Abstract
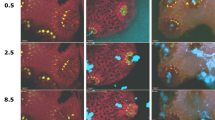
In many ecological communities, predation has a key role in regulating community structure or function. Although predation has been extensively explored in animals and microbial eukaryotes, predation by bacteria is less well understood. Here we show that predatory bacteria of the genus Halobacteriovorax are prevalent and active predators on the surface of several genera of reef-building corals. Across a library of 198 16S rRNA samples spanning three coral genera, 79% were positive for carriage of Halobacteriovorax. Cultured Halobacteriovorax from Porites asteroides corals tested positive for predation on the putative coral pathogens Vibrio corallyticus and Vibrio harveyii. Co-occurrence network analysis showed that Halobacteriovorax’s interactions with other bacteria are influenced by temperature and inorganic nutrient concentration, and further suggested that this bacterial predator’s abundance may be driven by prey availability. Thus, animal microbiomes can harbor active bacterial predators, which may regulate microbiome structure and protect the host by consuming potential pathogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Baum JK, Worm B . (2009). Cascading top-down effects of changing oceanic predator abundances. J Anim Ecol 78: 699–714.
Brussaard CPD, Wilhelm SW, Thingstad F, Weinbauer MG, Bratbak G, Heldal M et al. (2008). Global-scale processes with a nanoscale drive: the role of marine viruses. ISME J 2: 575–578.
De Boer W, Wagenaar A-M, Klein Gunnewiek PJA, van Veen JA . (2007). In vitro suppression of fungi caused by combinations of apparently non-antagonistic soil bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59: 177–185.
Faust K, Raes J . (2012). Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nat Rev Microbiol 10: 538–550.
Faust K, Sathirapongsasuti JF, Izard J, Segata N, Gevers D, Raes J et al. (2012). Microbial co-occurrence relationships in the human microbiome. PLoS Comput Biol 8: e1002606.
Fuhrman JA . (1999). Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects. Nature 399: 541–548.
Hosokawa T, Kikuchi Y, Nikoh N, Shimada M, Fukatsu T . (2006). Strict host-symbiont cospeciation and reductive genome evolution in insect gut bacteria. PLoS Biol 4: e337.
Li H, Chen C, Sun Q, Liu R, Cai J . (2014). Bdellovibrio and like organisms enhanced growth and survival of Penaeus monodon and altered bacterial community structures in its rearing water. Appl Environ Microbiol 80: 6346–6354.
Martínez JM, Schroeder DC, Larsen A, Bratbak G, Wilson WH . (2007). Molecular dynamics of Emiliania huxleyi and cooccurring viruses during two separate mesocosm studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: 554–562.
Martínez V, Jurkevitch E, García JL, Prieto MA . (2013). Reward for bdellovibrio bacteriovorus for preying on a polyhydroxyalkanoate producer. Environ Microbiol 15: 1204–1215.
Pineiro S, Chauhan A, Berhane T-K, Athar R, Zheng G, Wang C et al. (2013). Niche partition of bacteriovorax operational taxonomic units along salinity and temporal gradients in the chesapeake bay reveals distinct estuarine strains. Microb Ecol 65: 652–660.
Pineiro SA, Stine OC, Chauhan A, Steyert SR, Smith R, Williams HN . (2007). Global survey of diversity among environmental saltwater Bacteriovoracaceae. Environ Microbiol 9: 2441–2450.
Richards GP, Fay JP, Dickens KA, Parent MA, Soroka DS, Boyd EF . (2012). Predatory bacteria as natural modulators of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in seawater and oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol 78: 7455–7466.
Schoeffield AJ, Williams HN . (1990). Efficiencies of recovery of bdellovibrios from brackish- water environments by using various bacterial species as prey. Appl Envir Microbiol 56: 230–236.
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13: 2498–2504.
Sweet M, Bythell J . (2015). White syndrome in Acropora muricata: nonspecific bacterial infection and ciliate histophagy. Mol Ecol 24: 1150–1159.
Vega Thurber RL, Burkepile DE, Fuchs C, Shantz AA, McMinds R, Zaneveld JR . (2014). Chronic nutrient enrichment increases prevalence and severity of coral disease and bleaching. Glob Chang Biol 20: 544–554.
Wegley L, Edwards R, Rodriguez-Brito B, Liu H, Rohwer F . (2007). Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community associated with the coral Porites astreoides. Environ Microbiol 9: 2707–2719.
Williams HN, Lymperopoulou DS, Athar R, Chauhan A, Dickerson TL, Chen H et al. Halobacteriovorax, an underestimated predator on bacteria: potential impact relative to viruses on bacterial mortality. ISME J e-pub ahead of print 7 August 2015; doi:10.1038/ismej.2015.129.
Acknowledgements
We thank numerous volunteers for assistance with the experiment and the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary for permits (FKNMS-2009-047 and FKNMS-2011-090). This research was supported by National Science Foundation grant OCE-1130786 to DEB and RVT, Florida International University, and Oregon State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welsh, R., Zaneveld, J., Rosales, S. et al. Bacterial predation in a marine host-associated microbiome. ISME J 10, 1540–1544 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.219
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.219
This article is cited by
-
Community and single cell analyses reveal complex predatory interactions between bacteria in high diversity systems
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Host-specific symbioses and the microbial prey of a pelagic tunicate (Pyrosoma atlanticum)
ISME Communications (2021)
-
Identification and analysis of the biological activity of the new strain of Pseudoalteromonas piscicida isolated from the hemal fluid of the bivalve Modiolus kurilensis (F. R. Bernard, 1983)
Archives of Microbiology (2021)
-
Bradymonabacteria, a novel bacterial predator group with versatile survival strategies in saline environments
Microbiome (2020)
-
A predator-prey interaction between a marine Pseudoalteromonas sp. and Gram-positive bacteria
Nature Communications (2020)