Abstract
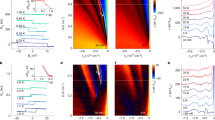
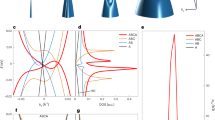
Electrons in a periodic lattice can propagate without scattering for macroscopic distances despite the presence of the non-uniform Coulomb potential due to the nuclei1. Such ballistic motion of electrons allows the use of a transverse magnetic field to focus electrons2. This phenomenon, known as transverse magnetic focusing (TMF), has been used to study the Fermi surface of metals3 and semiconductor heterostructures4, as well as to investigate Andreev reflection3 and spin–orbit interaction5, and to detect composite fermions6,7. Here we report on the experimental observation of TMF in high-mobility mono-, bi- and tri-layer graphene devices. The ability to tune the graphene carrier density enables us to investigate TMF continuously from the hole to the electron regime and analyse the resulting focusing fan. Moreover, by applying a transverse electric field to tri-layer graphene, we use TMF as a ballistic electron spectroscopy method to investigate controlled changes in the electronic structure of a material. Finally, we demonstrate that TMF survives in graphene up to 300 K, by far the highest temperature reported for any system, opening the door to new room-temperature applications based on electron-optics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloch, F. Über die Quantenmechanik der Elektronen in Kristallgittern. Z. Phys. 52, 555–600 (1929).
Tsoi, V. S. Focusing of electrons in a metal by a transverse magnetic field. JETP Lett. 19, 70–71 (1974).
Tsoi, V. S., Bass, J. & Wyder, P. Studying conduction-electron/interface interactions using transverse electron focusing. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 1641–1693 (1999).
Van Houten, H. et al. Coherent electron focusing with quantum point contacts in a two-dimensional electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 39, 8556–8575 (1989).
Rokhinson, L. P., Larkina, V., Lyanda-Geller, Y. B., Pfeiffer, L. N. & West, K. W. Spin separation in cyclotron motion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 146601 (2004).
Goldman, V. J., Su, B. & Jain, J. K. Detection of composite fermions by magnetic focusing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 2065–2068 (1994).
Smet, J. H. et al. Magnetic focusing of composite fermions through arrays of cavities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2272–2275 (1996).
Dean, C. R. et al. Boron nitride substrates for high-quality graphene electronics. Nature Nanotech. 5, 722–726 (2010).
Taychatanapat, T., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. & Jarillo-Herrero, P. Quantum Hall effect and Landau-level crossing of Dirac fermions in trilayer graphene. Nature Phys. 7, 621–625 (2011).
Mayorov, A. S. et al. Micrometer-scale ballistic transport in encapsulated graphene at room temperature. Nano Lett. 11, 2396–2399 (2011).
Beenakker, C. W. J., van Houten, H. & van Wees, B. J. Mode interference effect in coherent electron focusing. Europhys. Lett. 4, 359–364 (1988).
Aidala, K. E. et al. Imaging magnetic focusing of coherent electron waves. Nature Phys. 3, 464–468 (2007).
Rakyta, P., Kormányos, A., Cserti, J. & Koskinen, P. Exploring the graphene edges with coherent electron focusing. Phys. Rev. B 81, 115411 (2010).
Silvestrov, P. G. & Efetov, K. B. Charge accumulation at the boundaries of a graphene strip induced by a gate voltage: Electrostatic approach. Phys. Rev. B 77, 155436 (2008).
McCann, E. & Fal’ko, V. I. Landau-level degeneracy and quantum Hall effect in a graphite bilayer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 086805 (2006).
Lu, C. L., Chang, C. P., Huang, Y. C., Chen, R. B. & Lin, M. L. Influence of an electric field on the optical properties of few-layer graphene with AB stacking. Phys. Rev. B 73, 144427 (2006).
Guinea, F., Neto, A. H. C. & Peres, N. M. R. Electronic states and Landau levels in graphene stacks. Phys. Rev. B 73, 245426 (2006).
Latil, S. & Henrard, L. Charge carriers in few-layer graphene films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 036803 (2006).
Partoens, B. & Peeters, F. M. From graphene to graphite: Electronic structure around the K point. Phys. Rev. B 74, 075404 (2006).
Koshino, M. & McCann, E. Gate-induced interlayer asymmetry in ABA-stacked trilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 79, 125443 (2009).
Cheianov, V. V., Falk´o, V. & Altshuler, B. L. The focusing of electron flow and a veselago lens in graphene p–n junctions. Science 315, 1252–1255 (2007).
Hwang, E. H. & Das Sarma, S. Acoustic phonon scattering limited carrier mobility in two-dimensional extrinsic graphene. Phys. Rev. B 77, 115449 (2008).
Heremans, J., Fuller, B. K., Thrush, C. M. & Partin, D. L. Temperature dependence of electron focusing in In1−xGax As/InP heterojunctions. Phys. Rev. B 52, 5767–5772 (1995).
Schiefele, J., Sols, F. & Guinea, F. Temperature dependence of the conductivity of graphene on boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 85, 195420 (2012).
Liu, Z. et al. Direct growth of graphene/hexagonal boron nitride stacked layers. Nano Lett. 11, 2032–2037 (2011).
Mayorov, A. S. et al. Interaction-drive spectrum reconstruction in bilayer graphene. Science 333, 860–863 (2011).
Weitz, R. T., Allen, M. T., Feldman, B. E., Martin, J. & Yacoby, A. Broken-symmetry states in doubly gated suspended bilayer graphene. Science 330, 812–816 (2010).
Kotov, V. N., Uchoa, B., Pereira, V. M., Guinea, F. & Castro Neto, A. H. Electron–electron interactions in graphene: Current status and perspectives. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 1067–1125 (2012).
Guinea, F., Katsnelson, M. I. & Geim, A. K. Energy gaps and a zero-field quantum Hall effect in graphene by strain engineering. Nature Phys. 6, 30–33 (2010).
Levy, N. et al. Strain-induced pseudo-magnetic fields greater than 300 tesla in graphene nanobubbles. Science 329, 544–547 (2010).
Gomes, K. K., Mar, W., Ko, W., Guinea, F. & Manoharan, H. C. Designer Dirac fermions and topological phases in molecular graphene. Nature 483, 306–310 (2012).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Levitov and A. Yacoby for discussions. We acknowledge financial support from National Science Foundation Career Award No. DMR-0845287 and the Office of Naval Research GATE MURI. This work made use of the MRSEC Shared Experimental Facilities supported by the National Science Foundation under award No. DMR-0819762 and of Harvard’s Center for Nanoscale Systems (CNS), supported by the National Science Foundation under grant No. ECS-0335765.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T. Taychatanapat fabricated the samples and performed the experiments. K.W. and T. Taniguchi synthesized the hBN samples. T. Taychatanapat and P.J-H. carried out the data analysis and co-wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 2165 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taychatanapat, T., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. et al. Electrically tunable transverse magnetic focusing in graphene. Nature Phys 9, 225–229 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2549
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys2549
This article is cited by
-
Probing miniband structure and Hofstadter butterfly in gated graphene superlattices via magnetotransport
npj 2D Materials and Applications (2023)
-
Ballistic transport spectroscopy of spin-orbit-coupled bands in monolayer graphene on WSe2
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Study the optoelectronic properties of reduced graphene oxide doped on the porous silicon for photodetector
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2023)
-
Influence of Device Geometry and Imperfections on the Interpretation of Transverse Magnetic Focusing Experiments
Nanoscale Research Letters (2022)
-
Gate-tunable Veselago interference in a bipolar graphene microcavity
Nature Communications (2022)