Abstract
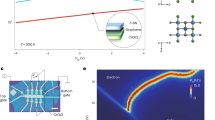
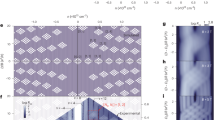
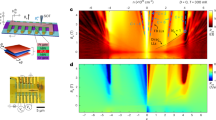
The physics of Dirac fermions in condensed-matter systems has received extraordinary attention following the discoveries of two new types of quantum Hall effect in single-layer and bilayer graphene1,2,3. The electronic structure of trilayer graphene (TLG) has been predicted to consist of both massless single-layer-graphene-like and massive bilayer-graphene-like Dirac subbands4,5,6,7, which should result in new types of mesoscopic and quantum Hall phenomena. However, the low mobility exhibited by TLG devices on conventional substrates has led to few experimental studies8,9. Here we investigate electronic transport in high-mobility (>100,000 cm2 V−1 s−1) TLG devices on hexagonal boron nitride, which enables the observation of Shubnikov–de Haas oscillations and an unconventional quantum Hall effect. The massless and massive characters of the TLG subbands lead to a set of Landau-level crossings, whose magnetic-field and filling-factor coordinates enable the determination of the Slonczewski–Weiss–McClure (SWMcC) parameters10 used to describe the peculiar electronic structure of TLG. Moreover, at high magnetic fields, the degenerate crossing points split into manifolds, indicating the existence of broken-symmetry quantum Hall states.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438, 197–200 (2005).
Zhang, Y., Tan, Y-W., Stormer, H. L. & Kim, P. Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase in graphene. Nature 438, 201–204 (2005).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Unconventional quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase of 2π in bilayer graphene. Nature Phys. 2, 177–180 (2006).
Lu, C. L., Chang, C. P., Huang, Y. C., Chen, R. B. & Lin, M. L. Influence of an electric field on the optical properties of few-layer graphene with AB stacking. Phys. Rev. B 73, 144427 (2006).
Guinea, F., Neto, A. H. C. & Peres, N. M. R. Electronic states and Landau levels in graphene stacks. Phys. Rev. B 73, 245426 (2006).
Latil, S. & Henrard, L. Charge carriers in few-layer graphene films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 036803 (2006).
Partoens, B. & Peeters, F. M. From graphene to graphite: Electronic structure around the K point. Phys. Rev. B 74, 075404 (2006).
Craciun, M. F. et al. Trilayer graphene is a semimetal with a gate-tunable band overlap. Nature Nanotech. 4, 383–388 (2009).
Zhu, W., Perebeinos, V., Freitag, M. & Avouris, P. Carrier scattering, mobilities, and electrostatic potential in monolayer, bilayer, and trilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 80, 235402 (2009).
Dresselhaus, M. S. & Dresselhaus, G. Intercalation compounds of graphite. Adv. Phys. 51, 1–186 (2002).
Li, G. & Andrei, E. Y. Observation of Landau levels of Dirac fermions in graphite. Nature Phys. 3, 623–627 (2007).
Niimi, Y., Kambara, H. & Fukuyama, H. Localized distributions of quasi-two-dimensional electronic states near defects artificially created at graphite surfaces in magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 026803 (2009).
Miller, D. L. et al. Observing the quantization of zero mass carriers in graphene. Science 324, 924–927 (2009).
McCann, E. & Fal’ko, V. L. Landau-level degeneracy and quantum Hall effect in a graphite bilayer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 086805 (2006).
Taniguchi, T. & Watanabe, K. Synthesis of high-purity boron nitride single crystals under high pressure by using Ba–Bn solvent. J. Cryst. Growth 303, 525–529 (2007).
Dean, C. R. et al. Boron nitride substrates for high-quality graphene electronics. Nature Nanotech. 5, 722–726 (2010).
Bao, W. et al. Magnetoconductance oscillations and evidence for fractional quantum Hall states in suspended bilayer and trilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 246601 (2010).
Du, X., Skachko, I., Barker, A. & Andrei, E. Y. Approaching ballistic transport in suspended graphene. Nature Nano. 3, 491–495 (2008).
Bolotin, K. I., Sikes, K. J., Hone, J., Stormer, H. L. & Kim, P. Temperature-dependent transport in suspended graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 096802 (2008).
Piazza, V. et al. First-order phase transitions in a quantum Hall ferromagnet. Nature 402, 638–641 (1999).
Zhang, X. C., Faulhaber, D. R. & Jiang, H. W. Multiple phases with the same quantized Hall conductance in a two-subband system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 216801 (2005).
Koshino, M. & McCann, E. Trigonal warping and Berry’s phase N π in ABC-stacked multilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 80, 165409 (2009).
Koshino, M. & McCann, E. Landau level spectra and the quantum Hall effect of multilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 83, 165443 (2011).
Zhang, Y. et al. Landau-level splitting in graphene in high magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 136806 (2006).
Checkelsky, J. G., Li, L. & Ong, N. P. Zero-energy state in graphene in a high magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 206801 (2008).
Feldman, B. E., Martin, J. & Yacoby, A. Broken-symmetry states and divergent resistance in suspended bilayer graphene. Nature Phys. 5, 889–893 (2009).
Zhao, Y., Cadden-Zimansky, P., Jiang, Z. & Kim, P. Symmetry breaking in the zero-energy Landau level in bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 066801 (2009).
Du, X., Skachko, I., Duerr, F., Luican, A. & Andrei, E. Y. Fractional quantum Hall effect and insulating phase of Dirac electrons in graphene. Nature 462, 192–195 (2009).
Song, Y. J. et al. High-resolution tunnelling spectroscopy of a graphene quartet. Nature 467, 185–189 (2010).
Jungwirth, T., Shukla, S. P., Smrčka, L., Shayegan, M. & MacDonald, A. H. Magnetic anisotropy in quantum Hall ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2328–2331 (1998).
Ezawa, M. Supersymmetry and unconventional quantum Hall effect in monolayer, bilayer and trilayer graphene. Physica E 40, 269–272 (2007).
Koshino, M. & McCann, E. Parity and valley degeneracy in multilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 81, 115315 (2010).
Moser, J., Barreiro, A. & Bachtold, A. Current-induced cleaning of graphene. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 163513 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Koshino and E. McCann for discussions and sharing their preliminary work on LLs in Bernal-stacked TLG. We also thank L. Levitov and P. Kim for discussions, A. F. Young for discussions and experimental help on hBN, and J. D. Sanchez-Yamagishi and J. Wang for experimental help. We acknowledge financial support from the Office of Naval Research GATE MURI and a National Science Foundation Career Award. This research has made use of the NSF-funded MIT CMSE and Harvard CNS facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T. Taychatanapat fabricated the samples and carried out the experiments. K.W. and T. Taniguchi synthesized the hBN samples. T. Taychatanapat and P.J-H. carried out the data analysis and co-wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 8714 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taychatanapat, T., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. et al. Quantum Hall effect and Landau-level crossing of Dirac fermions in trilayer graphene. Nature Phys 7, 621–625 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2008
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2008
This article is cited by
-
Topological Lifshitz transition and one-dimensional Weyl mode in HfTe5
Nature Materials (2023)
-
Dry release transfer of graphene and few-layer h-BN by utilizing thermoplasticity of polypropylene carbonate
npj 2D Materials and Applications (2019)
-
Multilayer graphene shows intrinsic resistance peaks in the carrier density dependence
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Electrical control of 2D magnetism in bilayer CrI3
Nature Nanotechnology (2018)
-
Low-energy band structure and even-odd layer number effect in AB-stacked multilayer graphene
Scientific Reports (2018)