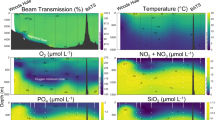
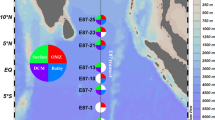
Abstract
Dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) supports a significant amount of heterotrophic production in the ocean. Yet, to date, the identity and diversity of microbial groups that transform DON are not well understood. To better understand the organisms responsible for transforming high molecular weight (HMW)-DON in the upper ocean, isotopically labeled protein extract from Micromonas pusilla, a eukaryotic member of the resident phytoplankton community, was added as substrate to euphotic zone water from the central California Current system. Carbon and nitrogen remineralization rates from the added proteins ranged from 0.002 to 0.35 μmol C l−1 per day and 0.03 to 0.27 nmol N l−1 per day. DNA stable-isotope probing (DNA-SIP) coupled with high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA genes linked the activity of 77 uncultivated free-living and particle-associated bacterial and archaeal taxa to the utilization of Micromonas protein extract. The high-throughput DNA-SIP method was sensitive in detecting isotopic assimilation by individual operational taxonomic units (OTUs), as substrate assimilation was observed after only 24 h. Many uncultivated free-living microbial taxa are newly implicated in the cycling of dissolved proteins affiliated with the Verrucomicrobia, Planctomycetes, Actinobacteria and Marine Group II (MGII) Euryarchaeota. In addition, a particle-associated community actively cycling DON was discovered, dominated by uncultivated organisms affiliated with MGII, Flavobacteria, Planctomycetes, Verrucomicrobia and Bdellovibrionaceae. The number of taxa assimilating protein correlated with genomic representation of TonB-dependent receptor (TBDR)-encoding genes, suggesting a possible role of TBDR in utilization of dissolved proteins by marine microbes. Our results significantly expand the known microbial diversity mediating the cycling of dissolved proteins in the ocean.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abram D, Castro e Melo J, Chou D . (1974). Penetration of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus into host cells. J Bacteriol 118: 663–680.
Alderkamp AC, Sintes E, Herndl GJ . (2006). Abundance and activity of major groups of prokaryotic plankton in the coastal North Sea during spring and summer. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 45: 237–246.
Aluwihare LI, Meador TB . (2009) Chemical composition of marine dissolved organic nitrogen. In: Capone DG, Bronk DA, Mulholland MR, Carpenter EJ (eds), Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, pp 95–133.
Aluwihare LI, Repeta DJ, Pantoja S, Johnson CG . (2005). Two chemically distinct pools of organic nitrogen accumulate in the ocean. Science 308: 1007–1010.
Apprill A, McNally S, Parsons R, Weber L . (2015). Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 75: 129–137.
Bano N, Hollibaugh JT . (2002). Phylogenetic composition of bacterioplankton assemblages from the Arctic Ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 505–518.
Billen G, Fontigny A . (1987). Dynamics of a Phaeocystis dominated spring bloom in Belgian coastal waters. II. Bacterioplankton dynamics. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 37: 249–257.
Bronk DA . (2002) Dynamics of DON. In: Hansell DA, Carlson CA (eds), Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic matter. Academic Press: San diego, CA, USA, pp 153–247.
Bronk DA, Steinberg DK . (2009) Nitrogen regeneration. In: Capone DG, Bronk DA, Mulholland MR, Carpenter EJ (eds), Nitrogen in the Marine Environment. Academic Pres: San Diego, CA, USA, pp 385–449.
Buckley DH, Huangyutitham V, Hsu SF, Nelson TA . (2007a). Stable isotope probing with 15N2 reveals novel noncultivated diazotrophs in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: 3196–3204.
Buckley DH, Huangyutitham V, Hsu SF, Nelson TA . (2007b). Stable isotope probing with 15N achieved by disentangling the effects of genome G+C content and isotope enrichment on DNA density. Appl Environ Microbiol 73: 3189–3195.
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK et al. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7: 335–336.
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N et al. (2012). Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6: 1621–1624.
Cardman Z, Arnosti C, Durbin A, Ziervogel K, Cox C, Steen AD et al. (2014). Verrucomicrobia are candidates for polysaccharide-degrading bacterioplankton in an arctic fjord of Svalbard. Appl Environ Microbiol 80: 3749–3756.
Carlson CA, Ducklow H . (1995). Dissolved organic carbon in the upper ocean of the central equatorial Pacific Ocean, 1992: Daily and finescale vertical variations. Deep Sea Res II 42: 639–656.
Cho BC, Azam F . (1988). Major role of bacteria in biogeochemical fluxes in the ocean's interior. Nature 332: 441–443.
Collins CA, Pennington JT, Castro CG, Rago TA, Chavez FP . (2003). The California Current system off Monterey, California: physical and biological coupling. Deep Sea Res II 50: 2389–2404.
Cottrell MT, Kirchman DL . (2000). Natural assemblages of marine proteobacteria and members of the Cytophaga-Flavobacteria cluster consuming low- and high- molecular weight dissolved organic matter. Appl Environ Microbiol 66: 1692–1697.
Crump BC, Armbrust V, Baross JA . (1999). Phylogenetic analysis of particle-attached and free-living bacterial communities in the Columbia River, its estuary, and the adjacent ocean. App Environ Microbiol 65: 3192–3204.
Cuvelier ML, Allen AE, Monier A, McCrow JP, Messie M et al. (2010). Targeted metagenomics and ecology of globally important uncultured eukaryotic phytoplankton. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 107: 14679–14684.
DeLong EF, Franks DG, Alldredge AL . (1993). Phylogenetic diversity of aggregate-attached vs. free-living marine bacterial assemblages. Limnol Oceanogr 38: 924–934.
Dugdale RC, Goering JJ . (1967). Uptake of new and regenerated forms of nitrogen in primary productivity. Limnol Oceanogr 12: 196–206.
Dunford EA, Neufeld JD . (2010). DNA stable-isotope probing (DNA-SIP). J Vis Exp; e-pub ahead of print 2 August 2010; doi:10.3791/2027.
Dupont CL, Rusch DB, Yooseph S, Lombardo MJ, Richter RA, Valas R et al. (2012). Genomic insights to SAR86, an abundant and uncultivated marine bacterial lineage. ISME J 6: 1186–1199.
Edgar RC . (2010). Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26: 2460–2461.
Fenton AK, Lambert C, Wagstaff PC, Sockett RE . (2010). Manipulating each MreB of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus gives diverse morphological and predatory phenotypes. J Bacteriol 192: 1299–1311.
Fernandez-Gomez B, Richter M, Schuler M, Pinhassi J, Acinas SG, Gonzalez JM et al. (2012). Ecology of marine Bacteroidetes: a comparative genomics approach. ISME J 7: 1026–1037.
Fogg GE . (1971). The extracellular products of algae in freshwater. Arch Hydrobiol 5: 1–25.
Freitas S, Hatosy S, Fuhrman JA, Huse SM, Welch DB, Sogin ML et al. (2014). Global distribution and diversity of marine Verrucomicrobia. ISME J 6: 1499–1505.
Frigaard NU, Martinez A, Mincer TJ, DeLong EF . (2006). Proteorhodopsin lateral gene transfer between marine planktonic Bacteria and Archaea. Nature 439: 847–850.
Fuchs BM, Woebken D, Zubkov MV, Burkill P, Amann R . (2005). Molecular identification of picoplankton populations in contrasting waters of the Arabian Sea. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 39: 145–157.
Fuerst JA . (1995). The planctomycetes: emerging models for microbial ecology, evolution and cell biology. Microbiology 141: 1493–1506.
Fuhrman JA . (1999). Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects. Nature 399: 541–548.
Giovannoni SJ, Britschgi TB, Moyer CL, Field KG . (1990). Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature 345: 60–63.
Guillard RRL, Hargraves PE . (1993). Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte. Phycologia 32: 234–236.
Heijs SK, Laverman AM, Forney LJ, Hardoim PR, van Elsas JD . (2008). Comparison of deep-sea sediment microbial communities in the Eastern Mediterranean. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64: 362–377.
Herleman DP, Lundin D, Labrenz M, Jürgens K, Zheng Z, Aspeborg H et al. (2013). Metagenomic de novo assembly of an aquatic representative of the verrucomicrobial class Spartobacteria. MBio 4: e00569–12.
Hobbie JE, Crawford CC, Webb KL . (1968). Amino acid flux in an estuary. Science 159: 1463–1464.
Hollibaugh JT, Azam F . (1983). Microbial degradation of proteins in seawater. Limnol Oceanogr 28: 1104–1116.
Holmes RM, Aminot A, Kerouel R, Hooker BA, Petersen BJ . (1999). A simple and precise method for measuring ammonium in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56: 1801–1808.
Hungate BA, Mau RL, Schwartz E, Caporaso JG, Dijkstra P, van Gestel N et al. (2015). Quantitative microbial ecology through stable isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 81: 7570–7581.
Iverson V, Morris RM, Frazar CD, Berthiaume CT, Morales RL, Armbrust EV . (2012). Untangling genomes from metagenomes: revealing an uncultured class of marine Euryarchaeota. Science 335: 587–590.
Kabisch A, Otto A, König S, Becher D, Albrecht D, Schüler M et al. (2014). Functional characterization of polysaccharide utilization loci in the marine Bacteroidetes 'Gramella forsetti' KT0803. IMSE J 8: 1492–1502.
Karl DM, Björkman KM, Dore JE, Fujieki L, Hebel DV, Houlihan T et al. (2001). Ecological nitrogen-to-phosphorus stoichiometry at station ALOHA. Deep Sea Res II 48: 1529–1566.
Keil RG, Kirchman DL . (1993). Dissolved combined amino acids: chemical form and utilization by marine bacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 38: 1256–1270.
Keil RG, Kirchman DL . (1994). Abiotic transformation of labile protein to refractory protein in sea water. Marine Chemistry 45: 187–196.
Keil RG, Tsamakis E, Hedges JI . (2000) Early diagenesis of particulate amino acids in marine systems. In: Goodfriend GA, Fogel MJ, Collins ML, Macko SA, Wehmiller JF (eds), Perspectives in Amino Acid and Protein Geochemistry. Oxford University Press: New York, pp 69–82.
Kerouel R, Aminot A . (1997). Fluorometric determination of ammonia in sea and estuarine waters by direct segmented flow analysis. Marine Chemistry 57: 265–275.
Kirchman DL . (2000) Uptake and regeneration of inorganic nutrients by marine heterotrophic bacteria. In: Kirchman DL. (ed) Microbial Ecology of the Oceans. Wiley-Liss: New York, pp 261–288.
Kirchman DL . (2002). The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39: 91–100.
Kozich JJ, Westcott SL, Baxter NT, Highlander SK, Schloss PD . (2013). Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl Environ Microbiol 79: 5112–5120.
Kuznetsova M, Lee C . (2002). Dissolved free and combined amino acids in nearshore seawater, sea surface microlayers and foams: Influence of extracellular hydrolysis. Aquatic Science 64: 1–17.
Lee C, Wakeham SG, Hedges JI . (2000). Composition and flux of particulate amino acids and chloropigments in equatorial Pacific seawater and sediments. Deep Sea Res I 47: 1535–1568.
Lipschultz F. (2008). Isotope tracer methods for studies of the marine nitrogen cycle. In: Capone DG, Bronk DA, Mulholland MR, Carpenter EJ (eds), Nitrogen in the Marine Environment, 2nd Edition, Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, pp 1345–1384.
Liu Z, Liu S, Liu J, Gardner WS . (2013). Differences in peptide decomposition rates and pathways between hypoxic and oxic coastal environments. Marine Chemistry 157: 67–77.
Lloyd KG, Schreiber L, Petersen DG, Kjeldsen KU, Lever MA, Steen AD et al. (2013). Predominant archaea in marine sediments degrade detrital proteins. Nature 496: 215–218.
Loh AN, Bauer JE, Druffel ER . (2004). Variable ageing and storage of dissolved organic components in the open ocean. Nature 430: 877–881.
Malmstrom RR, Cottrell MT, Elifantz H, Kirchman DL . (2005). Biomass production and assimilation of dissolved organic matter by SAR11 bacteria in the Northwest Atlantic Ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 2979–2986.
Malmstrom RR, Kiene RP, Cottrell MT, Kirchman DL . (2004). Contribution of SAR11 bacteria to dissolved dimethylsulfoniopropionate and amino acid uptake in the North Atlantic ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 4129–4135.
Mayali X, Stewart B, Mabery S, Weber PK Temporal succession in carbon incorporation from macromolecules by particle-attached bacteria in marine microcosms. Environ Microbiol Rep; e-pub ahead of print 3 November 2015; doi:10.1111/1758-2229.12352.
McCarren J, Becker JW, Repeta DJ, Shi Y, Young CR, Malmstrom RR et al. (2010). Microbial community transcriptomes reveal microbes and metabolic pathways associated with dissolved organic matter turnover in the sea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 16420–16427.
McCarthy M, Benner R, Lee C, Fogel MJ . (2007). Amino acid nitrogen isotopic fractionation patterns as indicators of heterotrophy in plankton, particulate, and dissolved organic matter. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 71: 4727–4744.
McCarthy M, Pratum T, Hedges JI, Benner R . (1997). Chemical composition of dissolved organic nitrogen in the ocean. Nature 390: 150–153.
McCarthy MD, Benner R, Lee C, Hedges JI, Fogel ML . (2004). Amino acid carbon isotopic fractionation patterns in oceanic dissolved organic matter: an unaltered photoautotrophic source for dissolved organic nitrogen in the ocean? Marine Chemistry 92: 123–124.
McCarthy MD, Hedges JI, Benner R . (1998). Major bacterial contribution to marine dissolved organic nitrogen. Science 281: 231–234.
Meador TB, Aluwihare LI, Mahaffey C . (2007). Isotopic heterogeneity and cycling of organic nitrogen in the oligotrophic ocean. Limnol Oceanogr 430: 877–881.
Morando M, Capone DG in review. Intraclade heterogeneity in nitrogen utilization by marine prokaryotes revealed using stable isotope probing coupled with tag sequencing (Tag-SIP).
Morris RM, Longnecker K, Giovannoni SJ . (2006). Pirellula and OM43 are among the dominant lineages identified in an Oregon coast diatom bloom. Environ Microbiol 8: 1361–1370.
Morris SA, Radajewski S, Willison TW, Murrell JC . (2002). Identification of the functionally active methanotroph population in a peat soil microcosm by stable-isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 1446–1453.
Nagata T, Fukuda R, Koike I, Kogure K, Kirchman DL . (1998). Degradation by bacteria of membrane and soluble protein in seawater. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 14: 29–37.
Nagata T, Meon B, Kirchman DL . (2003). Microbial degradation of peptidoglycan in seawater. Limnol Oceanogr 48: 745–754.
Nelson CE, Carlson CA . (2012). Tracking differential incorporation of dissolved organic carbon types among diverse lineages of Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Environ Microbiol 14: 1500–1516.
Neufeld JD, Vohra J, Dumont MG, Lueders T, Manefield M, Friedrich MW et al. (2007). DNA stable-isotope probing. Nat Protoc 2: 860–866.
Nguyen RT, Harvey RH . (1997). Protein and amino acid cycling during phytoplankton decomposition in oxic and anoxic waters. Organic Geochemistry 27: 115–128.
Nikrad MP, Cottrell MT, Kirchman DL . (2012). Abundance and single-cell activity of heterotrophic bacterial groups in the western Arctic Ocean in summer and winter. Appl Environ Microbiol 78: 2402–2409.
Nikrad MP, Cottrell MT, Kirchman DL . (2014). Uptake of dissolved organic carbon by gammaproteobacterial subgroups in coastal waters of the West Antarctic Peninsula. Appl Environ Microbiol 80: 3362–3368.
Noinaj N, Guillier M, Barnard TJ, Buchanan SK . (2010). TonB-dependent transporters: regulation, structure, and function. Ann Rev Microbiol 64: 43–60.
O'Sullivan LA, Rinna J, Humphreys G, Weightman AJ, Fry JC . (2005). Fluviicola taffensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel freshwater bacterium of the family Cryomorphaceae in the phylum 'Bacteroidetes'. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55: 2189–2194.
Orsi WD, Edgcomb VP, Christman GD, Biddle JF . (2013). Gene expression in the deep biosphere. Nature 499: 205–208.
Orsi WD, Smith JM, Wilcox HM, Swalwell JE, Carini P, Worden AZ et al. (2015). Ecophysiology of uncultivated marine euryarchaea is linked to particulate organic matter. ISME J 9: 1747–1763.
Pennington JT, Castro CG, Collins CA, Evans WWI, Friederich GE, Michisaki RP et al. (2010). The Northern and Central California Coastal Upwelling System. In: Liu K-K (ed), Carbon and Nutrient Fluxes in Continental Margins. Springer-Verlag: Berlin Heidelberg, pp 29–44.
Pennington TJ, Chavez FP . (2000). Seasonal fluctuations of temperature, salinity, nitrate, chlorophyll, and primary production at station H3/M1 over 1989-1996 in Monterey Bar, California. Deep Sea Res II 47: 947–973.
Pernthaler A, Preston CM, Pernthaler J, Delong EF, Amann R . (2002). Comparison of fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide and polynucleotide probes for the detection of pelagic marine bacteria and archaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 661–667.
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J et al. (2007). SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35: 7188–7196.
Rappe MS, Connon SA, Vergin KL, Giovannoni SJ . (2002). Cultivation of the ubiquitous SAR11 marine bacterioplankton clade. Nature 418: 630–633.
Rappe MS, Kemp PF, Giovannoni SJ . (1997). Phylogenetic diversity of marine coastal picoplankton 16S rRNA genes clones from the continental shelf off Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. Limnol Oceanogr 42: 811–826.
Ravenschlag K, Sahm K, Pernthaler J, Amann R . (1999). High bacterial diversity in permanently cold marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65: 3982–3989.
Reysenbach AL, Flores GE . (2008). Electron microscopy encounters with unusual thermophiles helps direct genomic analysis of Aciduliprofundum boonei. Geobiology 6: 331–336.
Rinta-Kanto JM, Sun S, Sharma S, Kiene RP, Moran MA . (2012). Bacterial community transcription patterns during a marine phytoplankton bloom. Environ Microbiol 14: 228–239.
Santoro AE, Casciotti KL, Francis CA . (2010). Activity, abundance and diversity of nitrifying archaea and bacteria in the central California Current. Environ Microbiol 12: 1989–2006.
Santoro AE, Dupont CL, Richter RA, Craig MT, Carini P, McIlvin MR et al. (2015). Genomic and proteomic characterization of ‘Candidatus Nitrosopelagicus brevis:’ An ammonia-oxidizing archaeon from the open ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 1173–1178.
Schauer K, Rodionov DA, de Reuse H . (2008). New substrates for TonB-dependent transport: do we only see the 'tip of the iceberg'? Trends Biochem Sci 33: 330–338.
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB et al. (2009). Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75: 7537–7541.
Sharma AK, Becker JW, Ottesen EA, Bryant JA, Duhamel S, Karl DM et al. (2014). Distinct dissolved organic matter sources induce rapid transcriptional responses in coexisting populations of Prochlorococcus, Pelagibacter and the OM60 clade. Environ Microbiol 16: 2815–2830.
Sigman DM, Casciotti KL, Andreani M, Barford C, Galanter M, Bohlke JK . (2001). A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater. Anal Chem 73: 4145–4153.
Sizemore RK, Stevenson LH . (1974). Environmental factors associated with proteolytic activity of estuarine bacteria. Life Sci 15: 1425–1432.
Smith DC, Simon M, Alldredge AL, Azam F . (1982). Intense hydrolytic enzyme activity on marine aggregates and implications for rapid particle dissolution. Nature 359: 139–142.
Smith JM, Chavez FP, Francis CA . (2014). Ammonium uptake by phytoplankton regulates nitrification in the sunlit ocean. PLoS One 9: e108173.
Stahl DA, Amann R . (1991) Development and application of nucleic acid probes. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds), Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, England, pp 205–248.
Stingl U, Desiderio RA, Cho JC, Vergin KL, Giovannoni SJ . (2007). The SAR92 clade: an abundant coastal clade of culturable marine bacteria possessing proteorhodopsin. App Environ Microbiol 73: 2290–2296.
Tanoue E, Nishiyama S, Kamo M, Tsugita A . (1995). Bacterial membranes: possible source of a major dissolved protein in seawater. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 59: 2643–2648.
Taylor GT . (1995). Microbial degradation of sorbed and dissolved protein in seawater. Limnol Oceanogr 40: 875–885.
Teeling H, Fuchs BM, Becher D, Klockow C, Gardebrecht A, Bennke CM et al. (2012). Substrate-controlled succession of marine bacterioplankton populations induced by a phytoplankton bloom. Science 336: 608–611.
Thomsen HA, Buck KR . (1998). Nanoflagellates of the central California waters: taxonomy, biogeography and abundance of primitive, green flagellates (Pedinophyceae, Prasinophyceae). Deep Sea Res II 45: 1687–1707.
Tiera E, Reinthaler T, Pernthaler J, Herndl GJ . (2004). Combining catalyzed reporter deposition-fluorescence in situ hybridization and microautoradiography to detect substrate utilization by bacteria and archaea in the deep ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 4411–4414.
Urbach E, Vergin KL, Young L, Morse A, Larson GL, Giovannoni SJ . (2001). Unusual bacterioplankton community structure in ultra-oligotrophic Crater Lake. Limnol Oceanogr 46: 557–572.
Worden AZ, Follows MJ, Giovannoni SJ, Wilken S, Zimmerman AE, Keeling PJ . (2015). Rethinking the marine carbon cycle: factoring in the multifarious lifestyles of microbes. Science 347: 1257594.
Yoon J, Matsuo Y, Adachi K, Nozawa M, Matsuda S, Kasai H et al. (2008). Description of Persicirhabdus sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseibacillus ishigakijimensis gen. nov., sp. nov., Roseibacillus ponti sp. nov., Roseibacillus persicicus sp. nov., Luteolibacter pohnpeiensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Luteolibacter algae sp. nov., six marine members of the phylum ‘Verrucomicrobia’, and emended descriptions of the class Verrucomicrobiae, the order Verrucomicrobiales and the family Verrucomicrobiaceae. Int J Sys Evol Microbiol 58: 998–1007.
Zeigler Allen L, Allen EE, Badger JH, McCrow JP, Paulsen IT, Elbourne LD et al. (2012). Influence of nutrients and currents on the genomic composition of microbes across an upwelling mosaic. ISME J 6: 1403–1414.
Zhang CL, Xie W, Martin-Cuadrado AB, Rodriguez-Valera F . (2015). Marine Group II Archaea, potentially important players in the global carbon cycle. Front Microbiol 6: 1108.
Acknowledgements
We thank the captain and crew of the R/V Western Flyer, J. Timothy Pennington, Marguerite Blum, Valeria Jimenez, Christopher Wahl, Noriko Okamoto, Jarred Swalwell and Francisco Chavez for logistical assistance prior to and during the cruise. We also thank Michael Morando and Elizabeth Kujawinski for advice and conversations on SIP methodology, and Mak Saito and Dawn Moran for advice on for protein extraction. We thank Amy Apprill for sharing the modified, barcoded PCR primers, Alexandra Welch for assistance with qPCR, and Paul Carini and Tristan Horner for discussions. We thank John Hobbie for discussions on protein remineralization rate kinetics, and three anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. Support for this work was provided by GBMF3307 to PJK, TAR, AZW and AES, United States National Science Foundation award DBI-1318455 to AES, and the David and Lucile Packard Foundation (to AZW). This is UMCES contribution number 5169.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orsi, W., Smith, J., Liu, S. et al. Diverse, uncultivated bacteria and archaea underlying the cycling of dissolved protein in the ocean. ISME J 10, 2158–2173 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2016.20
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2016.20
This article is cited by
-
Use of untargeted metabolomics to analyse changes in extractable soil organic matter in response to long-term fertilisation
Biology and Fertility of Soils (2023)
-
Rapid bacterioplankton transcription cascades regulate organic matter utilization during phytoplankton bloom progression in a coastal upwelling system
The ISME Journal (2022)
-
Carbon assimilating fungi from surface ocean to subseafloor revealed by coupled phylogenetic and stable isotope analysis
The ISME Journal (2022)
-
Catabolic protein degradation in marine sediments confined to distinct archaea
The ISME Journal (2022)
-
The structure of microbial communities of activated sludge of large-scale wastewater treatment plants in the city of Moscow
Scientific Reports (2022)