Abstract
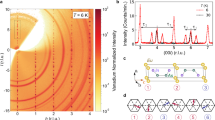
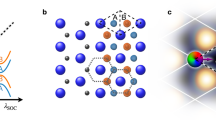
Topology of electron wavefunctions was first introduced to characterize the quantum Hall states in two dimensions discovered in 1980 (ref. 1). Over the past decade, it has been recognized that symmetry plays a crucial role in the classification of topological phases, leading to the broad notion of symmetry-protected topological phases2. As a primary example, topological insulators3,4 are distinguished from normal insulators in the presence of time-reversal symmetry ( ). A three-dimensional (3D) topological insulator3,4,5,6 exhibits an odd number of protected surface Dirac cones, a unique property that cannot be realized in any 2D systems. Importantly, the existence of topological insulators requires Kramers’ degeneracy in spin–orbit coupled electronic materials; this forbids any direct analogue in boson systems7. In this report, we discover a 3D topological photonic crystal phase hosting a single surface Dirac cone, which is protected by a crystal symmetry8,9,10—the nonsymmorphic glide reflection11,12,13 rather than
). A three-dimensional (3D) topological insulator3,4,5,6 exhibits an odd number of protected surface Dirac cones, a unique property that cannot be realized in any 2D systems. Importantly, the existence of topological insulators requires Kramers’ degeneracy in spin–orbit coupled electronic materials; this forbids any direct analogue in boson systems7. In this report, we discover a 3D topological photonic crystal phase hosting a single surface Dirac cone, which is protected by a crystal symmetry8,9,10—the nonsymmorphic glide reflection11,12,13 rather than  . Such a gapless surface state is fully robust against random disorder of any type14,15. This bosonic topological band structure is achieved by applying alternating magnetization to gap out the 3D ‘generalized Dirac points’ discovered in the bulk of our crystal. The Z2 bulk invariant is characterized through the evolution of Wannier centres16. Our proposal—readily realizable using ferrimagnetic materials at microwave frequencies17,18—expands the scope of 3D topological materials from fermions to bosons.
. Such a gapless surface state is fully robust against random disorder of any type14,15. This bosonic topological band structure is achieved by applying alternating magnetization to gap out the 3D ‘generalized Dirac points’ discovered in the bulk of our crystal. The Z2 bulk invariant is characterized through the evolution of Wannier centres16. Our proposal—readily realizable using ferrimagnetic materials at microwave frequencies17,18—expands the scope of 3D topological materials from fermions to bosons.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

 .
.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thouless, D. J., Kohmoto, M., Nightingale, M. P. & den Nijs, M. Quantized Hall conductance in a two-dimensional periodic potential. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 405–408 (1982).
Chiu, C.-K., Teo, J. C. Y., Schnyder, A. P & Ryu, S. Classification of topological quantum matter with symmetries. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/abs/1505.03535 (2015).
Hasan, M. & Kane, C. Colloquium: Topological insulators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3045–3067 (2010).
Qi, X.-L. & Zhang, S.-C. Topological insulators and superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 1057–1110 (2011).
Zhang, H. et al. Topological insulators in Bi2Se3, Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3 with a single Dirac cone on the surface. Nature Phys. 5, 438–442 (2009).
Moore, J. E. The birth of topological insulators. Nature 464, 194–198 (2010).
Lu, L., Joannopoulos, J. D. & Soljačić, M. Topological photonics. Nature Photon. 8, 821–829 (2014).
Fu, L. Topological crystalline insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 106802 (2011).
Hsieh, T. H. et al. Topological crystalline insulators in the SnTe material class. Nature Commun. 3, 982 (2012).
Ando, Y. & Fu, L. Topological crystalline insulators and topological superconductors: From concepts to materials. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 6, 361–381 (2015).
Liu, C.-X., Zhang, R.-X. & VanLeeuwen, B. K. Topological nonsymmorphic crystalline insulators. Phys. Rev. B 90, 085304 (2014).
Fang, C. & Fu, L. New classes of three-dimensional topological crystalline insulators: Nonsymmorphic and magnetic. Phys. Rev. B 91, 161105 (2015).
Shiozaki, K., Sato, M. & Gomi, K. Z 2 topology in nonsymmorphic crystalline insulators: Möbius twist in surface states. Phys. Rev. B 91, 155120 (2015).
Fu, L. & Kane, C. L. Topology, delocalization via average symmetry and the symplectic Anderson transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 246605 (2012).
Fulga, I. C., van Heck, B., Edge, J. M. & Akhmerov, A. R. Statistical topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 89, 155424 (2014).
Taherinejad, M., Garrity, K. F. & Vanderbilt, D. Wannier center sheets in topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 89, 115102 (2014).
Wang, Z., Chong, Y., Joannopoulos, J. D. & Soljačić, M. Observation of unidirectional backscattering-immune topological electromagnetic states. Nature 461, 772–775 (2009).
Skirlo, S. A., Lu, L., Igarashi, Y., Joannopoulos, J. & Soljacic, M. Experimental observation of large chern numbers in photonic crystals. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/abs/1504.04399 (2015).
Varjas, D., de Juan, F. & Lu, Y.-M. Bulk invariants and topological response in insulators and superconductors with nonsymmorphic symmetries. Phys. Rev. B 92, 195116 (2015).
Meiboom, S., Sammon, M. & Berreman, D. W. Lattice symmetry of the cholesteric blue phases. Phys. Rev. A 28, 3553–3560 (1983).
Young, S. M. et al. Dirac semimetal in three dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 140405 (2012).
Liu, Z. K. et al. Discovery of a three-dimensional topological Dirac semimetal, Na3Bi. Science 343, 864–867 (2014).
Wang, Z., Weng, H., Wu, Q., Dai, X. & Fang, Z. Three-dimensional Dirac semimetal and quantum transport in Cd3As2 . Phys. Rev. B 88, 125427 (2013).
Lu, L., Fu, L., Joannopoulos, J. D. & Soljačić, M. Weyl points and line nodes in gyroid photonic crystals. Nature Photon. 7, 294–299 (2013).
Lu, L. et al. Experimental observation of Weyl points. Science 349, 622–624 (2015).
Mock, A., Lu, L. & O’Brien, J. Space group theory and Fourier space analysis of two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguides. Phys. Rev. B 81, 155115 (2010).
Lu, L. et al. Three-dimensional photonic crystals by large-area membrane stacking. Opt. Lett. 37, 4726–4728 (2012).
Parameswaran, S. A., Turner, A. M., Arovas, D. P. & Vishwanath, A. Topological order and absence of band insulators at integer filling in non-symmorphic crystals. Nature Phys. 9, 299–303 (2013).
Roy, R. Space group symmetries and low lying excitations of many-body systems at integer fillings. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/abs/1212.2944 (2012).
Young, S. M. & Kane, C. L. Dirac semimetals in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 126803 (2015).
Watanabe, H., Po, H. C., Vishwanath, A. & Zaletel, M. Filling constraints for spin–orbit coupled insulators in symmorphic and nonsymmorphic crystals. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 14551–14556 (2015).
Haldane, F. D. M. & Raghu, S. Possible realization of directional optical waveguides in photonic crystals with broken time-reversal symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 013904 (2008).
Yu, R., Qi, X. L., Bernevig, A., Fang, Z. & Dai, X. Equivalent expression of Z2 topological invariant for band insulators using the non-abelian Berry connection. Phys. Rev. B 84, 075119 (2011).
Alexandradinata, A., Dai, X. & Bernevig, B. A. Wilson-loop characterization of inversion-symmetric topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 89, 155114 (2014).
Ludwig, A. W. W., Fisher, M. P. A., Shankar, R. & Grinstein, G. Integer quantum Hall transition: An alternative approach and exact results. Phys. Rev. B 50, 7526–7552 (1994).
Bardarson, J. H., Tworzydło, J., Brouwer, P. W. & Beenakker, C. W. J. One-parameter scaling at the Dirac point in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 106801 (2007).
Khanikaev, A. B. et al. Photonic topological insulators. Nature Mater. 12, 233–239 (2013).
Chen, W.-J. et al. Experimental realization of photonic topological insulator in a uniaxial metacrystal waveguide. Nature Commun. 5, 5782 (2014).
Wu, L.-H. & Hu, X. Scheme for achieving a topological photonic crystal by using dielectric material. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 223901 (2015).
Fang, K., Yu, Z. & Fan, S. Realizing effective magnetic field for photons by controlling the phase of dynamic modulation. Nature Photon. 6, 782–787 (2012).
Rechtsman, M. C. et al. Photonic Floquet topological insulators. Nature 496, 196–200 (2013).
Wang, P., Lu, L. & Bertoldi, K. Topological phononic crystals with one-way elastic edge waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 104302 (2015).
Liu, C.-X. Antiferromagnetic crystalline topological insulators. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/abs/1304.6455 (2013).
Alexandradinata, A., Fang, C., Gilbert, M. J. & Bernevig, B. A. Spin–orbit-free topological insulators without time-reversal symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 116403 (2014).
Wang, Z., Alexandradinata, A., Cava, R. J. & Bernevig, B. A. (in review, 2015).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. H. Hsieh, A. Alexandradinata, B. Andrei Bernevig, S. Skirlo, A. Men, J. Liu and F. Wang for discussions. S.G.J. and J.D.J. were supported in part by the US ARO. through the ISN, under Contract No. W911NF-13-D-0001. C.F. and L.F. were supported by the DOE Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering under Award No. DE-SC0010526. L.L. was supported in part by the MRSEC Program of the NSF under Award No. DMR-1419807. M.S. and L.L. (analysis and reading of the manuscript) were supported in part by the MIT S3TEC EFRC of DOE under Grant No. DE-SC0001299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.L. proposed the BP I structure and performed the calculations with the help of S.G.J. and C.F.; C.F. and L.F. conceived and analysed the band topology; all authors contributed to the discussion of the results and preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 611 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Fang, C., Fu, L. et al. Symmetry-protected topological photonic crystal in three dimensions. Nature Phys 12, 337–340 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3611
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3611
This article is cited by
-
Electrically-pumped compact topological bulk lasers driven by band-inverted bound states in the continuum
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Photonic helicoid-like surface states in chiral metamaterials
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Sensing performance of Fano resonance induced by the coupling of two 1D topological photonic crystals
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2023)
-
Fully integrated topological electronics
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Ideal nodal rings of one-dimensional photonic crystals in the visible region
Light: Science & Applications (2022)