Abstract
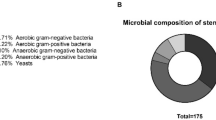
This study provides a comprehensive survey of the spatial and temporal bacterial composition of biliary stent biofilms. The bacterial diversity, distribution and dynamics of 59 biliary and 4 pancreatic stent communities from 40 patients being treated at two different hospitals, which implant stents either simultaneously or consecutively, were characterized by single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis. Fifty-one phylotypes belonging to 5 bacterial phyla and 24 bacterial families were detected across 63 stents. This is a much broader diversity than previously detected through culture-dependent methods, particularly in regard to the diversity of obligate anaerobes. Stent bacterial diversity was patient-dependent and more similar when stents were implanted simultaneously rather than consecutively. Stent bacterial community composition differed between hospitals specifically because of the difference in abundance of Bifidobacteria. Co-colonization of Veillonella sp., Streptococcus anginosus and organisms closely related to Fusobacterium nucleatum revealed a potentially important attachment and survival strategy that has yet to be reported in biliary stents. This work reveals a more complete survey of the identities of bacterial species that form biofilms in biliary stents, their co-colonization patterns and the natural variation in species composition between different patients, hospitals and locations along the stent. Consideration of the community composition from individual patients will allow tailoring of prophylactic antibiotic treatments and thus will make the management of stent biofilms more effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Ashelford KE, Chuzhanova NA, Fry JC, Jones AJ, Weightman AJ . (2006). New screening software shows that most recent large 16S rRNA gene clone libraries contain chimeras. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 5734–5741.
Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D . (2001). The control of false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat 29: 1165–1188.
Bolstad AI, Jensen HB, Bakken V . (1996). Taxonomy, biology, and periodontal aspects of Fusobacterium nucleatum. Clin Microbiol Rev 9: 55–71.
Chao A . (1987). Estimating the population size for capture-recapture data with unequal catchability. Biometrics 43: 783–791.
Clarke KR . (1993). Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecol 18: 117–143.
Clarke KR, Warwick RM . (2001). Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation. PRIMER-E Ltd: Plymouth, UK.
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM et al. (2007). The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res 35: D169–D172.
Demuth DR, Duan Y, Brooks W, Holmes AR, McNab R, Jenkinson HF . (1996). Tandem genes encode cell-surface polypeptides SspA and SspB which mediate adhesion of the oral bacterium Streptococcus gordonii to human and bacterial receptors. Mol Microbiol 20: 403–413.
Di Rosa R, Basoli A, Donelli G, Penni A, Salvatori FM, Fiocca F et al. (1999). A microbiological and morphological study of blocked biliary stents. Microb Ecol Health Dis 11: 84–88.
Diaz PI, Chalmers NI, Rickard AH, Kong C, Milburn CL, Palmer Jr RJ et al. (2006). Molecular characterization of subject-specific oral microflora during initial colonization of enamel. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 2837–2848.
Donelli G, Guaglianone E, Di Rosa R, Fiocca F, Basoli A . (2007). Plastic biliary stent occlusion: factors involved and possible preventive approaches. Clin Med Res 5: 53–60.
Dowidar N, Kolmos HJ, Lyon H, Matzen P . (1991). Clogging of biliary endoprostheses. A morphologic and bacteriologic study. Scand J Gastroenterol 26: 1137–1144.
Duncan SH, Scott KP, Ramsay AG, Harmsen HJ, Welling GW, Stewart CS et al. (2003). Effects of alternative dietary substrates on competition between human colonic bacteria in an anaerobic fermentor system. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 1136–1142.
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M et al. (2005). Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308: 1635–1638.
Gibson GR, Beatty ER, Wang X, Cummings JH . (1995). Selective stimulation of bifidobacteria in the human colon by oligofructose and inulin. Gastroenterology 108: 975–982.
Gueimonde M, Tolkko S, Korpimaki T, Salminen S . (2004). New real-time quantitative PCR procedure for quantification of bifidobacteria in human fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 4165–4169.
Hayashi H, Takahashi R, Nishi T, Sakamoto M, Benno Y . (2005). Molecular analysis of jejunal, ileal, caecal and recto-sigmoidal human colonic microbiota using 16S rRNA gene libraries and terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Med Microbiol 54: 1093–1101.
Hold GL, Pryde SE, Russell VJ, Furrie E, Flint HJ . (2002). Assessment of microbial diversity in human colonic samples by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39: 33–39.
Hughes CV, Kolenbrander PE, Andersen RN, Moore LV . (1988). Coaggregation properties of human oral Veillonella spp. relationship to colonization site and oral ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol 54: 1957–1963.
Jado I, Fenoll A, Casal J, Pérez A . (2001). Identification of the psaA gene, coding for pneumococcal surface adhesin A, in viridans group streptococci other than Streptococcus pneumoniae. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 8: 895–898.
Kleessen B, Hartmann L, Blaut M . (2001). Oligofructose and long-chain inulin: influence on the gut microbial ecology of rats associated with a human faecal flora. Br J Nutr 86: 291–300.
Klijn A, Mercenier A, Arigoni F . (2005). Lessons from the genomes of bifidobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29: 491–509.
Kolenbrander PE, Andersen RN, Blehert DS, Egland PG, Foster JS, Palmer Jr RJ . (2002). Communication among oral bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66: 486–505.
Lane DJ . (1991). 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds). Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics, John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, pp 115–148.
Larsen LA, Christiansen M, Vuust J, Andersen PS . (2001). Recent developments in high-throughput mutation screening. Pharmacogenomics 2: 387–399.
Lay C, Rigottier-Gois L, Holmstrom K, Rajilic M, Vaughan EE, de Vos WM et al. (2005). Colonic microbiota signatures across five northern European countries. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 4153–4155.
Leung JW, Liu Y, Chan RC, Tang Y, Mina Y, Cheng AF et al. (2000). Early attachment of anaerobic bacteria may play an important role in biliary stent blockage. Gastrointest Endosc 52: 725–729.
Liu Y, Leung JW, Libby ED, Cotton PB . (1996). Update on biliary stent occlusion. Chinese Med J—Peking 109: 892–896.
Mangin I, Suau A, Magne F, Garrido D, Gotteland M, Neut C et al. (2006). Characterization of human intestinal bifidobacteria using competitive PCR and PCR-TTGE. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55: 28–37.
Masco L, Huys G, De Brandt E, Temmerman R, Swings J . (2005). Culture-dependent and culture-independent qualitative analysis of probiotic products claimed to contain bifidobacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 102: 221–230.
Matsuda Y, Shimakura K, Akamatsu T . (1991). Factors affecting the patency of stents in malignant biliary obstructive disease: univariate and multivariate analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 86: 843–849.
Molinari G, Pugliese V, Schito GC, Guzman CA . (1996). Bacteria involved in the blockage of biliary stents and their susceptibility to antibacterial agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol 15: 88–92.
Nocker A, Burr M, Camper AK . (2007). Genotypic microbial community profiling: a critical technical review. Microb Ecol 54: 276–289.
Nyvad B, Kilian M . (1990). Comparison of the initial streptococcal microflora on dental enamel in caries-active and in caries-inactive individuals. Caries Res 24: 267–272.
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T . (1989). Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2766–2770.
Palmer Jr RJ, Diaz PI, Kolenbrander PE . (2006). Rapid succession within the Veillonella population of a developing human oral biofilm in situ. J Bacteriol 188: 4117–4124.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T . (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA.
Schloss PD, Handelsman J . (2005). Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 1501–1506.
Schmalenberger A, Schwieger F, Tebbe CC . (2001). Effect of primers hybridizing to different evolutionarily conserved regions of the small-subunit rRNA gene in PCR-based microbial community analyses and genetic profiling. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: 3557–3563.
Schwieger F, Tebbe CC . (1998). A new approach to utilize PCR-single-strand-conformation polymorphism for 16S rRNA gene-based microbial community analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 64: 4870–4876.
Smalla K, Oros-Sichler M, Milling A, Heuer H, Baumgarte S, Becker R et al. (2007). Bacterial diversity of soils assessed by DGGE, T-RFLP and SSCP fingerprints of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene fragments: do the different methods provide similar results? J Microbiol Methods 69: 470–479.
Speer AG, Cotton PB, Rode J, Seddon AM, Neal CR, Holton J et al. (1988). Biliary stent blockage with bacterial biofilm. A light and electron microscopy study. Ann Intern Med 108: 546–553.
Stone L, Roberts A . (1990). The checkerborad score and species distribution. Oecologia 85: 74–79.
Sung JJ . (1995). Bacterial biofilm and clogging of biliary stents. J Ind Microbiol 15: 152–155.
Sung JY, Leung JW, Shaffer EA, Lam K, Olson ME, Costerton JW . (1992). Ascending infection of the biliary tract after surgical sphincterotomy and biliary stenting. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 7: 240–245.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S . (2007). MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24: 1596–1599.
Ulrich W . (2008). Pairs–a FORTRAN program for studying pair-wise species associations in ecological matrices www.uni.torun.pl/∼ulrichw.
Ulrich W, Zalewski M . (2006). Abundance and co-occurrence patterns of core and satellite species of ground beetles on small lake islands. OIKOS 114: 338–348.
Vaughan EE, de Vries MC, Zoetendal EG, Ben-Amor K, Akkermans AD, de Vos WM . (2002). The intestinal LABs. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 82: 341–352.
Wang M, Ahrne S, Jeppsson B, Molin G . (2005). Comparison of bacterial diversity along the human intestinal tract by direct cloning and sequencing of 16S rRNA genes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54: 219–231.
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR . (2007). Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: 5261–5267.
Wilson M . (2005). Microbial Inhabitants of Humans—Their Ecology and Role in Health and Disease. Cambridge University Press: New York, USA.
Witzig R, Junca H, Hecht HJ, Pieper DH . (2006). Assessment of toluene/biphenyl dioxygenase gene diversity in benzene-polluted soils: links between benzene biodegradation and genes similar to those encoding isopropylbenzene dioxygenases. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 3504–3514.
Yu JL, Andersson R, Ljungh A . (1996). Protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion to biliary stent materials. J Surg Res 62: 69–73.
Zhang H, Tsang TK, Jack CA . (2003). Bile glycoprotein mucin in sludge occluding biliary stent. J Lab Clin Med 142: 58–65.
Zhang H, Tsang TK, Jack CA, Pollack J . (2002). Role of bile mucin in bacterial adherence to biliary stents. J Lab Clin Med 139: 28–34.
Zoetendal EG, Akkermans ADL, Vliet WMA-v, Arjan J, de Visser GM, de Vos WM . (2001). The host genotype affects the bacterial community in the human gastrointestinal tract. Microb Ecol Health D 13: 129–134.
Zoetendal EG, von Wright A, Vilpponen-Salmela T, Ben-Amor K, Akkermans AD, de Vos WM . (2002). Mucosa-associated bacteria in the human gastrointestinal tract are uniformly distributed along the colon and differ from the community recovered from feces. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 3401–3407.
Acknowledgements
We thank Agnes Waliczek for excellent technical assistance and Werner Ulrich for support in statistical analyses. Frank Schwieger is acknowledged for providing A. radiobacter DNA and Andrew Oxley for critically reading the manuscript. This work was funded by the European Graduate School ‘Pseudomonas: Pathogenicity and Biotechnology’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The ISME Journal website (http://www.nature.com/ismej)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheithauer, B., Wos-Oxley, M., Ferslev, B. et al. Characterization of the complex bacterial communities colonizing biliary stents reveals a host-dependent diversity. ISME J 3, 797–807 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.36