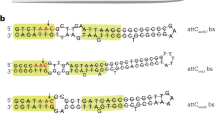
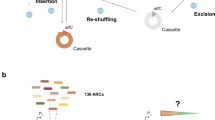
Abstract
Integrons are genetic elements that are common in bacteria and are hotspots for genome evolution. They facilitate the acquisition and reassembly of gene cassettes encoding a variety of functions, including drug resistance. Despite their importance in clinical settings, the selective forces responsible for the evolution and maintenance of integrons are poorly understood. We present a mathematical model of integron evolution within bacterial populations subject to fluctuating antibiotic exposures. Bacteria carrying a functional integrase that mediates reshuffling of cassette genes and thereby modulates gene expression patterns compete with bacteria without a functional integrase. Our results indicate that for a wide range of parameters, the functional integrase can be stably maintained in the population despite substantial fitness costs. This selective advantage arises because gene-cassette shuffling generates genetic diversity, thus enabling the population to respond rapidly to changing selective pressures. We also show that horizontal gene transfer promotes stable maintenance of the integrase and can also lead to de novo assembly of integrons. Our model generates testable predictions for integron evolution, including loss of functional integrases in stable environments and selection for intermediate gene-shuffling rates in changing environments. Our results highlight the need for experimental studies of integron population biology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abel zur Wiesch P, Kouyos R, Engelstädter J, Regoes RR, Bonhoeffer S . (2011). Population biological principles of drug-resistance evolution in infectious diseases. Lancet Infect Dis 11: 236–247.
Baquero F, Tedim AP, Coque TM . (2013). Antibiotic resistance shaping multi-level population biology of bacteria. Front Microbiol 4: 15.
Bergstrom CT, Lipsitch M, Levin BR . (2000). Natural selection, infectious transfer and the existence conditions for bacterial plasmids. Genetics 155: 1505–1519.
Bissonnette L, Champetier S, Buisson JP, Roy PH . (1991). Characterization of the nonenzymatic chloramphenicol resistance (cmlA) gene of the In4 integron of Tn1696: similarity of the product to transmembrane transport proteins. J Bacteriol 173: 4493–4502.
Boucher Y, Cordero OX, Takemura A, Hunt DE, Schliep K, Bapteste E et al. (2011). Local mobile gene pools rapidly cross species boundaries to create endemicity within global Vibrio cholerae populations. MBio 2: e00335–10.
Boucher Y, Labbate M, Koenig JE, Stokes HW . (2007). Integrons: mobilizable platforms that promote genetic diversity in bacteria. Trends Microbiol 15: 301–309.
Bouma JE, Lenski RE . (1988). Evolution of a bacteria plasmid association. Nature 335: 351–352.
Cagle CA, Shearer JE, Summers AO . (2011). Regulation of the integrase and cassette promoters of the class 1 integron by nucleoid-associated proteins. Microbiology 157: 2841–2853.
Cambray G, Guerout AM, Mazel D . (2010). Integrons. Annu Rev Genet 44: 141–166.
Cambray G, Sanchez-Alberola N, Campoy S, Guerin E, Da Re S, Gonzalez-Zorn B et al. (2011). Prevalence of SOS-mediated control of integron integrase expression as an adaptive trait of chromosomal and mobile integrons. Mob DNA 2: 6.
Collis CM, Grammaticopoulos G, Briton J, Stokes HW, Hall RM . (1993). Site-specific insertion of gene cassettes into integrons. Mol Microbiol 9: 41–52.
Collis CM, Hall RM . (1992). Site-specific deletion and rearrangement of integron insert genes catalyzed by the integron DNA integrase. J Bacteriol 174: 1574–1585.
Collis CM, Hall RM . (1995). Expression of antibiotic-resistance genes in the integrated cassettes of integrons. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39: 155–162.
Collis CM, Kim MJ, Stokes HW, Hall RM . (2002). Integron-encoded IntI integrases preferentially recognize the adjacent cognate attI site in recombination with a 59-be site. Mol Microbiol 46: 1415–1427.
Collis CM, Recchia GD, Kim MJ, Stokes HW, Hall RM . (2001). Efficiency of recombination reactions catalyzed by class 1 integron integrase IntI1. J Bacteriol 183: 2535–2542.
Coyne S, Guigon G, Courvalin P, Perichon B . (2010). Screening and quantification of the expression of antibiotic resistance genes in Acinetobacter baumannii with a microarray. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54: 333–340.
Dahlberg C, Chao L . (2003). Amelioration of the cost of conjugative plasmid carriage in Eschericha coli K12. Genetics 165: 1641–1649.
Davies J, Davies D . (2010). Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74: 417–433.
Denamur E, Matic I . (2006). Evolution of mutation rates in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 60: 820–827.
Dubois V, Debreyer C, Litvak S, Quentin C, Parissi V . (2007). A new in vitro strand transfer assay for monitoring bacterial class 1 integron recombinase IntI1 activity. PLoS One 2: e1315.
Dubois V, Debreyer C, Quentin C, Parissi V . (2009). In vitro recombination catalyzed by bacterial class 1 integron integrase IntI1 involves cooperative binding and specific oligomeric intermediates. PLoS One 4: e5228.
Elsaied H, Stokes HW, Kitamura K, Kurusu Y, Kamagata Y, Maruyama A . (2011). Marine integrons containing novel integrase genes, attachment sites, attI, and associated gene cassettes in polluted sediments from Suez and Tokyo Bays. ISME J 5: 1162–1177.
Escudero JA, Loot C, Nivina A, Mazel D . (2015). The integron: adaptation on demand. Microbiol Spectr 3: MDNA3-0019–2014.
Fluit AC, Schmitz FJ . (1999). Class 1 integrons, gene cassettes, mobility, and epidemiology. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 18: 761–770.
Gillings MR . (2014). Integrons: past, present, and future. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 78: 257–277.
Gillings MR, Gaze WH, Pruden A, Smalla K, Tiedje JM, Zhu YG . (2014). Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J 9: 1269–1279.
Gillings MR, Holley MP, Stokes HW, Holmes AJ . (2005). Integrons in Xanthomonas: a source of species genome diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 4419–4424.
Gillings MR, Xuejun D, Hardwick SA, Holley MP, Stokes HW . (2009). Gene cassettes encoding resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds: a role in the origin of clinical class 1 integrons? ISME J 3: 209–215.
Guerin E, Cambray G, Sanchez-Alberola N, Campoy S, Erill I, Da Re S et al. (2009). The SOS response controls integron recombination. Science 324: 1034–1034.
Guerin E, Jove T, Tabesse A, Mazel D, Ploy MC . (2011). High-level gene cassette transcription prevents integrase expression in class 1 integrons. J Bacteriol 193: 5675–5682.
Gullberg E, Albrecht LM, Karlsson C, Sandegren L, Andersson DI . (2014). Selection of a multidrug resistance plasmid by sublethal levels of antibiotics and heavy metals. MBio 5: e01918–14.
Hall RM . (2012). Integrons and gene cassettes: hotspots of diversity in bacterial genomes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1267: 71–78.
Hansson K, Sundstrom L, Pelletier A, Roy PH . (2002). IntI2 integron integrase in Tn7. J Bacteriol 184: 1712–1721.
Harms K, Starikova I, Johnsen PJ . (2013). Costly Class-1 integrons and the domestication of the the functional integrase. Mob Genet Elements 3: e24774.
Jacquier H, Zaoui C, Sanson-Le Pors MJ, Mazel D, Bercot B . (2009). Translation regulation of integrons gene cassette expression by the attC sites. Mol Microbiol 72: 1475–1486.
Johnsen PJ, Townsend JP, Bohn T, Simonsen GS, Sundsfjord A, Nielsen KM . (2009). Factors affecting the reversal of antimicrobial-drug resistance. Lancet Infect Dis 9: 357–364.
Jove T, Da Re S, Denis F, Mazel D, Ploy MC . (2010). Inverse correlation between promoter strength and excision activity in class 1 integrons. PLoS Genet 6: e1000793.
Koenig JE, Bourne DG, Curtis B, Dlutek M, Stokes HW, Doolittle WF et al. (2011). Coral-mucus-associated Vibrio integrons in the Great Barrier Reef: genomic hotspots for environmental adaptation. ISME J 5: 962–972.
Levin BR, Baquero F, Johnsen PJ . (2014). A model-guided analysis and perspective on the evolution and epidemiology of antibiotic resistance and its future. Curr Opin Microbiol 19: 83–89.
Loot C, Ducos-Galand M, Escudero JA, Bouvier M, Mazel D . (2012). Replicative resolution of integron cassette insertion. Nucleic Acids Res 40: 8361–8370.
Naas T, Mikami Y, Imai T, Poirel L, Nordmann P . (2001). Characterization of In53, a class 1 plasmid- and composite transposon-located integron of Escherichia coli which carries an unusual array of gene cassettes. J Bacteriol 183: 235–249.
Nemergut DR, Robeson MS, Kysela RF, Martin AP, Schmidt SK, Knight R . (2008). Insights and inferences about integron evolution from genomic data. BMC Genomics 9: 261.
Partridge SR, Tsafnat G, Coiera E, Iredell JR . (2009). Gene cassettes and cassette arrays in mobile resistance integrons. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33: 757–784.
Raynes Y, Sniegowski PD . (2014). Experimental evolution and the dynamics of genomic mutation rate modifiers. Heredity 113: 375–380.
Recchia GD, Stokes HW, Hall RM . (1994). Characterisation of specific and secondary recombination sites recognised by the integron DNA integrase. Nucleic Acids Res 22: 2071–2078.
Rowe-Magnus DA, Guerout AM, Biskri L, Bouige P, Mazel D . (2003). Comparative analysis of superintegrons: engineering extensive genetic diversity in the Vibrionaceae. Genome Res 13: 428–442.
San Millan AS, Pena-Miller R, Toll-Riera M, Halbert ZV, Mclean AR, Cooper BS et al. (2014). Positive selection and compensatory adaptation interact to stabilize non-transmissible plasmids. Nat Commun 5: 5208.
Servedio MR, Brandvain Y, Dhole S, Fitzpatrick CL, Goldberg EE, Stern CA et al. (2014). Not just a theory–the utility of mathematical models in evolutionary biology. PLoS Biol 12: e1002017.
Starikova I, Al-Haroni M, Werner G, Roberts AP, Sorum V, Nielsen KM et al. (2013). Fitness costs of various mobile genetic elements in Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis. J Antimicrob Chemother 68: 2755–2765.
Starikova I, Harms K, Haugen P, Lunde TT, Primicerio R, Samuelsen O et al. (2012). A Trade-off between the fitness cost of functional integrases and long-term stability of integrons. PLoS Pathog 8: e1003043.
Stokes HW, Hall RM . (1989). A novel family of potentially mobile dna elements encoding site-specific gene-integration functions - integrons. Mol Microbiol 3: 1669–1683.
Stokes HW, Hall RM . (1991). Sequence analysis of the inducible chloramphenicol resistance determinant in the Tn1696 integron suggests regulation by translational attenuation. Plasmid 26: 10–19.
Szekeres S, Dauti M, Wilde C, Mazel D, Rowe-Magnus DA . (2007). Chromosomal toxin-antitoxin loci can diminish large-scale genome reductions in the absence of selection. Mol Microbiol 63: 1588–1605.
Top EM, Springael D . (2003). The role of mobile genetic elements in bacterial adaptation to xenobiotic organic compounds. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14: 262–269.
Touchon M, Bobay LM, Rocha EPC . (2014). The chromosomal accommodation and domestication of mobile genetic elements. Curr Opin Microbiol 22: 22–29.
Weldhagen GF . (2004). Integrons and beta-lactamases–a novel perspective on resistance. Int J Antimicrob Agents 23: 556–562.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the editor and three anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments on a previous version of this paper. This work was supported by an Australian Research Council Future Fellowship to JE (project number FT140100907), a postdoctoral fellowship by the Danish National Research Foundation to KH and grants by the Norwegian Research Council (project number 204263) and the Northern Norway Regional Health Authority to PJJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website .
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engelstädter, J., Harms, K. & Johnsen, P. The evolutionary dynamics of integrons in changing environments. ISME J 10, 1296–1307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.222
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.222
This article is cited by
-
Petroleum exploitation enriches the sulfonamide resistance gene sul2 in offshore sediments
Journal of Oceanology and Limnology (2021)
-
Promoter activity of ORF-less gene cassettes isolated from the oral metagenome
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Class 1 integrons are low-cost structures in Escherichia coli
The ISME Journal (2017)
-
Lateral Antimicrobial Resistance Genetic Transfer is active in the open environment
Scientific Reports (2017)