Abstract
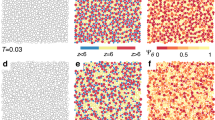
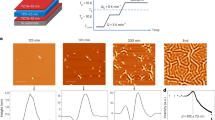
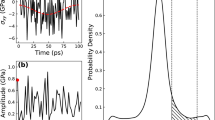
Glasses are dynamically arrested states of matter that do not exhibit the long-range periodic structure of crystals1,2,3,4. Here we develop new insights from theory and simulation into the impact of quantum fluctuations on glass formation. As intuition may suggest, we observe that large quantum fluctuations serve to inhibit glass formation as tunnelling and zero-point energy allow particles to traverse barriers facilitating movement. However, as the classical limit is approached a regime is observed in which quantum effects slow down relaxation making the quantum system more glassy than the classical system. This dynamical ‘reentrance’ occurs in the absence of obvious structural changes and has no counterpart in the phenomenology of classical glass-forming systems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debenedetti, P. G. & Stillinger, F. H. Supercooled liquids and the glass transition. Nature 410, 259–267 (2001).
Berthier, L. et al. Direct experimental evidence of a growing length scale accompanying the glass transition. Science 310, 1797–1800 (2005).
Biroli, G. et al. Thermodynamic signature of growing amorphous order in glass-forming liquids. Nature Phys. 4, 771–775 (2008).
Hedges, L. O., Jack, R. L., Garrahan, J. P. & Chandler, D. E. Dynamic order–disorder in atomistic models of structural glass formers. Science 323, 1309–1313 (2009).
Amir, A., Oreg, Y. & Imry, Y. Slow relaxations and aging in the electron glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 126403 (2009).
Wu, W. H. et al. From classical to quantum glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 2076–2079 (1991).
Boninsegni, M., Prokof’ev, N. & Svistunov, B. Superglass phase of 4He. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 105301 (2006).
Biroli, G., Chamon, C. & Zamponi, F. Theory of the superglass phase. Phys. Rev. B 78, 224306 (2008).
Hunt, B. et al. Evidence for a superglass state in solid 4He. Science 324, 632–636 (2009).
Götze, W. Complex Dynamics of Glass-Forming Liquids: A Mode-Coupling Theory (Oxford Univ. Press, 2009).
Biroli, G., Bouchard, J., Miyazaki, K. & Reichman, D. R. Inhomogeneous mode-coupling theory and growing dynamic length in supercooled liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 195701 (2006).
Dawson, K. et al. Higher-order glass-transition singularities in colloidal systems with attractive interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 011401 (2001).
Götze, W. & Voightmann, Th. Effect of composition changes on the structural relaxation of a binary mixture. Phys. Rev. E 67, 021502 (2003).
Zaccarelli, E. et al. Confirmation of anomalous dynamical arrest in attractive colloids: A molecular dynamics study. Phys. Rev. E 66, 041402 (2002).
Foffi, G. et al. Mixing effects for the structural relaxation in binary hard-sphere liquids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 085701 (2003).
Pham, K. N. et al. Multiple glassy states in a simple model system. Science 296, 104–106 (2002).
Götze, W. & Lücke, M. Dynamical structure factor S(q,ω) of liquid helium II at zero temperature. Phys. Rev. B 13, 3825–3842 (1976).
Pusey, P. N. & van Megen, W. Observation of a glass transition in suspensions of spherical colloidal particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2083–2086 (1987).
Foffi, G. et al. α-relaxation processes in binary hard-sphere mixtures. Phys. Rev. E 69, 011505 (2004).
Craig, I. R. & Manolopoulos, D. E. Quantum statistics and classical mechanics: Real time correlation functions from ring polymer molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 121, 3368–3373 (2004).
Miller, T. F. & Manolopoulos, D. E. Quantum diffusion in liquid water from ring polymer molecular dynamic. J. Chem. Phys. 123, 154504 (2005).
Richardson, J. O. & Althorpe, S. C. Ring-polymer molecular dynamics rate-theory in the deep-tunneling regime: Connection with semiclassical instanton theory. J. Chem. Phys. 131, 214106 (2009).
Kob, W. & Andersen, H. C. Testing mode-coupling theory for a supercooled binary Lennard-Jones mixture I: The van Hove correlation function. Phys. Rev. E 51, 4626–4641 (1995).
Rounder, E. Hydrophobic solvation, quantum nature, and diffusion of atomic hydrogen in liquid water. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 72, 201–206 (2005).
Wipf, H. Hydrogen in Metals III: Properties and Applications (Springer, 1997).
Markland, T. E., Habershon, S. & Manolopoulos, D. E. Quantum diffusion of hydrogen and muonium atoms in liquid water and hexagonal ice. J. Chem. Phys. 128, 194506 (2008).
Westfahl, H., Schmalian, J. & Wolynes, P. G. Dynamical mean-field theory of quantum stripe glass. Phys. Rev. B 68, 134203 (2003).
Lee, Y. & Berne, B. J. Global optimization: Quantum thermal annealing with path integral Monte Carlo. J. Phys. Chem. A 104, 86–95 (2000).
Das, A. & Chakrabati, B. K. Quantum annealing and analog quantum computation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1061–1081 (2008).
Foini, L., Semerjian, G. & Zamponi, F. Solvable model of quantum random optimization problems. Phys. Rev. Lett 105, 167204 (2010).
Acknowledgements
B.J.B. acknowledges support from NSF grant No. CHE-0910943. D.R.R. would like to thank the NSF through grant No. CHE-0719089. K.M. acknowledges support from Kakenhi grant No. 21015001 and 2154016. The authors acknowledge G. Biroli and L. Cugliandolo for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.R.R. and E.R. developed the QMCT approach. K.M. and E.R. carried out the QMCT calculations. T.E.M. carried out the RPMD calculations and analysed the results with B.J.B. and J.A.M. All authors contributed to the preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 283 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markland, T., Morrone, J., Berne, B. et al. Quantum fluctuations can promote or inhibit glass formation. Nature Phys 7, 134–137 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1865
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1865
This article is cited by
-
Quantum effects on dislocation motion from ring-polymer molecular dynamics
npj Computational Materials (2018)
-
A Tentative Replica Theory of Glassy Helium 4
Journal of Low Temperature Physics (2012)
-
Quantum glass forging
Nature Physics (2011)