Abstract
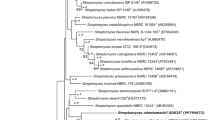
A moderate growing strain designated as MPKL 26T was isolated from a soil sample of Bidar Fort, Karnataka, India. The strain MPKL 26T was Gram positive, bent rod in shape. The optimum pH and temperature for growth was 7.0 and 30 °C, respectively. The 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequence analysis revealed that strain MPKL 26T was closely related to S. atrocyanea DSM 20127T (98.09%), S. flava CW 108T (98.04%), S. soli CW 59T (97.99%) and S. notoginsengisoli SYP-B575T (97.0%) and showed DNA–DNA hybridization relatedness (46.05±1.2, 33.56±2.55, 32.56±1.7 and 26.79±2.5, respectively, between these strains) less than the threshold value for the delineation of genomic species. The peptidoglycon type was A3α type with glycine, alanine, lysine and glutamic acid as the amino acids. The whole-cell sugars were fructose, ribose, mannose, glucose and galactose. The polar lipids were diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol along with three unknown polar lipids. The fatty acid profile contained C14:0, C16:0, iso-C14:0, iso-C15:0, iso-C16:0, iso-C17:0, anteiso-C15:0, anteiso-C17:0 and summed feature 4 (17:1 iso I/anteiso B). The predominant respiratory quinine was MK-9(H2) with MK-10(H2), MK-8(H2) and MK-8(H4) as minor respiratory quinines. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 68.8 mol%. On the basis of phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and molecular characteristics, the strain MPKL 26T represents a novel species of the genus Sinomonas, for which the name Sinomonas mesophila sp. nov. is proposed with MPKL 26T as the type strain (=NCIM 5552T= JCM 30094T).
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Zhou, Y . et al. Proposal of Sinomonas flava gen. nov., sp. nov., and description of Sinomonas atrocyanea comb. nov. to accommodate Arthrobacter atrocyaneus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 259–263 (2009).
Zhou, Y . et al. Description of Sinomonas soli sp. nov., reclassification of Arthrobacter echigonensis and Arthrobacter albidus (Ding et al. 2009) as Sinomonas echigonensis comb. nov. and Sinomonas albida comb. nov., respectively, and emended description of the genus Sinomonas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 764–769 (2012).
Zhang, M. Y . et al. Sinomonas notoginsengisoli sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of Panax notoginseng. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 106, 827–835 (2014).
Ding, L., Hirose, T . & Yokota, A. Four novel Arthrobacter species isolated from filtration substrate. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 856–862 (2009).
Shirling, E. B . & Gottlieb, D. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 16, 313–340 (1966).
Kuhn, D. A . & Starr, M. P. Arthrobacter atrocyaneus, nov. sp., and its blue pigment. Arch. Microbiol. 36, 175–181 (1960).
Wieser, M . et al. Emended descriptions of the genus Micrococcus Micrococcus luteus (Cohn 1872) and Micrococcus lylae (Kloos et al. 1974). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 629–637 (2002).
Xu, P . et al. Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Oxalobacteraceae isolated from China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 1149–1153 (2005).
Kovacs, N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature 178, 703–704 (1956).
Gonzalez, C., Gutierrez, C . & Ramirez, C. Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov., an amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can. J. Microbiol. 24, 710–715 (1978).
MacFaddin, J. F. in Biochemical tests for identification of medical bacteria, Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, (1980).
Hasegawa, T., Takizawa, M . & Tanida, S. A rapid analysis for chemical grouping of aerobic actinomycetes. J. Gen. Microbiol. 29, 319–322 (1983).
Lechevalier, M. P . & Lechevalier, H. A. Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 20, 435–443 (1970).
Tang, S. K . et al. Zhihengliuella alba sp. nov., and emended description of the genus Zhihengliuella. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 2025–2032 (2009a).
Tang, S. K . et al. Kocuria halotolerans sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from a saline soil in China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 1316–1320 (2009b).
Minnikin, D. E., Collins, M. D . & Goodfellow, M. Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 47, 87–95 (1979).
Collins, M. D . & Jones, D. Lipids in the classification and identification of coryneform bacteria containing peptidoglycan based on 2, 4-diaminobutyric acid. Appl. Bacteriol. 48, 459–470 (1980).
Collins, M. D., Pirouz, T., Goodfellow, M . & Minnikin, D. E. Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 100, 221–230 (1977).
Kroppenstedt, R. M. Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 5, 2359–2367 (1982).
Li, W. J . et al. Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China) and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 1424–1428 (2007).
Kim, O. S . et al. Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 716–721 (2012).
Tamura, K . et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 2731–2739 (2011).
Thompson, J. D . et al. The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882 (1997).
Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111–120 (1980).
Saitou, N . & Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 (1987).
Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–79 (1985).
Fitch, W. M. Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 20, 406–416 (1971).
Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17, 368–376 (1981).
Mesbah, M., Premachandran, U . & Whitman, W. B. Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 159–167 (1989).
Ezaki, T., Hashimoto, Y . & Yabuuchi, E. Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 224–229 (1989).
Wayne, L. G . et al. International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464 (1987).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor Dr Hans-Peter Klenk (DSMZ, Germany) and Dr Yu Zhou (Institute of Quality and Standard for Agro-products, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China) for their kind providing the reference type strains, and Dr Syed G Dastager (CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, Pune) for his help in performing API ZYM experiment. This work was funded jointly by projects of China tobacco Yunnan industrial (Nos. 2012JC07 and 2012FL02). WH and WJL extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through the research group no RGP-205. W-J Li was also supported by Guangdong Province Higher Vocational Colleges & Schools Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on The Journal of Antibiotics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhu, D., Quadri, S., Cheng, J. et al. Sinomonas mesophila sp. nov., isolated from ancient fort soil. J Antibiot 68, 318–321 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.161
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.161
This article is cited by
-
Sinomonas cellulolyticus sp. nov., isolated from Loktak lake
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2023)
-
First report of Sinomonas halotolerans from Parkinsonia aculeata rhizosphere
Biologia (2023)
-
Amycolatopsis alkalitolerans sp. nov., isolated from Gastrodia elata Blume
The Journal of Antibiotics (2020)
-
Sinomonas halotolerans sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from a soil sample
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (2015)