Abstract
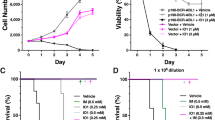
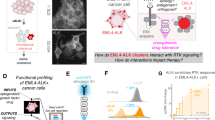
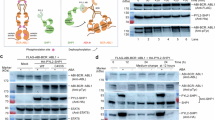
The non-receptor tyrosine kinase Abl participates in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)-induced actin cytoskeleton remodelling, a signalling pathway in which the function of Rac is pivotal. More importantly, the activity of Rac is indispensable for the leukaemogenic ability of the BCR-Abl oncoprotein. Thus, Rac might function downstream of Abl and be activated by it. Here, we elucidate the molecular mechanisms through which Abl signals to Rac in RTK-activated pathways. We show that Sos-1, a dual guanine nucleotide-exchange factor (GEF), is phosphorylated on tyrosine, after activation of RTKs, in an Abl-dependent manner. Sos-1 and Abl interact in vivo, and Abl-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of Sos-1 is sufficient to elicit its Rac-GEF activity in vitro. Genetic or pharmacological interference with Abl (and the related kinase Arg) resulted in a marked decrease in Rac activation induced by physiological doses of growth factors. Thus, our data identify the molecular connections of a pathway RTKs–Abl–Sos-1–Rac that is involved in signal transduction and actin remodelling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plattner, R., Kadlec, L., DeMali, K.A., Kazlauskas, A. & Pendergast, A.M. c-Abl is activated by growth factors and Src family kinases and has a role in the cellular response to PDGF. Genes Dev. 13, 2400–2411 (1999).
Koleske, A.J. et al. Essential roles for the Abl and Arg tyrosine kinases in neurulation. Neuron 21, 1259–1272 (1998).
Woodring, P.J. et al. Modulation of the F-actin cytoskeleton by c-Abl tyrosine kinase in cell spreading and neurite extension. J. Cell Biol. 156, 879–892 (2002).
Renshaw, M.W., Lea-Chou, E. & Wang, J.Y. Rac is required for v-Abl tyrosine kinase to activate mitogenesis. Curr. Biol. 6, 76–83 (1996).
Melo, J.V. The diversity of BCR-ABL fusion proteins and their relationship to leukemia phenotype. Blood 88, 2375–2384 (1996).
Skorski, T. et al. The SH3 domain contributes to BCR/ABL-dependent leukemogenesis in vivo: role in adhesion, invasion, and homing. Blood 91, 406–418 (1998).
Hall, A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279, 509–514 (1998).
Schmidt, A. & Hall, A. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho GTPases: turning on the switch. Genes Dev. 16, 1587–1609 (2002).
Fleming, I.N., Elliott, C.M., Buchanan, F.G., Downes, C.P. & Exton, J.H. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulates Tiam1 by reversible protein phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 12753–12758 (1999).
Crespo, P., Schuebel, K.E., Ostrom, A.A., Gutkind, J.S. & Bustelo, X.R. Phosphotyrosine-dependent activation of Rac-1 GDP/GTP exchange by the vav proto-oncogene product. Nature 385, 169–172 (1997).
Kiyono, M., Satoh, T. & Kaziro, Y. G protein beta gamma subunit-dependent Rac-guanine nucleotide exchange activity of Ras-GRF1/CDC25(Mm). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 4826–4831 (1999).
Aghazadeh, B., Lowry, W.E., Huang, X.Y. & Rosen, M.K. Structural basis for relief of autoinhibition of the Dbl homology domain of proto-oncogene Vav by tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell 102, 625–633 (2000).
Scita, G. et al. EPS8 and E3B1 transduce signals from Ras to Rac. Nature 401, 290–293 (1999).
Mettouchi, A. et al. Integrin-specific activation of Rac controls progression through the G(1) phase of the cell cycle. Mol Cell 8, 115–127 (2001).
Lewis, J.M., Baskaran, R., Taagepera, S., Schwartz, M.A. & Wang, J.Y. Integrin regulation of c-Abl tyrosine kinase activity and cytoplasmic- nuclear transport. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 15174–15179 (1996).
Wedegaertner, P.B. & Gill, G.N. Effect of carboxyl terminal truncation on the tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 292, 273–280 (1992).
Walton, G.M., Chen, W.S., Rosenfeld, M.G. & Gill, G.N. Analysis of deletions of the carboxyl terminus of the epidermal growth factor receptor reveals self-phosphorylation at tyrosine 992 and enhanced in vivo tyrosine phosphorylation of cell substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 1750–1754 (1990).
Shi, Y., Alin, K. & Goff, S.P. Abl-interactor-1, a novel SH3 protein binding to the carboxy-terminal portion of the Abl protein, suppresses v-abl transforming activity. Genes Dev. 9, 2583–2597 (1995).
Dai, Z. & Pendergast, A.M. Abi-2, a novel SH3-containing protein interacts with the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and modulates c-Abl transforming activity. Genes Dev. 9, 2569–2582 (1995).
Pluk, H., Dorey, K. & Superti-Furga, G. Autoinhibition of c-Abl. Cell 108, 247–259 (2002).
Pendergast, A.M. et al. Evidence for regulation of the human ABL tyrosine kinase by a cellular inhibitor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 5927–5931 (1991).
Mayer, B.J. & Baltimore, D. Mutagenic analysis of the roles of SH2 and SH3 domains in regulation of the Abl tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2883–2894 (1994).
Innocenti, M. et al. Mechanisms through which Sos-1 coordinates the activation of Ras and Rac. J. Cell Biol. 156, 125–136 (2002).
Juang, J.L. & Hoffmann, F.M. Drosophila abelson interacting protein (dAbi) is a positive regulator of abelson tyrosine kinase activity. Oncogene 18, 5138–5147 (1999).
Fazioli, F. et al. Eps8, a substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase, enhances EGF-dependent mitogenic signals. EMBO J. 12, 3799–3808 (1993).
Biesova, Z., Piccoli, C. & Wong, W.T. Isolation and characterization of e3B1, an eps8 binding protein that regulates cell growth. Oncogene 14, 233–241 (1997).
Tanis, K.Q., Veach, D., Duewel, H.S., Bornmann, W.G. & Koleske, A.J. Two distinct phosphorylation pathways have additive effects on Abl family kinase activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 3884–3896 (2003).
Sastry, L. et al. Quantitative analysis of Grb2–Sos1 interaction: the N-terminal SH3 domain of Grb2 mediates affinity. Oncogene 11, 1107–1112 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank E. Frittoli and I. Ponzanelli for technical assistance, and M. A. Pearson for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from: Associazione Italiana Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) to G.S. and P.P.D.F.; Telethon Foundation, the Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (Target project Biotechnology) and the European Community (V and VI Framework) to P.P.D.F.; the Swiss National Science foundation to A.C.; and the Italian Ministry of Health (Grant R.F. 02/184) to G.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary figures
Supplementary Information, Fig. S1 (PDF 486 kb)
Supplementary Information, Fig. S2
Supplementary Information, Fig. S3
Supplementary Information, Fig. S4
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sini, P., Cannas, A., Koleske, A. et al. Abl-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Sos-1 mediates growth-factor-induced Rac activation. Nat Cell Biol 6, 268–274 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1096
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1096
This article is cited by
-
Clinics and genetic background of hereditary gingival fibromatosis
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2021)
-
BMP-dependent synaptic development requires Abi-Abl-Rac signaling of BMP receptor macropinocytosis
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Phosphorylation of SOS1 on tyrosine 1196 promotes its RAC GEF activity and contributes to BCR-ABL leukemogenesis
Leukemia (2018)
-
Enabling Tumor Growth and Progression: Recent Progress in Unraveling the Functions of ABL Kinases in Solid Tumor Cells
Current Pharmacology Reports (2018)
-
Abl kinase regulation by BRAF/ERK and cooperation with Akt in melanoma
Oncogene (2017)