Abstract
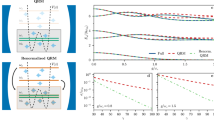
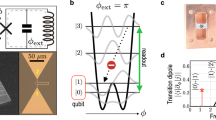
In circuit quantum electrodynamics1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 (QED), where superconducting artificial atoms are coupled to on-chip cavities, the exploration of fundamental quantum physics in the strong-coupling regime has greatly evolved. In this regime, an atom and a cavity can exchange a photon frequently before coherence is lost. Nevertheless, all experiments so far are well described by the renowned Jaynes–Cummings model11. Here, we report on the first experimental realization of a circuit QED system operating in the ultrastrong-coupling limit12,13, where the atom–cavity coupling rate g reaches a considerable fraction of the cavity transition frequency ωr. Furthermore, we present direct evidence for the breakdown of the Jaynes–Cummings model. We reach remarkable normalized coupling rates g/ωr of up to 12% by enhancing the inductive coupling14 of a flux qubit to a transmission line resonator. Our circuit extends the toolbox of quantum optics on a chip towards exciting explorations of ultrastrong light–matter interaction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blais, A., Huang, R-S., Wallraff, A., Girvin, S. M. & Schoelkopf, R. J. Cavity quantum electrodynamics for superconducting electrical circuits: An architecture for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 69, 062320 (2004).
Wallraff, A. et al. Strong coupling of a single photon to a superconducting qubit using circuit quantum electrodynamics. Nature 431, 162–167 (2004).
Chiorescu, I. et al. Coherent dynamics of a flux qubit coupled to a harmonic oscillator. Nature 431, 159–162 (2004).
Johansson, J. et al. Vacuum Rabi oscillations in a macroscopic superconducting qubit LC oscillator system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 127006 (2006).
Schuster, D. I. et al. Resolving photon number states in a superconducting circuit. Nature 445, 515–518 (2007).
Astafiev, O. et al. Single artificial-atom lasing. Nature 449, 588–590 (2007).
Deppe, F. et al. Two-photon probe of the Jaynes–Cummings model and controlled symmetry breaking in circuit QED. Nature Phys. 4, 686–691 (2008).
Fink, J. et al. Climbing the Jaynes–Cummings ladder and observing its nonlinearity in a cavity QED system. Nature 454, 315–318 (2008).
Abdumalikov, A., Astafiev, O., Nakamura, Y., Pashkin, Y. & Tsai, J. Vacuum Rabi splitting due to strong coupling of a flux qubit and a coplanar-waveguide resonator. Phys. Rev. B 78, 180502 (2008).
Hofheinz, M. et al. Synthesizing arbitrary quantum states in a superconducting resonator. Nature 459, 546–549 (2009).
Jaynes, E. T. & Cummings, F. W. Comparison of quantum and semiclassical radiation theories with application to the beam maser. Proc. IEEE 51, 89–109 (1963).
Ciuti, C. & Carusotto, I. Input–output theory of cavities in the ultrastrong coupling regime: The case of time-independent cavity parameters. Phys. Rev. A 74, 033811 (2006).
Devoret, M., Girvin, S. & Schoelkopf, R. Circuit-QED: How strong can the coupling between a Josephson junction atom and a transmission line resonator be? Ann. Phys. 16, 767–779 (2007).
Bourassa, J. et al. Ultrastrong coupling regime of cavity QED with phase-biased flux qubits. Phys. Rev. A 80, 032109 (2009).
Niemczyk, T. et al. Fabrication technology of and symmetry breaking in superconducting quantum circuits. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 22, 034009 (2009).
Schoelkopf, R. J. & Girvin, S. M. Wiring up quantum systems. Nature 451, 664–669 (2008).
Bishop, L. et al. Nonlinear response of the vacuum Rabi resonance. Nature Phys. 5, 105–109 (2008).
Thompson, R. J., Rempe, G. & Kimble, H. J. Observation of normal-mode splitting for an atom in an optical cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 1132–1135 (1992).
Walther, H., Varcoe, B. T. H., Englert, B-G. & Becker, T. Cavity quantum electrodynamics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, 1325–1382 (2006).
Haroche, S. & Raimond, J-M. Exploring the Quantum (Oxford Univ. Press, 2006).
Reithmaier, J. P. et al. Strong coupling in a single quantum dot semiconductor microcavity system. Nature 432, 197–200 (2004).
Gröblacher, S., Hammerer, K., Vanner, M. R. & Aspelmeyer, M. Observation of strong coupling between a micromechanical resonator and an optical cavity field. Nature 460, 724–727 (2009).
Günter, G. et al. Sub-cycle switch-on of ultrastrong light–matter interaction. Nature 458, 178–181 (2009).
Anappara, A. et al. Signatures of the ultrastrong light–matter coupling regime. Phys. Rev. B 79, 201303 (2009).
Mooij, J. E. et al. Josephson persistent-current qubit. Science 285, 1036–1039 (1999).
Schuster, D. I. et al. Ac stark shift and dephasing of a superconducting qubit strongly coupled to a cavity field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 123602 (2005).
Sabin, C., Garcia-Ripoll, J. J., Solano, E. & Leon, J. Dynamics of entanglement via propagating microwave photons. Phys. Rev. B 81, 184501 (2010).
Hines, A. P., Dawson, C. M., McKenzie, R. H. & Milburn, G. J. Entanglement and bifurcations in Jahn-Teller models. Phys. Rev. A 70, 022303 (2004).
Peropadre, B., Forn-Diaz, P., Solano, E. & Garcia-Ripoll, J. J. Switchable ultrastrong coupling in circuit QED. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 023601 (2010).
Zueco, D., Reuther, G. M., Kohler, S. & Hanggi, P. Qubit-oscillator dynamics in the dispersive regime: Analytical theory beyond the rotating-wave approximation. Phys. Rev. A 80, 033846 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We thank G. M. Reuther for discussions and T. Brenninger, C. Probst and K. Uhlig for technical support. We acknowledge financial support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft through SFB 631 and the German Excellence Initiative through NIM. E.S. acknowledges financial support from UPV/EHU Grant GIU07/40, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación FIS2009-12773-C02-01, Basque Government Grant IT472-10, European Projects EuroSQIP and SOLID. D.Z. acknowledges financial support from FIS2008-01240 and FIS2009-13364-C02-0 (MICINN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.N. fabricated the sample, conducted the experiment and analysed the data presented in this work. F.D. provided important contributions regarding the interpretation of the results. T.N. and F.D. co-wrote the manuscript. J.J.G-R. provided the basic idea and the techniques for the numerical analysis of the data. E.S. and J.J.G-R. supervised the interpretation of the data. D.Z. and T.H. contributed to the understanding of the results and developed an analytical model of our system. H.H. contributed to the numerical analysis and helped with the experiment. E.P.M. contributed strongly to the experimental set-up. M.J.S. and F.H. contributed to discussions and helped edit the manuscript. A.M. and R.G. supervised the experimental part of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niemczyk, T., Deppe, F., Huebl, H. et al. Circuit quantum electrodynamics in the ultrastrong-coupling regime. Nature Phys 6, 772–776 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1730
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1730
This article is cited by
-
Sudden change of the photon output field marks phase transitions in the quantum Rabi model
Communications Physics (2024)
-
Ultrastrong to nearly deep-strong magnon-magnon coupling with a high degree of freedom in synthetic antiferromagnets
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Preparation of maximally-entangled states with multiple cat-state qutrits in circuit QED
Frontiers of Physics (2024)
-
On the two-photon quantum Rabi model at the critical coupling strength
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2024)
-
Generation of a hybrid W entangled state of three photonic qubits with different encodings
Quantum Information Processing (2024)