Abstract
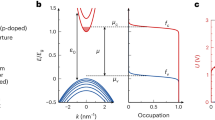
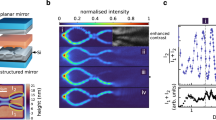
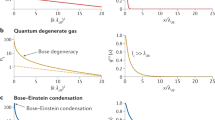
Bose–Einstein condensation1, the macroscopic accumulation of bosonic particles in the energetic ground state below a critical temperature, has been demonstrated in several physical systems2,3,4,5,6,7,8. The perhaps best known example of a bosonic gas, blackbody radiation9, however exhibits no Bose–Einstein condensation at low temperatures10. Instead of collectively occupying the lowest energy mode, the photons disappear in the cavity walls when the temperature is lowered—corresponding to a vanishing chemical potential. Here we report on evidence for a thermalized two-dimensional photon gas with a freely adjustable chemical potential. Our experiment is based on a dye-filled optical microresonator, acting as a ‘white wall’ box for photons. Thermalization is achieved in a photon-number-conserving way by photon scattering off the dye molecules, and the cavity mirrors provide both an effective photon mass and a confining potential—key prerequisites for the Bose–Einstein condensation of photons. As a striking example of the unusual system properties, we demonstrate a yet unobserved light concentration effect into the centre of the confining potential, an effect with prospects for increasing the efficiency of diffuse solar light collection11.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Einstein, A. Quantentheorie des einatomigen idealen Gases. Zweite Abhandlung. Sitz.ber. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. 1, 3–14 (1925).
Anderson, M. H., Ensher, J. R., Matthews, M. R., Wieman, C. E. & Cornell, E. A. Observation of Bose–Einstein condensation in a dilute atomic vapor. Science 269, 198–201 (1995).
Davis, K. B., Mewes, M-O., Andrews, M. R., van Druten, N. J., Kurn, D. M. & Ketterle, W. Bose–Einstein condensation in a gas of sodium atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3969–3973 (1995).
Bradley, C. C., Sackett, C. A. & Hulet, R. G. Bose–Einstein condensation of lithium: Observation of limited condensate number. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 985–989 (1997).
Jochim, S. et al. Bose–Einstein condensation of molecules. Science 302, 2101–2103 (2003).
Deng, H., Weihs, G., Santori, C., Bloch, J. & Yamamoto, Y. Condensation of semiconductor microcavity exciton polaritons. Science 298, 199–2002 (2002).
Kasprzak, J. et al. Bose–Einstein condensation of exciton polaritons. Nature 443, 409–414 (2006).
Balili, R., Hartwell, V., Snoke, D., Pfeiffer, L. & West, K. Bose–Einstein condensation of microcavity polaritons in a trap. Science 316, 1007–1010 (2007).
Planck, M. Über das Gesetz der Energieverteilung im Normalspectrum. Ann. Phys. 4, 553–563 (1901).
Huang, K. Statistical Mechanics 2nd edn, 293–294 (Wiley, 1987).
Van Sark, W. G. J. H. M. et al. Luminescent solar concentrators—a review of recent results. Opt. Exp. 16, 21773–21792 (2008).
Chiao, R. Y. Bogoliubov dispersion relation for a ‘photon fluid’: Is this a superfluid? Opt. Commun. 179, 157–166 (2000).
Bolda, E. L., Chiao, R. Y. & Zurek, W. H. Dissipative optical flow in a nonlinear Fabry–Pérot cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 416–419 (2001).
Mitchell, M. W., Hancox, C. I. & Chiao, R. Y. Dynamics of atom-mediated photon–photon scattering. Phys. Rev. A 62, 043819 (2000).
Jhe, W. et al. Suppression of spontaneous decay at optical frequencies: Test of vacuum-field anisotropy in confined space. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 666–669 (1987).
De Martini, F., Jacobovitz, G. R. & Mataloni, P. Anomalous spontaneous emission time in a microscopic optical cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2955–2958 (1987).
De Martini, F. & Jacobovitz, G. R. Anomalous spontaneous–stimulated-decay phase transition and zero-threshold laser action in a microscopic cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 1711–1714 (1988).
Raimond, J. M., Goy, P., Gross, M., Fabre, C. & Haroche, S. Collective absorption of blackbody radiation by Rydberg atoms in a cavity: An experiment on Bose statistics and Brownian motion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 117–120 (1982).
Bagnato, V. & Kleppner, D. Bose–Einstein condensation in low-dimensional traps. Phys. Rev. A 44, 7439–7441 (1991).
Mullin, W. J. Bose–Einstein condensation in a harmonic potential. J. Low Temp. Phys. 106, 615–641 (1997).
Bohr, N. in Albert Einstein: Philosopher–Scientist (ed. Schilpp, P. A.) (The Library of Living Philosophers, Vol. VII, Open Court. La Salle, 1949).
Magde, D., Wong, R. & Seybold, P. G. Fluorescence quantum yields and their relation to lifetimes of rhodamine 6G and fluorescein in nine solvents: Improved absolute standards for quantum yields. Photochem. Photobiol. 75, 327–334 (2002).
Noda, S., Tomoda, K., Yamamoto, N. & Chutinan, A. Full three-dimensional photonic bandgap crystals at near-infrared wavelengths. Science 289, 604–606 (2000).
Jonkers, J. High power extreme ultra-violet (EUV) light sources for future lithography. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15, S8–S16 (2006).
Metropolis, N., Rosenbluth, A. W., Rosenbluth, M. N., Teller, A. H. & Teller, E. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. J. Chem. Phys. 21, 1087–1092 (1953).
Kennard, E. H. The excitation of fluorescence in fluorescein. Phys. Rev. 29, 466–477 (1927).
McCumber, D. E. Einstein relations connecting broadband emission and absorption spectra. Phys. Rev. 136, A954–A957 (1964).
Sawicki, D. A. & Knox, R. S. Universal relationship between optical emission and absorption of complex systems: An alternative approach. Phys. Rev. A 54, 4837–4841 (1996).
Kogelnik, H. & Li, T. Laser beams and resonators. Appl. Opt. 5, 1550–1567 (1966).
Acknowledgements
We thank F. Schelle for experimental contributions during the early phase of this project. Financial support from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the focused research unit FOR557 is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.K. and M.W. contributed to the experimental idea; J.K. carried out the experiments. All authors analysed the experimental data and discussed the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klaers, J., Vewinger, F. & Weitz, M. Thermalization of a two-dimensional photonic gas in a ‘white wall’ photon box. Nature Phys 6, 512–515 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1680
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1680
This article is cited by
-
Dispersive and dissipative coupling of photon Bose-Einstein condensates
Communications Physics (2022)
-
Dressed photon-excitons in a Fabry–Pérot cavity filled with a nonlinear semiconductor
Applied Physics B (2022)
-
Modified Bose-Einstein condensation in an optical quantum gas
Nature Communications (2021)
-
A weakly-interacting many-body system of Rydberg polaritons based on electromagnetically induced transparency
Communications Physics (2021)
-
Dynamics of the Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless transition in a photon fluid
Nature Photonics (2020)