Abstract
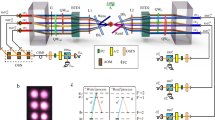
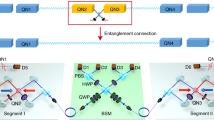
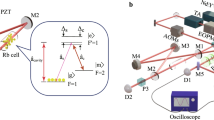
Quantum memories are regarded as one of the fundamental building blocks of linear-optical quantum computation1 and long-distance quantum communication2. A long-standing goal to realize scalable quantum information processing is to build a long-lived and efficient quantum memory. There have been significant efforts distributed towards this goal. However, either efficient but short-lived3,4 or long-lived but inefficient quantum memories5,6,7 have been demonstrated so far. Here we report a high-performance quantum memory in which long lifetime and high retrieval efficiency meet for the first time. By placing a ring cavity around an atomic ensemble, employing a pair of clock states, creating a long-wavelength spin wave and arranging the set-up in the gravitational direction, we realize a quantum memory with an intrinsic spin wave to photon conversion efficiency of 73(2)% together with a storage lifetime of 3.2(1) ms. This realization provides an essential tool towards scalable linear-optical quantum information processing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knill, E., Laflamme, R. & Milburn, G. J. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001).
Duan, L-M., Lukin, M. D., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 414, 413–418 (2001).
Simon, J., Tanji, H., Thompson, J. K. & Vuletic, V. Interfacing collective atomic excitations and single photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 183601 (2007).
Hedges, M. P., Longdell, J. J., Li, Y. & Sellars, M. J. Efficient quantum memory for light. Nature 465, 1052–1056 (2010).
Zhao, B. et al. A millisecond quantum memory for scalable quantum networks. Nature Phys. 5, 95–99 (2009).
Zhao, R. et al. Long-lived quantum memory. Nature Phys. 5, 100–104 (2009).
Radnaev, A. G. et al. A quantum memory with telecom-wavelength conversion. Nature Phys. 6, 894–899 (2010).
Browne, D. E. & Rudolph, T. Resource-efficient linear optical quantum computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 010501 (2005).
Briegel, H. J., Dur, W., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Quantum repeaters: The role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5932–5935 (1998).
Bodiya, T. P. & Duan, L-M. Scalable generation of graph-state entanglement through realistic linear optics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 143601 (2006).
Zhao, B., Chen, Z-B., Chen, Y-A., Schmiedmayer, J. & Pan, J-W. Robust creation of entanglement between remote memory qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 240502 (2007).
Sangouard, N. et al. Robust and efficient quantum repeaters with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 77, 062301 (2008).
Varnava, M., Browne, D. E. & Rudolph, T. How good must single photon sources and detectors be for efficient linear optical quantum computation? Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 060502 (2008).
Chaneliere, T. et al. Storage and retrieval of single photons transmitted between remote quantum memories. Nature 438, 833–836 (2005).
Eisaman, M. D. et al. Electromagnetically induced transparency with tunable single-photon pulses. Nature 438, 837–841 (2005).
Sherson, J. F. et al. Quantum teleportation between light and matter. Nature 443, 557–560 (2006).
Saglamyurek, E. et al. Broadband waveguide quantum memory for entangled photons. Nature 469, 512–515 (2011).
Clausen, C. et al. Quantum storage of photonic entanglement in a crystal. Nature 469, 508–511 (2011).
Specht, H. P. et al. A single-atom quantum memory. Nature 473, 190–193 (2011).
Chou, C-W. et al. Functional quantum nodes for entanglement distribution over scalable quantum networks. Science 316, 1316–1320 (2007).
Yuan, Z-S. et al. Experimental demonstration of a BDCZ quantum repeater node. Nature 454, 1098–1101 (2008).
Pan, J-W., Simon, C., Brukner, C. & Zeilinger, A. Entanglement purification for quantum communication. Nature 410, 1067–1070 (2001).
Barrett, S. D., Rohde, P. P. & Stace, T. M. Scalable quantum computing with atomic ensembles. New J. Phys. 12, 093032 (2010).
Kuzmich, A. et al. Generation of nonclassical photon pairs for scalable quantum communication with atomic ensembles. Nature 423, 731–734 (2003).
Felinto, D., Chou, C. W., de Riedmatten, H., Polyakov, S. V. & Kimble, H. J. Control of decoherence in the generation of photon pairs from atomic ensembles. Phys. Rev. A 72, 053809 (2005).
Fleischhauer, M., Imamoglu, A. & Marangos, J. P. Electromagnetically induced transparency: Optics in coherent media. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 633–673 (2005).
Kimble, H. J. The quantum internet. Nature 453, 1023–1030 (2008).
Duan, L. M. & Monroe, C. Colloquium: Quantum networks with trapped ions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1209–1224 (2010).
Bao, X-H. et al. Generation of narrow-band polarization-entangled photon pairs for atomic quantum memories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 190501 (2008).
Grangier, P., Roger, G. & Aspect, A. Experimental evidence for a photon anticorrelation effect on a beam splitter: A new light on single-photon interferences. Europhys. Lett. 1, 173–179 (1986).
Matsukevich, D. N. et al. Deterministic single photons via conditional quantum evolution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 013601 (2006).
Gorshkov, A. V., André, A., Lukin, M. D. & Sørensen, A. S. Photon storage in Λ-type optically dense atomic media. i. cavity model. Phys. Rev. A 76, 033804 (2007).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Commission through the ERC Grant, the STREP project HIP, the CAS, the NNSFC and the National Fundamental Research Program (Grant No. 2011CB921300) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X-H.B., A.D., B.Z. and J-W.P. conceived and designed the experiment. A.D., P.D., A.R., T.S. and X-H.B. built the set-up. X-H.B., A.R., P.D. and J.R. carried out the experiment. X-H.B., A.R., L.L., N-L.L. and B.Z. analysed the data. X-H.B. and B.Z. wrote the paper with substantial contributions by all authors. J-W.P. supervised the whole project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, XH., Reingruber, A., Dietrich, P. et al. Efficient and long-lived quantum memory with cold atoms inside a ring cavity. Nature Phys 8, 517–521 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2324
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2324
This article is cited by
-
Entangling motional atoms and an optical loop at ambient condition
npj Quantum Information (2023)
-
Photonic integrated beam delivery for a rubidium 3D magneto-optical trap
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Lifetime reductions and read-out oscillations due to imperfect initial level preparations of atoms in a long-lived DLCZ-like quantum memory
Applied Physics B (2022)
-
Proposal for space-borne quantum memories for global quantum networking
npj Quantum Information (2021)
-
Long-lived and multiplexed atom-photon entanglement interface with feed-forward-controlled readouts
Communications Physics (2021)