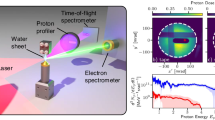
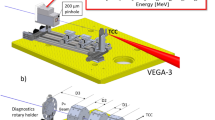
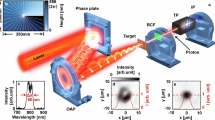
Abstract
Recent progress in generating high-energy (>50 MeV) protons from intense laser–matter interactions (1018–1021 W cm−2; refs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) has opened up new areas of research, with applications in radiography8, oncology9, astrophysics10, medical imaging11, high-energy-density physics12,13,14, and ion-proton beam fast ignition15,16,17,18,19. With the discovery of proton focusing with curved surfaces20,21, rapid advances in these areas will be driven by improved focusing technologies. Here we report on the first investigation of the generation and focusing of a proton beam using a cone-shaped target. We clearly show that the focusing is strongly affected by the electric fields in the beam in both open and enclosed (cone) geometries, bending the trajectories near the axis. Also in the cone geometry, a sheath electric field effectively ‘channels’ the proton beam through the cone tip, substantially improving the beam focusing properties. These results agree well with particle simulations and provide the physics basis for many future applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatchett, S. P. et al. Electron, photon, and ion beams from the relativistic interaction of Petawatt laser pulses with solid targets. Phys. Plasmas 7, 2076–2082 (2000).
Snavely, R. A. et al. Intense high-energy proton beams from petawatt-laser irradiation of solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 2945–2948 (2000).
Wilks, S. C. et al. Energetic proton generation in ultra-intense laser-solid interactions. Phys. Plasmas 8, 542–549 (2001).
Borghesi, M. et al. Multi-MeV proton source investigations in ultraintense laser-foil interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 055003 (2004).
Fuchs, J. et al. Laser-driven proton scaling laws and new paths towards energy increase. Nature Phys. 2, 48–54 (2006).
Hegelich, B. M. et al. Laser acceleration of quasi-monoenergetic MeV ion beams. Nature 439, 441–444 (2006).
Robson, L. et al. Scaling of proton acceleration driven by petawatt-laser-plasma interactions. Nature Phys. 3, 58–62 (2007).
Mackinnon, A. J. et al. Proton radiography of a laser-driven implosion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 045001 (2006).
Bulanov, S. V. & Khoroshkov, V. S. Feasibility of using laser ion accelerators in proton therapy. Plasma Phys. Rep. 28, 453–456 (2002).
Baraffe, I. The structure and evolution of giant planets. Space Sci. Rev. 116, 67–76 (2005).
Fritzier, S. et al. Proton beams generated with high-intensity lasers: Applications to medical isotope production. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 3039–3041 (2003).
Dyer, G. M. et al. Equation of state measurements of dense plasma heated with fast protons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 015002 (2008).
Mason, T. E. Pulsed neutron scattering for the 21st century. Phys. Today 59, 44–49 (May, 2006).
Higginson, D. P. et al. Laser generated neutron source for neutron resonance spectroscopy. Phys. Plasmas 17, 100701 (2010).
Key, M. H. et al. Study of electron and proton isochoric heating for fast ignition. J. Phys. IV France 133, 371–378 (2006).
Key, M. H. et al. Proton fast ignition. Fusion Sci. Tech. 49, 440–452 (2006).
Roth, M. et al. Fast ignition by intense laser-accelerated proton beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 436–439 (2001).
Temporal, M. & Honrubia, J. J. Numerical study of fast ignition of ablatively imploded deuterium–tritium fusion capsules by ultra-intense proton beams. Phys. Plasmas 9, 3098–3107 (2002).
Tabak, M. et al. Ignition and gain with ultrapowerful lasers. Phys. Plasmas 1, 1626–1634 (1994).
Snavely, R. A. et al. Laser generated proton beam focusing and high temperature isochoric heating of solid matter. Phys. Plasmas 14, 092703 (2007).
Patel, P. K. et al. Isochoric heating of solid-density matter with an ultrafast proton beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 125004 (2003).
Green, J. S. et al. Surface heating of wire plasma using laser—irradiated cone geometries. Nature Phys. 3, 853–856 (2007).
Kodama, R. et al. Fast heating of ultra-high density plasma as a step toward laser fusion ignition. Nature 412, 798–802 (2001).
Hey, D. S. et al. Laser-accelerated proton conversion efficiency thickness scaling. Phys. Plasmas 16, 123108 (2009).
Toncian, T. et al. Ultrafast laser- driven microlens to focus and energy-select mega-electron volt protons. Science 312, 410–413 (2006).
Kar, S. et al. Dynamic control of laser-produced proton beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 105004 (2008).
Kar, S. et al. Ballistic focusing of polyenergetic protons driven by petawatt laser pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 225003 (2011).
Batha, S., Aragonez, R. & Archuleta, F. TRIDENT high-energy-density facility experimental capabilities and diagnostics. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 10F305 (2008).
Foord, M. E. et al. Proton generation and efficiency from an intense laser irradiated foil. High Energy. Density Phys. 3, 365–370 (2007).
Nürnberg, F. et al. Radiochromic film imaging spectroscopy of laser-accelerated proton beams. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 033301 (2009).
Welch, D. R., Rose, D. V., Oliver, B. V. & Clark, R. E. Simulation techniques for heavy ion fusion chamber transport. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 464, 134–139 (2001).
Offermann, D. T. et al. Characterization and focusing of light ion beams generated by ultra-intensely irradiated thin foils at the kilojoule scale. Phys. Plasmas 18, 056713 (2011).
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank P. Norreys for helpful discussions concerning this work and gratefully acknowledge the support of the staff at the TRIDENT laser facility at Los Alamos National Laboratory. We would also like to thank T. Yabuuchi for useful discussions. T.B. is supported through the Lawrence Scholar Program at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. This work was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract DE-SC0001265. M.R., A.O. and D.K. are supported by the BMBF 06DA9044I.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.N.B., M.E.F., P.K.P., R.B.S., M.H.K., H.S.M., E.M.G. M.S.W. and T.B. were involved in the project planning and target design. T.B., K.A.F., D.T.O., S.A.G., L.C.J., D.P.H., D.C.G., A.O., D.K. and M.R. contributed to the experimental work. T.B. and C.B. carried out the data analysis and wrote the letter along with F.N.B. and M.E.F., where M.E.F. performed the simulations.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartal, T., Foord, M., Bellei, C. et al. Focusing of short-pulse high-intensity laser-accelerated proton beams. Nature Phys 8, 139–142 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2153
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2153
This article is cited by
-
Focused Energy, A New Approach Towards Inertial Fusion Energy
Journal of Fusion Energy (2023)
-
Defect engineering of silicon with ion pulses from laser acceleration
Communications Materials (2023)
-
Low divergent MeV-class proton beam with micrometer source size driven by a few-cycle laser pulse
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Super-strong magnetic field-dominated ion beam dynamics in focusing plasma devices
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
High energy implementation of coil-target scheme for guided re-acceleration of laser-driven protons
Scientific Reports (2021)