Abstract
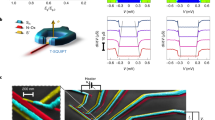
When a superconductor is placed close to a non-superconducting metal, it can induce superconducting correlations in the metal 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10, known as the ‘proximity effect’11. Such behaviour modifies the density of states (DOS) in the normal metal12,13,14,15 and opens a minigap12,13,16 with an amplitude that can be controlled by changing the phase of the superconducting order parameter12,15. Here, we exploit such behaviour to realize a new type of interferometer, the superconducting quantum interference proximity transistor (SQUIPT), for which the operation relies on the modulation with the magnetic field of the DOS of a proximized metal embedded in a superconducting loop. Even without optimizing its design, this device shows extremely low flux noise, down to ∼10−5 Φ0Hz−1/2 (Φ0≃2×10−15 Wb is the flux quantum) and dissipation several orders of magnitude smaller than in conventional superconducting interferometers17,18,19. With optimization, the SQUIPT could significantly increase the sensitivity with which small magnetic moments are detected.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 June 2010
In the original version of this Letter published online, we had inadvertently neglected to cite some prior works that described a related device known as an Andreev interferometer. We apologize for this oversight.
References
Heersche, H. B., Jarillo-Herrero, P., Oostinga, J. B., Vandersypen, L. M. K. & Morpurgo, A. F. Bipolar supercurrent in graphene. Nature 446, 56–59 (2007).
Jarillo-Herrero, P., van Dam, J. A. & Kouwenhoven, L. P. Quantum supercurrent transistors in carbon nanotubes. Nature 439, 953–956 (2006).
Morpurgo, A. F., Kong, J., Marcus, C. M. & Dai, H. Gate-controlled superconducting proximity effect in carbon nanotubes. Science 286, 263–265 (1999).
Kasumov, A. Yu. et al. Proximity-induced superconductivity in DNA. Science 291, 280–282 (2001).
Cleuziou, J.-P., Wernsdorfer, W., Bouchiat, V., Ondarcuhu, T. & Monthioux, M. Carbon nanotube superconducting quantum interference device. Nature Nanotech. 1, 53–59 (2006).
Doh, Y.-J. et al. Tunable supercurrent through semiconductor nanowires. Science 309, 272–275 (2005).
Pothier, H., Guéron, S., Esteve, D. & Devoret, M. H. Flux-modulated Andreev current caused by electronic interference. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 2488–2491 (1994).
Courtois, H., Gandit, Ph. & Pannetier, B. Proximity-induced superconductivity in a narrow metallic wire. Phys. Rev. B 52, 1162–1166 (1995).
Giazotto, F. et al. Resonant transport in Nb/GaAs/AlGaAs heterostructures: Realization of the de Gennes–Saint–James model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 216808 (2001).
Baselmans, J. J. A., Morpurgo, A. F., van Wees, B. J. & Klapwijk, T. M. Reversing the direction of the supercurrent in a controllable Josephson junction. Nature 397, 43–45 (1999).
de Gennes, P. G. Superconductivity of Metals and Alloys (W. A. Benjamin, 1966).
Belzig, W., Wilhelm, F. K., Bruder, C., Schön, G. & Zaikin, A. D. Quasiclassical Greens function approach to mesoscopic superconductivity. Superlattices Microstruct. 25, 1251–1288 (1999).
Belzig, W., Bruder, C. & Schön, G. Local density of states in a dirty normal metal connected to a superconductor. Phys. Rev. B 54, 9443–9448 (1996).
Guéron, S., Pothier, H., Birge, N. O., Esteve, D. & Devoret, M. H. Superconducting proximity effect probed on a mesoscopic length scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3025–3028 (1996).
le Sueur, H., Joyez, P., Pothier, H., Urbina, C. & Esteve, D. Phase controlled superconducting proximity effect probed by tunneling spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 197002 (2008).
Zhou, F., Charlat, P., Spivak, B. & Pannetier, B. Density of states in superconductor–normal metal–superconductor junctions. J. Low Temp. Phys. 110, 841–850 (1998).
Clarke, J. & Braginski, A. I. (eds) The SQUID Handbook (Wiley–VCH, 2004).
Tinkham, M. Introduction to Superconductivity 2nd edn (McGraw-Hill, 1996).
Likharev, K. K. Dynamics of Josephson Junctions and Circuits (Gordon and Breach, 1986).
Courtois, H., Meschke, M., Peltonen, J. T. & Pekola, J. P. Origin of hysteresis in a proximity Josephson junction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 067002 (2008).
Timofeev, A. V. et al. Recombination-limited energy relaxation in a Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer superconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 017003 (2009).
Pascual García, C. & Giazotto, F. Josephson current in nanofabricated V/Cu/V mesoscopic junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 132508 (2009).
Giazotto, F., Heikkilá, T. T., Luukanen, A., Savin, A. M. & Pekola, J. P. Opportunities for mesoscopics in thermometry and refrigeration: Physics and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 217–274 (2006).
Foley, C. P. & Hilgenkamp, H. Why nanoSQUIDs are important: An introduction to the focus issue. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 22, 1–5 (2009).
Raufast, C. et al. Microwave-assisted magnetization reversal in individual isolated clusters of cobalt. IEEE Trans. Magn. 44, 2812–2815 (2008).
Hao, L. et al. Inductive sensor based on nano-scale SQUIDs. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 15, 514–517 (2005).
Gallop, J. SQUIDs: Some limits to measurement. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 16, 1575–1582 (2003).
Hao, L. et al. Novel methods of fabrication and metrology of superconducting nanostructures. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 56, 392–395 (2007).
Usadel, K. D. Generalized diffusion equation for superconducting alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 25, 507–509 (1970).
Wolf, E. L. Principles of Electron Tunneling Spectroscopy (Oxford Univ. Press, 1985).
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge O. Astafiev, L. Faoro, R. Fazio, M. E. Gershenson, T. T. Heikkilä, L. B. Ioffe, V. Piazza, P. Pingue, F. Portier, H. Pothier, H. Rabani, F. Taddei and A. S. Vasenko for fruitful discussions. The work was partially supported by the INFM-CNR Seed project ‘Quantum-Dot Refrigeration: Accessing the μK Regime in Solid-State Nanosystems’, and by the NanoSciERA project ‘NanoFridge’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.G. conceived and carried out the experiment, analysed the data, carried out the calculations and wrote the manuscript. M.M. took part in the early stage of measurements, contributed to the cryogenic set-up and to writing the manuscript. J.T.P. designed and fabricated the samples, and contributed to writing the manuscript. J.P.P. took part in the early stage of measurements, contributed to the cryogenic set-up, took part in the interpretation of the data and contributed to writing the manuscript. F.G. and J.P.P. discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giazotto, F., Peltonen, J., Meschke, M. et al. Superconducting quantum interference proximity transistor. Nature Phys 6, 254–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1537
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1537
This article is cited by
-
Calorimetry of a phase slip in a Josephson junction
Nature Physics (2023)
-
Axial Higgs mode detected by quantum pathway interference in RTe3
Nature (2022)
-
Steady Floquet–Andreev states in graphene Josephson junctions
Nature (2022)
-
Thermal superconducting quantum interference proximity transistor
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Preliminary demonstration of a persistent Josephson phase-slip memory cell with topological protection
Nature Communications (2021)