Abstract
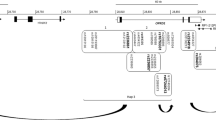
The opioid system is involved in the action of opiate drugs, opioid addiction, pain experience and analgesia. Individual differences in opioid effect may be attributed in part to genetic variations. Long-range cis regulatory elements and intronic variants are potential sources of functional diversity. Recently, we have detected association of two intronic OPRM1 variants with heroin addiction in European Americans. In this study, we analyzed the genetic variations in the OPRM1 100 kb 5′-flanking region and intron 1 in the HapMap Caucasian population. Four major linkage disequilibrium blocks were identified, consisting of 28, 22, 15 and 42 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), respectively. The locations of these blocks are (−100 to −90), (−90 to −67), (−20 to −1) and (+1 to +44) kb, respectively. The two intronic variants, indicated in our recent study, are part of a distinct haplogroup that includes SNPs from intron 1, and the proximal 5′ region. The 118G (rs1799971) allele is part of a different haplogroup that includes several variants in the distal 5′ region that may have a regulatory potential. These findings were corroborated by genotyping eight SNPs in a sample of European Americans and suggest an extended OPRM1 locus with potential new regulatory regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Oertel, B. G., Kettner, M., Scholich, K., Renne, C., Roskam, B., Geisslinger, G. et al. A common human mu-opioid receptor genetic variant diminishes the receptor signaling efficacy in brain regions processing the sensory information of pain. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 6530–6535 (2009).
Wand, G. S., McCaul, M., Yang, X., Reynolds, J., Gotjen, D., Lee, S. et al. The mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism (A118G) alters HPA axis activation induced by opioid receptor blockade. Neuropsychopharmacology 26, 106–114 (2002).
Hernandez-Avila, C. A., Covault, J., Wand, G., Zhang, H., Gelernter, J. & Kranzler, H. R. Population-specific effects of the Asn40Asp polymorphism at the mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) on HPA-axis activation. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17, 1031–1038 (2007).
Hernandez-Avila, C. A., Wand, G., Luo, X., Gelernter, J. & Kranzler, H. R. Association between the cortisol response to opioid blockade and the Asn40Asp polymorphism at the mu-opioid receptor locus (OPRM1). Am. J. Med. Genet B. Neuropsychiatr. Genet 118, 60–65 (2003).
Bart, G., Heilig, M., LaForge, K. S., Pollak, L., Leal, S. M., Ott, J. et al. Substantial attributable risk related to a functional mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism in association with heroin addiction in central Sweden. Mol. Psychiatry 9, 547–549 (2004).
Kapur, S., Sharad, S., Singh, R. A. & Gupta, A. K. A118g polymorphism in mu opioid receptor gene (oprm1): association with opiate addiction in subjects of Indian origin. J. Integr. Neurosci. 6, 511–522 (2007).
Bart, G., Kreek, M. J., Ott, J., LaForge, K. S., Proudnikov, D., Pollak, L. et al. Increased attributable risk related to a functional mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism in association with alcohol dependence in central Sweden. Neuropsychopharmacology 30, 417–422 (2005).
Glatt, S. J., Bousman, C., Wang, R. S., Murthy, K. K., Rana, B. K., Lasky-Su, J. A. et al. Evaluation of OPRM1 variants in heroin dependence by family-based association testing and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend 90, 159–165 (2007).
Levran, O., Londono, D., O’Hara, K., Nielsen, D. A., Peles, E., Rotrosen, J. et al. Genetic susceptibility to heroin addiction: a candidate gene association study. Genes Brain Behav. 7, 720–729 (2008).
Walter, C. & Lotsch, J. Meta-analysis of the relevance of the OPRM1 118A>G genetic variant for pain treatment. Pain 146, 270–275 (2009).
Skorpen, F., Laugsand, E. A., Klepstad, P. & Kaasa, S. Variable response to opioid treatment: any genetic predictors within sight? Palliat Med 22, 310–327 (2008).
Kosarac, B., Fox, A. A. & Collard, C. D. Effect of genetic factors on opioid action. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 22, 476–482 (2009).
Kreek, M. J., Bart, G., Lilly, C., LaForge, K. S. & Nielsen, D. A. Pharmacogenetics and human molecular genetics of opiate and cocaine addictions and their treatments. Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 1–26 (2005).
Birney, E., Stamatoyannopoulos, J. A., Dutta, A., Guigo, R., Gingeras, T. R., Margulies, E. H. et al. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 447, 799–816 (2007).
Xu, J., Xu, M., Hurd, Y. L., Pasternak, G. W. & Pan, Y. X. Isolation and characterization of new exon 11-associated N-terminal splice variants of the human mu opioid receptor gene. J. Neurochem. 108, 962–972 (2009).
Pan, Y. X., Xu, J., Mahurter, L., Xu, M., Gilbert, A. K. & Pasternak, G. W. Identification and characterization of two new human mu opioid receptor splice variants, hMOR-1O and hMOR-1X. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 301, 1057–1061 (2003).
Pan, Y. X. Identification of alternatively spliced variants from opioid receptor genes. Methods Mol. Med. 84, 65–75 (2003).
Pan, L., Xu, J., Yu, R., Xu, M. M., Pan, Y. X. & Pasternak, G. W. Identification and characterization of six new alternatively spliced variants of the human mu opioid receptor gene, Oprm. Neuroscience 133, 209–220 (2005).
Choi, H. S., Kim, C. S., Hwang, C. K., Song, K. Y., Wang, W., Qiu, Y. et al. The opioid ligand binding of human mu-opioid receptor is modulated by novel splice variants of the receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 343, 1132–1140 (2006).
Shabalina, S. A., Zaykin, D. V., Gris, P., Ogurtsov, A. Y., Gauthier, J., Shibata, K. et al. Expansion of the human mu-opioid receptor gene architecture: novel functional variants. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 1037–1051 (2009).
Abbadie, C., Pan, Y. X. & Pasternak, G. W. Immunohistochemical study of the expression of exon11-containing mu opioid receptor variants in mouse brain. Neuroscience 127, 419–430 (2004).
Pan, Y. X., Xu, J., Mahurter, L., Bolan, E., Xu, M. & Pasternak, G. W. Generation of the mu opioid receptor (MOR-1) protein by three new splice variants of the Oprm gene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 14084–14089 (2001).
Pan, Y. X. Identification and characterization of a novel promoter of the mouse mu opioid receptor gene (Oprm) that generates eight splice variants. Gene 295, 97–108 (2002).
Kleinjan, D. A. & Lettice, L. A. Long-range gene control and genetic disease. Adv. Genet 61, 339–388 (2008).
Bayerer, B., Stamer, U., Hoeft, A. & Stuber, F. Genomic variations and transcriptional regulation of the human mu-opioid receptor gene. Eur. J. Pain 11, 421–427 (2007).
Hoehe, M. R., Kopke, K., Wendel, B., Rohde, K., Flachmeier, C., Kidd, K. K. et al. Sequence variability and candidate gene analysis in complex disease: association of mu opioid receptor gene variation with substance dependence. Hum. Mol. Genet 9, 2895–2908 (2000).
Luo, X., Kranzler, H. R., Zhao, H. & Gelernter, J. Haplotypes at the OPRM1 locus are associated with susceptibility to substance dependence in European-Americans. Am. J. Med. Genet B. Neuropsychiatr. Genet 120, 97–108 (2003).
Hodgkinson, C. A., Yuan, Q., Xu, K., Shen, P. H., Heinz, E., Lobos, E. A. et al. Addictions biology: haplotype-based analysis for 130 candidate genes on a single array. Alcohol Alcohol 43, 505–515 (2008).
Zhang, H., Luo, X., Kranzler, H. R., Lappalainen, J., Yang, B. Z., Krupitsky, E. et al. Association between two mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) haplotype blocks and drug or alcohol dependence. Hum. Mol. Genet 15, 807–819 (2006).
Zhang, D., Shao, C., Shao, M., Yan, P., Wang, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Effect of mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphisms on heroin-induced subjective responses in a Chinese population. Biol. Psychiatry 61, 1244–1251 (2007).
Levran, O., Londono, D., O’Hara, K., Randesi, M., Rotrosen, J., Casadonte, P. et al. Heroin addiction in African Americans: a hypothesis-driven association study. Genes Brain Behav. 8, 531–540 (2009).
Nielsen, D. A., Ji, F., Yuferov, V., Ho, A., Chen, A., Levran, O. et al. Genotype patterns that contribute to increased risk for or protection from developing heroin addiction. Mol. Psychiatry 13, 417–428 (2008).
Taylor, J., Tyekucheva, S., King, D. C., Hardison, R. C., Miller, W. & Chiaromonte, F. ESPERR: learning strong and weak signals in genomic sequence alignments to identify functional elements. Genome. Res. 16, 1596–1604 (2006).
Pritchard, J. K., Stephens, M. & Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155, 945–959 (2000).
Enoch, M. A., Shen, P. H., Xu, K., Hodgkinson, C. & Goldman, D. Using ancestry-informative markers to define populations and detect population stratification. J. Psychopharmacol 20, 19–26 (2006).
Barrett, J. C., Fry, B., Maller, J. & Daly, M. J. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21, 263–265 (2005).
Rozen, S. & Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods. Mol. Biol. 132, 365–386 (2000).
Adoue, V., Chavanas, S., Coudane, F., Mechin, M. C., Caubet, C., Ying, S. et al. Long-range enhancer differentially regulated by c-Jun and JunD controls peptidylarginine deiminase-3 gene in keratinocytes. J. Mol. Biol. 384, 1048–1057 (2008).
Coop, G., Pickrell, J. K., Novembre, J., Kudaravalli, S., Li, J., Absher, D. et al. The role of geography in human adaptation. PLoS Genet 5, e1000500 (2009).
Arias, A., Feinn, R. & Kranzler, H. R. Association of an Asn40Asp (A118G) polymorphism in the mu-opioid receptor gene with substance dependence: a meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend 83, 262–268 (2006).
Xuei, X., Flury-Wetherill, L., Bierut, L., Dick, D., Nurnberger Jr, J., Foroud, T et al. The opioid system in alcohol and drug dependence: family-based association study. Am. J. Med. Genet B. Neuropsychiatr. Genet 144, 877–884 (2007).
Oroszi, G., Anton, R. F., O’Malley, S., Swift, R., Pettinati, H., Couper, D. et al. OPRM1 Asn40Asp predicts response to naltrexone treatment: a haplotype-based approach. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 33, 383–393 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Pei-Hong Shen and David Goldman from the Laboratory of Neurogenetics (NIAAA) for the AIMs analysis, to the clinical staff including Elizabeth Ducat, Brenda Ray, Dorothy Melia, and Lisa Borg, for patient recruitment and ascertainment, and to Vadim Yuferov, Ann Ho, David Nielsen, Matthew Randesi and Susan Russo for their contributions. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (P60- DA 05130 to MJK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levran, O., Awolesi, O., Linzy, S. et al. Haplotype block structure of the genomic region of the mu opioid receptor gene. J Hum Genet 56, 147–155 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2010.150
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2010.150
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Population-specific genetic background for the OPRM1 variant rs1799971 (118A>G): implications for genomic medicine and functional analysis
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
The frequency of DRD2 rs1076560 and OPRM1 rs1799971 in substance use disorder patients from the United Arab Emirates
Annals of General Psychiatry (2018)
-
OPRM1 genetic polymorphisms are associated with the plasma nicotine metabolite cotinine concentration in methadone maintenance patients: a cross sectional study
Journal of Human Genetics (2013)
-
The genetics of the opioid system and specific drug addictions
Human Genetics (2012)