Abstract
Purpose
To investigate longitudinal changes in peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness in patients with retinitis pigmentosa (RP).
Methods
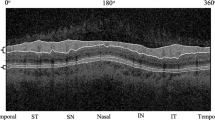
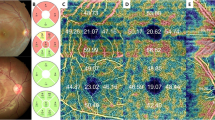
We re-examined 103 RP patients whose RNFL thickness was previously examined and reported. RNFL thickness was measured using Stratus optical coherence tomography and was compared with the previous measurements. The results were also compared with that of previously reported normal subjects. Association between the decrease rate and visual acuity, and visual field was also investigated.
Results
The mean follow-up period was 56.9 months. After excluding the patients in whom RNFL images were of poor quality, 88 patients were eventually analyzed. The average RNFL thickness decreased from 105.8 to 98.2 μm during the period, with the average rate of decrease being 1.6 μm/year. The decrease in RNFL was more evident in superior and inferior sectors. Cross-sectional linear regression analysis also revealed an age-dependent decrease in RNFL, with the slower rate of decrease being 0.94 μm/year. The decrease in RNFL thickness was significantly faster than that reported in normal subjects. The decrease rate was not associated with visual functions.
Conclusion
Age-dependent RNFL thinning occurs at a faster rate in RP patients as compared with that in normal subjects. The result supports the notion that pathologic changes involve inner retina as well as outer retina in eyes with RP. Considering the discrepancy in the rate of RNFL thinning estimated from trend analysis and longitudinal measurement, care should be taken when interpreting the result of cross-sectional analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hartong DT, Berson EL, Dryja TP . Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 2006; 368 (9549): 1795–1809.
Sahni JN, Angi M, Irigoyen C, Semeraro F, Romano MR, Parmeggiani F . Therapeutic challenges to retinitis pigmentosa: from neuroprotection to gene therapy. Curr Genomics 2011; 12 (4): 276–284.
Weiland JD, Cho AK, Humayun MS . Retinal prostheses: current clinical results and future needs. Ophthalmology 2011; 118 (11): 2227–2237.
Kuno N, Fujii S . Biodegradable intraocular therapies for retinal disorders: progress to date. Drugs Aging 2010; 27 (2): 117–134.
Hood DC, Lin CE, Lazow MA, Locke KG, Zhang X, Birch DG . Thickness of receptor and post-receptor retinal layers in patients with retinitis pigmentosa measured with frequency-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009; 50 (5): 2328–2336.
Huang Q, Chowdhury V, Coroneo MT . Evaluation of patient suitability for a retinal prosthesis using structural and functional tests of inner retinal integrity. J Neural Eng 2009; 6 (3): 035010.
Stone JL, Barlow WE, Humayun MS, de Juan E, Milam AH . Morphometric analysis of macular photoreceptors and ganglion cells in retinas with retinitis pigmentosa. Arch Ophthalmol 1992; 110 (11): 1634–1639.
Santos A, Humayun MS, de Juan E, Greenburg RJ, Marsh MJ, Klock IB et al. Preservation of the inner retina in retinitis pigmentosa. A morphometric analysis. Arch Ophthalmol 1997; 115 (4): 511–515.
Humayun MS, Prince M, de Juan E, Barron Y, Moskowitz M, Klock IB et al. Morphometric analysis of the extramacular retina from postmortem eyes with retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999; 40 (1): 143–148.
Eng JG, Agrawal RN, Tozer KR, Ross-Cisneros FN, Dagnelie G, Greenberg RJ et al. Morphometric analysis of optic nerves and retina from an end-stage retinitis pigmentosa patient with an implanted active epiretinal array. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011; 52 (7): 4610–4616.
Walia S, Fishman GA, Edward DP, Lindeman M . Retinal nerve fiber layer defects in RP patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48 (10): 4748–4752.
Walia S, Fishman GA . Retinal nerve fiber layer analysis in RP patients using Fourier-domain OCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008; 49 (8): 3525–3528.
Hwang YH, Kim SW, Kim YY, Na JH, Kim HK, Sohn YH . Optic nerve head, retinal nerve fiber layer, and macular thickness measurements in young patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Curr Eye Res 2012; 37 (10): 914–920.
Oishi A, Otani A, Sasahara M, Kurimoto M, Nakamura H, Kojima H et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Eye 2009; 23 (3): 561–566.
Anastasakis A, Genead MA, McAnany JJ, Fishman GA . Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with retinitis pigmentosa using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Retina 2012; 32 (2): 358–363.
Garcia-Martin E, Pinilla I, Sancho E, Almarcegui C, Dolz I, Rodriguez-Mena D et al. Optical coherence tomography in retinitis pigmentosa: reproducibility and capacity to detect macular and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness alterations. Retina 2012; 32 (8): 1581–1591.
Leung CK, Yu M, Weinreb RN, Ye C, Liu S, Lai G et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a prospective analysis of age-related loss. Ophthalmology 2012; 119 (4): 731–737.
Rizzo JF . Embryology anatomy and physiology of the afferent visual pathway. In: Miller NR, Newman NJ, (eds), Walsh, Hoyt’s Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology 6th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2005 pp 3–82.
Parikh RS, Parikh SR, Sekhar GC, Prabakaran S, Babu JG, Thomas R . Normal age-related decay of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Ophthalmology 2007; 114 (5): 921–926.
Budenz DL, Anderson DR, Varma R, Schuman J, Cantor L, Savell J et al. Determinants of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmology 2007; 114 (6): 1046–1052.
Sung KR, Wollstein G, Bilonick RA, Townsend KA, Ishikawa H, Kagemann L et al. Effects of age on optical coherence tomography measurements of healthy retinal nerve fiber layer, macula, and optic nerve head. Ophthalmology 2009; 116 (6): 1119–1124.
Feuer WJ, Budenz DL, Anderson DR, Cantor L, Greenfield DS, Savell J et al. Topographic differences in the age-related changes in the retinal nerve fiber layer of normal eyes measured by Stratus optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma 2011; 20 (3): 133–138.
Cheung CY, Leung CK, Lin D, Pang CP, Lam DS . Relationship between retinal nerve fiber layer measurement and signal strength in optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2008; 115 (8): 1347–1351 1351 e1341-1342.
Vizzeri G, Bowd C, Medeiros FA, Weinreb RN, Zangwill LM . Effect of signal strength and improper alignment on the variability of stratus optical coherence tomography retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements. Am J Ophthalmol 2009; 148 (2): 249–255 e241.
Knight OJ, Chang RT, Feuer WJ, Budenz DL . Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer measurements using time domain and spectral domain optical coherent tomography. Ophthalmology 2009; 116 (7): 1271–1277.
Sung KR, Kim DY, Park SB, Kook MS . Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Cirrus HD and Stratus optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2009; 116 (7): 1264–1270 1270 e1261.
Vizzeri G, Weinreb RN, Gonzalez-Garcia AO, Bowd C, Medeiros FA, Sample PA et al. Agreement between spectral-domain and time-domain OCT for measuring RNFL thickness. Br J Ophthalmol 2009; 93 (6): 775–781.
Seibold LK, Mandava N, Kahook MY . Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normal eyes using time-domain and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 2010; 150 (6): 807–814.
Tamaki M, Matsuo T . Optical coherence tomographic parameters as objective signs for visual acuity in patients with retinitis pigmentosa, future candidates for retinal prostheses. J Artif Organs 2011; 14 (2): 140–150.
Sliesoraityte I, Troeger E, Bernd A, Kurtenbach A, Zrenner E . Correlation between spectral domain OCT retinal nerve fibre layer thickness and multifocal pattern electroretinogram in advanced retinitis pigmentosa. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012; 723: 471–478.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
N Yoshimura is a paid advisory board member of Nidek and Topcon. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Eye website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oishi, A., Ogino, K., Nakagawa, S. et al. Longitudinal analysis of the peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thinning in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Eye 27, 597–604 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.34
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.34
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of imaging biomarkers and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in RPGR-associated retinitis pigmentosa
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2021)
-
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography to Estimate Retinal Blood Flow in Eyes with Retinitis Pigmentosa
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Structure-function correlations in Retinitis Pigmentosa patients with partially preserved vision: a voxel-based morphometry study
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Increased aqueous flare is associated with thickening of inner retinal layers in eyes with retinitis pigmentosa
Scientific Reports (2016)