Abstract
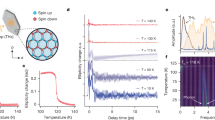
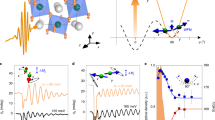
Light fields at terahertz and mid-infrared frequencies allow for the direct excitation of collective modes in condensed matter, which can be driven to large amplitudes. For example, excitation of the crystal lattice1,2 has been shown to stimulate insulator–metal transitions3,4, melt magnetic order5,6 or enhance superconductivity7,8,9. Here, we generalize these ideas and explore the simultaneous excitation of more than one lattice mode, which are driven with controlled relative phases. This nonlinear mode mixing drives rotations as well as displacements of the crystal-field atoms, mimicking the application of a magnetic field and resulting in the excitation of spin precession in the rare-earth orthoferrite ErFeO3. Coherent control of lattice rotations may become applicable to other interesting problems in materials research—for example, as a way to affect the topology of electronic phases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Först, M. et al. Nonlinear phononics as an ultrafast route to lattice control. Nat. Phys. 7, 854–856 (2011).
Subedi, A., Cavalleri, A. & Georges, A. Theory of nonlinear phononics for coherent light control of solids. Phys. Rev. B 89, 220301(R) (2014).
Rini, M. et al. Control of the electronic phase of a manganite by mode-selective vibrational excitation. Nature 449, 72–74 (2007).
Caviglia, A. D. et al. Ultrafast strain engineering in complex oxide heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 136801 (2012).
Först, M. et al. Driving magnetic order in a manganite by ultrafast lattice excitation. Phys. Rev. B 84, 241104(R) (2011).
Först, M. et al. Spatially resolved ultrafast magnetic dynamics launched at a complex-oxide hetero-interface. Nat. Mater. 14, 883–888 (2015).
Kaiser, S. et al. Optically induced coherent transport far above Tc in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6+δ . Phys. Rev. B 89, 184516 (2014).
Hu, W. et al. Optically enhanced coherent transport in YBa2Cu3O6.5 by ultrafast redistribution of interlayer coupling. Nat. Mater. 13, 705–711 (2014).
Mitrano, M. et al. Possible light-induced superconductivity in K3C60 at high temperature. Nature 530, 461–464 (2016).
Tsymbal, L. T. et al. Natural behavior of the magnetization under spontaneous reorientation: TmFeO3, ErFeO3 . Low Temp. Phys. 31, 277–282 (2005).
Gupta, H. C. et al. Lattice dynamic investigation of Raman and infrared wavenumbers at the zone center of orthorhombic RFeO3 (R = Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm) perovskites. J. Raman Spectrosc. 33, 67–70 (2002).
Korenev, V. L. et al. Long-range p–d exchange interaction in a ferromagnet–semiconductor hybrid structure. Nat. Phys. 12, 85–91 (2016).
Kubacka, T. et al. Large-amplitude spin dynamics driven by a THz pulse in resonance with an electromagnon. Science 343, 1333–1336 (2014).
Katsura, H., Nagaosa, N. & Balatsky, A. V. Spin current and magnetoelectric effect in noncollinear magnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 057205 (2005).
Spaldin, N. A. & Fiebig, M. The renaissance of magnetoelectric multiferroics. Science 309, 391–392 (2005).
Koshizuka, N. & Ushioda, S. Inelastic-light-scattering study of magnon softening in ErFeO3 . Phys. Rev. B 22, 5394–5399 (1980).
White, R. M., Nemanich, R. J. & Herring, C. Light scattering from magnetic excitations in orthoferrites. Phys. Rev. B 25, 1822–1836 (1982).
Pisarev, R. V. et al. Charge transfer transitions in multiferroic BiFeO3 and related ferrite insulators. Phys. Rev. B 79, 235128 (2009).
Fleury, P. A. & Loudon, R. Scattering of light by one- and two-magnon excitations. Phys. Rev. 166, 514 (1968).
Pershan, P. S., van der Ziel, J. P. & Malmstrom, L. D. Theoretical discussion of the inverse Faraday effect, Raman scattering, and related phenomena. Phys. Rev. 143, 574–583 (1966).
Kirilyuk, A., Kimel, A. V. & Rasing, T. Ultrafast optical manipulation of magnetic order. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 2731–2784 (2010).
Yamaguchi, K. et al. Terahertz time-domain observation of spin reorientation in orthoferrite ErFeO3 through magnetic free induction decay. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 137204 (2013).
Iida, R. et al. Spectral dependence of photoinduced spin precession in DyFeO3 . Phys. Rev. B 84, 064402 (2011).
Kimel, A. V. et al. Ultrafast non-thermal control of magnetization by instantaneous photomagnetic pulses. Nature 435, 655–657 (2005).
Mikhaylovskiy, R. V. et al. Ultrafast optical modification of exchange interactions in iron oxides. Nat. Commun. 6, 8190 (2015).
Abedi, A., Maitra, N. T. & Gross, E. K. U. Correlated electron-nuclear dynamics: exact factorization of the molecular wavefunction. J. Chem. Phys. 137, 22A530 (2012).
Min, S. K., Abedi, A., Kim, K. S. & Gross, E. K. U. Is the molecular Berry phase an artifact of the Born–Oppenheimer approximation? Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 263004 (2014).
Sentef, M. A. et al. Theory of Floquet band formation and local pseudospin textures in pump–probe photoemission of graphene. Nat. Commun. 6, 7047 (2015).
Wang, Y. H. et al. Observation of Floquet–Bloch states on the surface of a topological insulator. Science 342, 453–457 (2013).
Deng, G. et al. The magnetic structures and transitions of a potential multiferroic orthoferrite ErFeO3 . J. Appl. Phys. 117, 164105 (2015).
Cerullo, G., Baltuška, A., Mücke, O. D. & Vozzi, C. Few-optical-cycle light pulses with passive carrier-envelope phase stabilization. Laser Photon. Rev. 5, 323–351 (2011).
Sell, A., Scheu, R., Leitenstorfer, A. & Huber, R. Field-resolved detection of phase-locked infrared transients from a compact Er:fiber system tunable between 55 and 107 THz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 251107 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to A. Subedi, D. M. Juraschek, M. Fechner and N. A. Spaldin for sharing the calculated phonon eigenvectors and for useful discussions. We thank R. V. Pisarev for providing the samples. We additionally acknowledge support from J. Harms (for graphics), D. Nicoletti (for FTIR measurements) and G. Meier (for sample characterization). A.V.K., R.V.M. and D.B. thank I. Razdolski for fruitful discussions of the first experiments and Th. Rasing for continuous support. The research leading to these results received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013)/ERC Grant Agreement no. 319286 (QMAC). We acknowledge support from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft via the excellence cluster ‘The Hamburg Centre for Ultrafast Imaging—Structure, Dynamics and Control of Matter at the Atomic Scale’. A.V.K., R.V.M. and D.B. acknowledge partial support by the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) Grant No. 281043 (Femtospin).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.Cavalleri conceived the project together with T.F.N. T.F.N. and A.Cartella built the mid-infrared pump/Faraday-rotation probe experimental set-up with help from A.Cantaluppi and M.F. T.F.N. and A.Cartella performed the measurements. A.Cartella and T.F.N. developed the 1D-FDTD code and performed the simulations with help from R.V.M. (for the solution of the Landau–Lifshitz equation). T.F.N. analysed the experimental data. A.V.K., R.V.M. and D.B. identified the material system for the project and helped in the analysis of the data. R.M. collaborated in the interpretation of the data. The manuscript was written by T.F.N. and A.Cavalleri, with feedback from all co-authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 892 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nova, T., Cartella, A., Cantaluppi, A. et al. An effective magnetic field from optically driven phonons. Nature Phys 13, 132–136 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3925
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3925
This article is cited by
-
On demand laser-induced frequency tuning of coherent magnons in a nanometer-thick magnet at room temperature
Nature Communications (2026)
-
Chiral phonons in polar LiNbO3
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Ultrafast simultaneous manipulation of multiple ferroic orders through nonlinear phonon excitation
npj Quantum Materials (2025)
-
Time-domain study of coupled collective excitations in quantum materials
npj Quantum Materials (2025)
-
Spontaneously formed phonon frequency combs in van der Waals solid CrGeTe3 and CrSiTe3
Nature Communications (2025)