Abstract
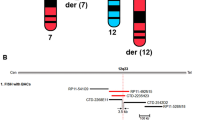
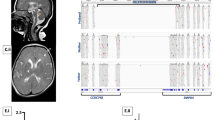
Subtelomeric deletions of 1q44 cause mental retardation, developmental delay and brain anomalies, including abnormalities of the corpus callosum (ACC) and microcephaly in most patients. We report the cases of six patients with 1q44 deletions; two patients with interstitial deletions of 1q44; and four patients with terminal deletions of 1q. One of the patients showed an unbalanced translocation between chromosome 5. All the deletion regions overlapped with previously reported critical regions for ACC, microcephaly and seizures, indicating the recurrent nature of the core phenotypic features of 1q44 deletions. The four patients with terminal deletions of 1q exhibited severe volume loss in the brain as compared with patients who harbored interstitial deletions of 1q44. This indicated that telomeric regions have a role in severe volume loss of the brain. In addition, two patients with terminal deletions of 1q43, beyond the critical region for 1q44 deletion syndrome exhibited delayed myelination. As the deletion regions identified in these patients extended toward centromere, we conclude that the genes responsible for delayed myelination may be located in the neighboring region of 1q43.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Knight, S. J., Regan, R., Nicod, A., Horsley, S. W., Kearney, L., Homfray, T. et al. Subtle chromosomal rearrangements in children with unexplained mental retardation. Lancet 354, 1676–1681 (1999).
Shimojima, K., Sugiura, C., Takahashi, H., Ikegami, M., Takahashi, Y., Ohno, K. et al. Genomic copy number variations at 17p13.3 and epileptogenesis. Epilepsy Res. 89, 303–309 (2010).
Cardoso, C., Leventer, R. J., Ward, H. L., Toyo-Oka, K., Chung, J., Gross, A. et al. Refinement of a 400-kb critical region allows genotypic differentiation between isolated lissencephaly, Miller-Dieker syndrome, and other phenotypes secondary to deletions of 17p13.3. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72, 918–930 (2003).
Gentile, M., Di Carlo, A., Volpe, P., Pansini, A., Nanna, P., Valenzano, M. C. et al. FISH and cytogenetic characterization of a terminal chromosome 1q deletion: clinical case report and phenotypic implications. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 117A, 251–254 (2003).
Puthuran, M. J., Rowland-Hill, C. A., Simpson, J., Pairaudeau, P. W., Mabbott, J. L., Morris, S. M. et al. Chromosome 1q42 deletion and agenesis of the corpus callosum. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 138, 68–69 (2005).
van Bever, Y., Rooms, L., Laridon, A., Reyniers, E., van Luijk, R., Scheers, S. et al. Clinical report of a pure subtelomeric 1qter deletion in a boy with mental retardation and multiple anomalies adds further evidence for a specific phenotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 135, 91–95 (2005).
Boland, E., Clayton-Smith, J., Woo, V. G., McKee, S., Manson, F. D., Medne, L. et al. Mapping of deletion and translocation breakpoints in 1q44 implicates the serine/threonine kinase AKT3 in postnatal microcephaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 292–303 (2007).
Hill, A. D., Chang, B. S., Hill, R. S., Garraway, L. A., Bodell, A., Sellers, W. R. et al. A 2-Mb critical region implicated in the microcephaly associated with terminal 1q deletion syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 143A, 1692–1698 (2007).
Merritt, J. L., Zou, Y., Jalal, S. M., Michels, V. V. Delineation of the cryptic 1qter deletion phenotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 143, 599–603 (2007).
Andrieux, J., Cuvellier, J. C., Duban-Bedu, B., Joriot-Chekaf, S., Dieux-Coeslier, A., Manouvrier-Hanu, S. et al. A 6.9 Mb 1qter deletion/4.4 Mb 18pter duplication in a boy with extreme microcephaly with simplified gyral pattern, vermis hypoplasia and corpus callosum agenesis. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 51, 87–91 (2008).
Hiraki, Y., Okamoto, N., Ida, T., Nakata, Y., Kamada, M., Kanemura, Y. et al. Two new cases of pure 1q terminal deletion presenting with brain malformations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 146A, 1241–1247 (2008).
Poot, M., Kroes, H. Y., Hochstenbach, R. AKT3 as a candidate gene for corpus callosum anomalies in patients with 1q44 deletions. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 51, 689–690 (2008).
van Bon, B. W., Koolen, D. A., Borgatti, R., Magee, A., Garcia-Minaur, S., Rooms, L. et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of 1qter microdeletion syndrome: delineating a critical region for corpus callosum agenesis/hypogenesis. J. Med. Genet. 45, 346–354 (2008).
Orellana, C., Rosello, M., Monfort, S., Oltra, S., Quiroga, R., Ferrer, I. et al. Corpus callosum abnormalities and the controversy about the candidate genes located in 1q44. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 127, 5–8 (2009).
Caliebe, A., Kroes, H. Y., van der Smagt, J. J., Martin-Subero, J. I., Tonnies, H., van’t Slot, R. et al. Four patients with speech delay, seizures and variable corpus callosum thickness sharing a 0.440 Mb deletion in region 1q44 containing the HNRPU gene. Eur. J. Med. Genet 53, 179–185 (2010).
Nagamani, S. C., Erez, A., Bay, C., Pettigrew, A., Lalani, S. R., Herman, K. et al. Delineation of a deletion region critical for corpus callosal abnormalities in chromosome 1q43-q44. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 20, 176–179 (2012).
Ballif, B. C., Rosenfeld, J. A., Traylor, R., Theisen, A., Bader, P. I., Ladda, R. L. et al. High-resolution array CGH defines critical regions and candidate genes for microcephaly, abnormalities of the corpus callosum, and seizure phenotypes in patients with microdeletions of 1q43q44. Hum. Genet. 131, 145–156 (2012).
Roos, A., Eggermann, T., Zerres, K., Schuler, H. M. Polymorphic subtelomeric deletion 1q demonstrates the need to reevaluate subtelomere screening methods: determination of the boundary between pathogenic deletion and benign variant for subtelomere 1q. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 146A, 795–798 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their parents for their gracious participation and support. This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Research Activity Start-up for KS and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) for TY from the Japan Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimojima, K., Okamoto, N., Suzuki, Y. et al. Subtelomeric deletions of 1q43q44 and severe brain impairment associated with delayed myelination. J Hum Genet 57, 593–600 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.77
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.77
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Maternal interchromosomal insertional translocation leading to 1q43-q44 deletion and duplication in two siblings
Molecular Cytogenetics (2018)
-
Infantile spasms related to a 5q31.2-q31.3 microdeletion including PURA
Human Genome Variation (2018)
-
Characteristics of rare and private deletions identified in phenotypically normal individuals
Human Genome Variation (2017)
-
Contribution of copy number variants (CNVs) to congenital, unexplained intellectual and developmental disabilities in Lebanese patients
Molecular Cytogenetics (2015)
-
Molecular karyotyping by array CGH in a Russian cohort of children with intellectual disability, autism, epilepsy and congenital anomalies
Molecular Cytogenetics (2012)