Abstract
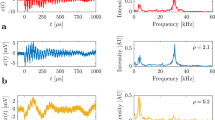
The study of critical phenomena and universal power laws has been one of the central advances in statistical mechanicsduring the second half of the past century, explaining traditional thermodynamic critical points1, avalanche behaviour near depinning transitions2,3 and a wide variety of other phenomena4. Scaling, universality and the renormalization group claim to predict all behaviour at long length and timescales asymptotically close to critical points. In most cases, the comparison between theory and experiments has been limited to the evaluation of the critical exponents of the power-law distributions predicted at criticality. An excellent area for investigating scaling phenomena is provided by systems exhibiting crackling noise, such as the Barkhausen effect in ferromagnetic materials5. Here we go beyond power-law scaling and focus on the average functional form of the noise emitted by avalanches—the average temporal avalanche shape4. By analysing thin permalloy films and improving the data analysis methods, our experiments become quantitatively consistent with our calculation for the multivariable scaling function in the presence of a demagnetizing field and finite field-ramp rate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson, K. G. The renormalization group: Critical phenomena and the Kondo problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 47, 773–840 (1975).
Fisher, D. S. Collective transport in random media: From superconductors to earthquakes. Phys. Rep. 301, 113–150 (1998).
Doussal, P. L. & Wiese, K. J. Size distributions of shocks and static avalanches from the functional renormalization group. Phys. Rev. E 79, 051106 (2009).
Sethna, J. P., Dahmen, K. & Myers, C. R. Crackling noise. Nature 410, 242–250 (2001).
Durin, G. & Zapperi, S. in The Science of Hysteresis Vol. II (eds Bertotti, G. & Mayergoyz, I.) Ch. III, 181–267 (Academic, 2006).
Mehta, A. P., Mills, A. C., Dahmen, K. A. & Sethna, J. P. Universal pulse shape scaling function and exponents: Critical test for avalanche models applied to Barkhausen noise. Phys. Rev. E 65, 046139 (2002).
Laurson, L. & Alava, M. J. 1/f noise and avalanche scaling in plastic deformation. Phys. Rev. E 74, 066106 (2006).
Chrzan, D. C. & Mills, M. J. Criticality in the plastic deformation of L12 intermetallic compounds. Phys. Rev. B 50, 30–42 (1994).
Kuntz, M. C. & Sethna, J. P. Noise in disordered systems: The power spectrum and dynamic exponents in avalanche models. Phys. Rev. B 62, 11699–11708 (2000).
Colaiori, F. Exactly solvable model of avalanches dynamics for Barkhausen crackling noise. Adv. Phys. 57, 287–359 (2008).
Durin, G. & Zapperi, S. On the power spectrum of magnetization noise. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 242–245, 1085–1088 (2002).
Zapperi, S., Castellano, C., Colaiori, F. & Durin, G. Signature of effective mass in crackling-noise asymmetry. Nature Phys. 1, 46–49 (2005).
Alessandro, B., Beatrice, C., Bertotti, G. & Montorsi, A. Domain-wall dynamics and Barkhausen effect in metallic ferromagnetic materials. I. Theory. J. Appl. Phys. 68, 2901–2907 (1990).
Sethna, J. P. et al. Hysteresis and hierarchies: Dynamics of disorder-driven first-order phase transformations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 3347–3350 (1993).
Laurson, L., Illa, X. & Alava, M. J. The effect of thresholding on temporal avalanche statistics. J. Stat. Mech. P01019 (2009).
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T. & Flannery, B. P. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1988).
Durin, G. & Zapperi, S. Scaling exponents for Barkhausen avalanches in polycrystalline and amorphous ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 4705–4708 (2000).
Zapperi, S., Cizeau, P., Durin, G. & Stanley, H. E. Dynamics of a ferromagnetic domain wall: Avalanches, depinning transition, and the Barkhausen effect. Phys. Rev. B 58, 6353–6366 (1998).
Zaiser, M. Scale invariance in plastic flow of crystalline solids. Adv. Phys. 55, 185–245 (2006).
Fisher, D. S., Dahmen, K., Ramanathan, S. & Ben-Zion, Y. Statistics of earthquakes in simple models of heterogeneous faults. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 4885–4888 (1997).
Ryu, K-S., Akinaga, H. & Shin, S-C. Tunable scaling behaviour observed in Barkhausen criticality of a ferromagnetic film. Nature Phys. 3, 547–550 (2007).
Colaiori, F., Zapperi, S. & Durin, G. Shape of a Barkhausen pulse. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272–276, E533–E534 (2004).
O’Brien, K. P. & Weissman, M. B. Statistical characterization of Barkhausen noise. Phys. Rev. E 50, 3446–3452 (1994).
Bertotti, G. Hysteresis in Magnetism (Academic, 1998).
Baldassarri, A., Colaiori, F. & Castellano, C. Average shape of a fluctuation: Universality in excursions of stochastic processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 060601 (2003).
Kampen, N. G. V. Stochastic Processes in Physics and Chemistry (Elsevier, 2007).
Bray, A. J. Random walks in logarithmic and power-law potentials, non-universal persistence, and vortex dynamics in the two-dimensional XY model. Phys. Rev. E 62, 103–112 (2000).
Hubert, A. & Schäfer, R. Magnetic Domains: The Analysis of Magnetic Microstructures (Springer, 1998).
Viegas, A. D. C. et al. Thickness dependence of the high-frequency magnetic permeability in amorphous Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 033908 (2007).
Santi, L. et al. Effects of thickness on the statistical properties of the Barkhausen noise in amorphous films. Physica B 384, 144–146 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank F. Colaiori, K. Daniels and K. Dahmen for enlightening discussions. F.B. would like to thank M. Carara and L. F. Schelp for their experimental contributions and fruitful discussions. S.Z. acknowledges financial support from the short-term mobility programme of CNR. S.P. and J.P.S. were supported by DOE-BES. R.L.S. and F.B. were supported by CNPq, CAPES, FAPERJ and FAPERGS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.B., G.D. and R.L.S. were responsible for the experiments. S.P., S.Z. and J.P.S. were responsible for the implementation of the Wiener filtering methods. S.P. was responsible for the theoretical analysis of the avalanche shapes, the simulations and wrote the original text of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 591 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papanikolaou, S., Bohn, F., Sommer, R. et al. Universality beyond power laws and the average avalanche shape. Nature Phys 7, 316–320 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1884
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1884
This article is cited by
-
Mild-to-wild plastic transition is governed by athermal screw dislocation slip in bcc Nb
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Simulating the mechanisms of serrated flow in interstitial alloys with atomic resolution over diffusive timescales
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Time-dependent branching processes: a model of oscillating neuronal avalanches
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
On interevent time distributions of avalanche dynamics
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Waiting-time statistics in magnetic systems
Scientific Reports (2020)