Abstract
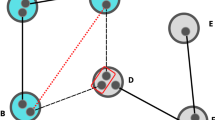
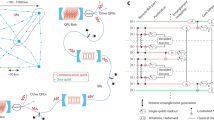
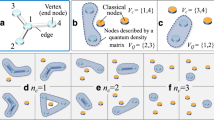
Quantum networks are composed of nodes that can send and receive quantum states by exchanging photons1. Their goal is to facilitate quantum communication between any nodes, something that can be used to send secret messages in a secure way2,3, and to communicate more efficiently than in classical networks4. These goals can be achieved, for instance, via teleportation5. Here we show that the design of efficient quantum-communication protocols in quantum networks involves intriguing quantum phenomena, depending both on the way the nodes are connected and on the entanglement between them. These phenomena can be used to design protocols that overcome the exponential decrease of signals with the number of nodes. We relate the problem of establishing maximally entangled states between nodes to classical percolation in statistical mechanics6, and demonstrate that phase transitions7 can be used to optimize the operation of quantum networks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cirac, J. I., Zoller, P., Kimble, H. J. & Mabuchi, H. Quantum state transfer and entanglement distribution among distant nodes in a quantum network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3221–3224 (1997).
Bennett, C. H. & Brassard, G. in Proc. Int. Conf. on Computer Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore 175–179 (IEEE, New York, 1984).
Ekert, A. K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–664 (1991).
Buhrman, H., Cleve, R., Watrous, J. & de Wolf, R. Quantum fingerprinting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 167902 (2001).
Bennett, C. H. et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolski–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1898 (1993).
Grimmett, G. Percolation (Springer, Berlin, 1999).
Sachdev, S. Quantum Phase Transitions (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1999).
Knill, E., Laflamme, R. & Milburn, G. J. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001).
Duan, L. M., Lukin, M. D., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 414, 413–418 (2001).
Briegel, H. J., Dür, W., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Quantum repeaters: The role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5932–5935 (1998).
Chanelière, T. et al. Storage and retrieval of single photons transmitted between remote quantum memories. Nature 438, 833–836 (2005).
Tanzilli, S. et al. A photonic quantum information interface. Nature 437, 116–120 (2005).
Törmä, P. Transitions in quantum networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2185–2189 (1998).
Leung, D., Oppenheim, J. & Winter, A. Quantum network communication—the butterfly and beyond. Preprint at <http://arxiv.org/abs/quant-ph/0608223> (2006).
Verstraete, F., Popp, M. & Cirac, J. I. Entanglement versus correlations in spin systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 027901 (2004).
Popp, M., Verstraete, F., Martín-Delgado, M. A. & Cirac, J. I. Localizable entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 71, 042306 (2005).
Nielsen, M. A. & Chuang, I. L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2000).
Verstraete, F. & Cirac, J. I. Renormalization algorithms for quantum-many body systems in two and higher dimensions. Preprint at <http://arxiv.org/abs/cond-mat/0407066> (2004).
Osterloh, A., Amico, L., Falci, G. & Fazio, R. Scaling of entanglement close to a quantum phase transition. Nature 416, 608–610 (2002).
Osborne, T. J. & Nielsen, M. A. Entanglement in a simple quantum phase transition. Phys. Rev. A 66, 032110 (2002).
Vidal, G., Latorre, J. I., Rico, E. & Kitaev, A. Entanglement in quantum critical phenomena. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 227902 (2003).
Vidal, G. Entanglement of pure states for a single copy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1046–1049 (1999).
Żukowski, M., Zeilinger, A., Horne, M. A. & Ekert, A. K. Event-ready detectors Bell experiment via entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 4287–4290 (1993).
Wootters, W. K. Entanglement of formation of an arbitrary state of two qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2245–2248 (1998).
Verstraete, F., Martín-Delgado, M. A. & Cirac, J. I. Diverging entanglement length in gapped quantum spin systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 087201 (2004).
Nielsen, M. A. Conditions for a class of entanglement transformations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 436–439 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank F. Verstraete, J. Wehr and M. M. Wolf for discussion. We acknowledge support from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, EU IP Programmes ‘SCALA’ and ‘QAP’, European Science Foundation PESC QUDEDIS, MEC (Spanish Government) under contracts FIS 2005-04627, FIS 2004-05639, ‘Ramón y Cajal’ and Consolider QOIT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acín, A., Cirac, J. & Lewenstein, M. Entanglement percolation in quantum networks. Nature Phys 3, 256–259 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys549
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys549
This article is cited by
-
Entanglement generation in a quantum network at distance-independent rate
npj Quantum Information (2022)
-
Anti-Zeno purification of spin baths by quantum probe measurements
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Effective routing design for remote entanglement generation on quantum networks
npj Quantum Information (2021)
-
A quantum network node with crossed optical fibre cavities
Nature Physics (2020)
-
Percolation transition control in quantum networks
Quantum Information Processing (2020)