Abstract
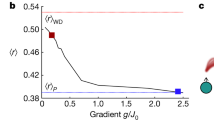
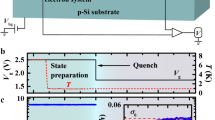
When a system thermalizes it loses all memory of its initial conditions. Even within a closed quantum system, subsystems usually thermalize using the rest of the system as a heat bath. Exceptions to quantum thermalization have been observed, but typically require inherent symmetries1,2 or noninteracting particles in the presence of static disorder3,4,5,6. However, for strong interactions and high excitation energy there are cases, known as many-body localization (MBL), where disordered quantum systems can fail to thermalize7,8,9,10. We experimentally generate MBL states by applying an Ising Hamiltonian with long-range interactions and programmable random disorder to ten spins initialized far from equilibrium. Using experimental and numerical methods we observe the essential signatures of MBL: initial-state memory retention, Poissonian distributed energy level spacings, and evidence of long-time entanglement growth. Our platform can be scaled to more spins, where a detailed modelling of MBL becomes impossible.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kinoshita, T., Wenger, T. & Weiss, D. S. A quantum Newton’s cradle. Nature 440, 900–903 (2006).
Gring, M. et al. Relaxation and prethermalization in an isolated quantum system. Science 337, 1318–1322 (2012).
Anderson, P. W. Absence of diffusion in certain random lattices. Phys. Rev. 109, 1492–1505 (1958).
Wiersma, D. S., Bartolini, P., Lagendijk, A. & Righini, R. Localization of light in a disordered medium. Nature 390, 671–673 (1997).
Billy, J. et al. Direct observation of Anderson localization of matter waves in a controlled disorder. Nature 453, 891–894 (2008).
Roati, G. et al. Anderson localization of a non-interacting Bose–Einstein condensate. Nature 453, 895–898 (2008).
Basko, D. M., Aleiner, I. L. & Altshuler, B. L. Possible experimental manifestations of the many-body localization. Phys. Rev. B 76, 052203 (2007).
Oganesyan, V. & Huse, D. A. Localization of interacting fermions at high temperature. Phys. Rev. B 75, 155111 (2007).
Pal, A. & Huse, D. A. Many-body localization phase transition. Phys. Rev. B 82, 174411 (2010).
Serbyn, M., Papić, Z. & Abanin, D. A. Local conservation laws and the structure of the many-body localized states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 127201 (2013).
Yao, N. et al. Many-body localization in dipolar systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 243002 (2014).
Kondov, S., McGehee, W., Xu, W. & DeMarco, B. Disorder-induced localization in a strongly correlated atomic hubbard gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 083002 (2015).
Schreiber, M. et al. Observation of many-body localization of interacting fermions in a quasi-random optical lattice. Science 349, 842–845 (2015).
Mølmer, K. & Sørensen, A. Multiparticle entanglement of hot trapped ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 1835–1838 (1999).
Islam, R. et al. Emergence and frustration of magnetism with variable-range interactions in a quantum simulator. Science 340, 583–587 (2013).
Wu, Y.-L. & Das Sarma, S. Understanding analog quantum simulation dynamics in coupled ion-trap qubits. Phys. Rev. A 93, 022332 (2016).
Richerme, P. et al. Non-local propagation of correlations in quantum systems with long-range interactions. Nature 511, 198–201 (2014).
Jurcevic, P. et al. Quasiparticle engineering and entanglement propagation in a quantum many-body system. Nature 511, 202–205 (2014).
Deutsch, J. M. Quantum statistical mechanics in a closed system. Phys. Rev. A 43, 2046–2049 (1991).
Srednicki, M. Chaos and quantum thermalization. Phys. Rev. E 50, 888–901 (1994).
Rigol, M., Dunjko, V. & Olshanii, M. Thermalization and its mechanism for generic isolated quantum systems. Nature 452, 854–858 (2008).
Hauke, P. & Heyl, M. Many-body localization and quantum ergodicity in disordered long-range Ising models. Phys. Rev. B 92, 134204 (2015).
Burin, A. L. Localization in a random XY model with long-range interactions: intermediate case between single-particle and many-body problems. Phys. Rev. B 92, 104428 (2015).
Nandkishore, R. & Huse, D. A. Many-body localization and thermalization in quantum statistical mechanics. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 6, 15–38 (2015).
Bardarson, J. H., Pollmann, F. & Moore, J. E. Unbounded growth of entanglement in models of many-body localization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 017202 (2012).
Pino, M. Entanglement growth in many-body localized systems with long-range interactions. Phys. Rev. B 90, 174204 (2014).
Haeffner, H. et al. Scalable multiparticle entanglement of trapped ions. Nature 438, 643–646 (2005).
Helstrom, C. W. Quantum Detection and Estimation Theory (Academic, 1976).
Braunstein, S. L. & Caves, C. M. Statistical distance and the geometry of quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 3439–3443 (1994).
Pezzé, L. & Smerzi, A. in Proc. Int. School Phys. (eds Tino, G. & Kasevich, M.) 691–741 (IOS Press, 2014).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Duan, Z.-X. Gong, T. Grover, C. Laumann, S. Wang, N. Yao and J. Zhang for helpful discussions. This work is supported by the ARO Atomic and Molecular Physics Program, the AFOSR MURI on Quantum Measurement and Verification, the IARPA MQCO Program, and the NSF Physics Frontier Center at JQI. M.H. acknowledges the Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina (grant No. LPDS 2013-07 and LPDR 2015-01) and P.H. acknowledges the EU IP SIQS, the SFB FoQuS (FWF Project No. F4016-N23) and the ERC synergy grant UQUAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.S., A.L., P.R., B.N., P.W.H. and C.M. performed the experimental work and P.H., M.H. and D.A.H. performed the theoretical work. All authors contributed to the preparation of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2397 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, J., Lee, A., Richerme, P. et al. Many-body localization in a quantum simulator with programmable random disorder. Nature Phys 12, 907–911 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3783
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3783
This article is cited by
-
Emergence of highly coherent two-level systems in a noisy and dense quantum network
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Theory of localization-hindered thermalization in nonlinear multimode photonics
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Reviving product states in the disordered Heisenberg chain
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Down-conversion of a single photon as a probe of many-body localization
Nature (2023)
-
Engineering random spin models with atoms in a high-finesse cavity
Nature Physics (2023)