Abstract
Arising from: K. Nalley, S. A. Johnston & T. Kodadek Nature 442, 1054–1057 (2006)10.1038/nature05067; Nalley et al. reply
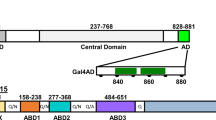
Growing evidence supports the notion that proteasome-mediated destruction of transcriptional activators can be intimately coupled to their function1,2. Recently, Nalley et al.3 challenged this view by reporting that the prototypical yeast activator Gal4 does not dynamically associate with chromatin, but rather ‘locks in’ to stable promoter complexes that are resistant to competition. Here we present evidence that the assay used to reach this conclusion is unsuitable, and that promoter-bound, active Gal4 is indeed susceptible to competition in vivo. Our data challenge the key evidence that Nalley et al.3 used to reach their conclusion, and indicate that Gal4 functions in vivo within the context of dynamic promoter complexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Enjoying our latest content?
Log in or create an account to continue
- Access the most recent journalism from Nature's award-winning team
- Explore the latest features & opinion covering groundbreaking research
or
References
Lipford, J. R. & Deshaies, R. J. Diverse roles for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis in transcriptional activation. Nature Cell Biol. 5, 845–850 (2003)
Muratani, M. & Tansey, W. P. How the ubiquitin-proteasome system controls transcription. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 192–201 (2003)
Nalley, K., Johnston, S. A. & Kodadek, T. Proteolytic turnover of the Gal4 transcription factor is not required for function in vivo . Nature 442, 1054–1057 (2006)
Lipford, J. R., Smith, G. T., Chi, Y. & Deshaies, R. J. A putative stimulatory role for activator turnover in gene expression. Nature 438, 113–116 (2005)
Muratani, M., Kung, C., Shokat, K. M. & Tansey, W. P. The F box protein Dsg1/Mdm30 is a transcriptional coactivator that stimulates Gal4 turnover and cotranscriptional mRNA processing. Cell 120, 887–899 (2005)
Salghetti, S. E., Muratani, M., Wijnen, H., Futcher, B. & Tansey, W. P. Functional overlap of sequences that activate transcription and signal ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3118–3123 (2000)
Giniger, E. & Ptashne, M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 382–386 (1988)
Ezhkova, E. & Tansey, W. P. Chromatin immunoprecipitation to study protein-DNA interactions in budding yeast. Methods Mol. Biol. 313, 225–244 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collins, G., Lipford, J., Deshaies, R. et al. Gal4 turnover and transcription activation. Nature 461, E7 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08406
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08406
This article is cited by
-
Cell cycle–dependent localization of the proteasome to chromatin
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Genome-wide measurement of protein-DNA binding dynamics using competition ChIP
Nature Protocols (2013)
-
Nalley et al. reply
Nature (2009)