The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 2002; 12: 996–1006.
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP et al: ClustalW and ClustalX version 2. Bioinformatics 2007; 23: 2947–2948.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Government of the Russian Federation (No. 14.B25.31.0033). We thank Oleg Balanovsky and Michail Ignashkin for assistance with ancestry and paternity analysis and Walter J Lukiw, Arya Byragin and anonymous reviewers for providing helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Protasova, M., Grigorenko, A., Tyazhelova, T. et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies a novel ABCB7 gene mutation for X-linked congenital cerebellar ataxia in a large family of Mongolian ancestry. Eur J Hum Genet 24, 550–555 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.139
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.139
This article is cited by
-
Novel genes bearing mutations in rare cases of early-onset ataxia with cerebellar hypoplasia
European Journal of Human Genetics (2022)
-
Chronic Pressure Overload Results in Deficiency of Mitochondrial Membrane Transporter ABCB7 Which Contributes to Iron Overload, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Metabolic Shift and Worsens Cardiac Function
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Clinical and genetic aspects of defects in the mitochondrial iron–sulfur cluster synthesis pathway
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2018)