Abstract
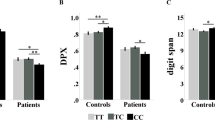
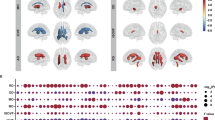
Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder share genetic risk, brain vulnerability, and clinical symptoms. The ZNF804A risk variant, rs1344706, confers susceptibility for both disorders. This study aimed to identify neural mechanisms common to both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder through this variant's potential effects on cortical thickness, white matter tract integrity, and cognitive function. Imaging, genetics, and cognitive measures were ascertained in 62 healthy adults aged between 18 and 59 years. High-resolution multimodal MRI/DTI imaging was used to measure cortical thickness and major frontotemporal and interhemispheric white matter tracts. The general linear model was used to examine the influence of the ZNF804A rs1344706 risk variant on cortical thickness, white matter tract integrity, and cognitive measures. Individuals homozygous for the risk variant (‘A’ allele) demonstrated reduced cortical gray matter thickness in the superior temporal gyrus, and in the anterior and posterior cingulate cortices compared with C-allele carriers. No effect of the risk variant on microstructural integrity of white matter tracts was found. Reduced attention control was found in risk allele homozygotes, aligning with findings in the anterior cingulate cortex. Our data provide a novel, genetically based neural risk mechanism for the major psychoses by effects of the ZNF804A risk variant on neural structures and cognitive function susceptible in both disorders. Our findings link genetic, imaging, and cognitive susceptibility relevant to both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ad-Dab’bagh Y, Singh V, Robbins S, Lerch J, Lyttleton O, Fombonne E et al (2005). Native Space Cortical Thickness Measurement and the Absence of Correlation to Cerebral Volume. Paper presented at the Organization of Human Brain Mapping: Toronto.
Alexander A, Lobaugh N (2007). Insights into brain connectivity using quantitative MRI measures of white matter. In: AR McIntosh, Jirsa VK (eds). Handbook of Brain Connectivity. Springer: Berlin.
Balog Z, Kiss I, Keri S (2010). ZNF804A may be associated with executive control of attention. Genes Brain Behav 2011: 223–227.
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996). Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111: 209–219.
Bora E, Fornito A, Yucel M, Pantelis C (2010). Voxel-wise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 67: 1097–1105.
Calhoun VD, Maciejewski PK, Pearlson GD, Kiehl KA (2008). Temporal lobe and ‘default’ hemodynamic brain modes discriminate between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 29: 1265–1275.
Catani M, Allin MP, Husain M, Pugliese L, Mesulam MM, Murray RM et al (2007). Symmetries in human brain language pathways correlate with verbal recall. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 17163–17168.
Catani M, Howard RJ, Pajevic S, Jones DK (2002). Virtual in vivo interactive dissection of white matter fasciculi in the human brain. Neuroimage 17: 77–94.
Catani M, Jones DK, ffytche DH (2005). Perisylvian language networks of the human brain. Ann Neurol 57: 8–16.
Craddock N, Owen MJ (2010). The Kraepelinian dichotomy—going, going... but still not gone. Br J Psychiatry 196: 92–95.
Donohoe G, Rose E, Frodl T, Morris D, Spoletini I, Adriano F et al (2011). ZNF804A risk allele is associated with relatively intact gray matter volume in patients with schizophrenia. Neuroimage 54: 2132–2137.
Ennis DB, Kindlmann G (2006). Orthogonal tensor invariants and the analysis of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance images. Magn Reson Med 55: 136–146.
Esslinger C, Walter H, Kirsch P, Erk S, Schnell K, Arnold C et al (2009). Neural mechanisms of a genome-wide supported psychosis variant. Science 324: 605.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1995). Strucutured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders, Patient Edition (SCID-P), Version. Biometrics Research: New York.
Fornito A, Yucel M, Dean B, Wood SJ, Pantelis C (2009). Anatomical abnormalities of the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia: bridging the gap between neuroimaging and neuropathology. Schizophr Bull 35: 973–993.
Genovese CR, Lazar NA, Nichols T (2002). Thresholding of statistical maps in functional neuroimaging using the false discovery rate. Neuroimage 15: 870–878.
Hill SK, Harris MS, Herbener ES, Pavuluri M, Sweeney JA (2008). Neurocognitive allied phenotypes for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Bull 34: 743–759.
Hollingshead AB (1975). Four Factor Index of Social Status. Yale University: New Haven, CT.
Kasai K, Shenton ME, Salisbury DF, Hirayasu Y, Lee CU, Ciszewski AA et al (2003). Progressive decrease of left superior temporal gyrus gray matter volume in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 160: 156–164.
Kim JS, Singh V, Lee JK, Lerch J, Ad-Dab’bagh Y, MacDonald D et al (2005). Automated 3-D extraction and evaluation of the inner and outer cortical surfaces using a Laplacian map and partial volume effect classification. Neuroimage 27: 210–221.
Koo MS, Levitt JJ, Salisbury DF, Nakamura M, Shenton ME, McCarley RW (2008). A cross-sectional and longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study of cingulate gyrus gray matter volume abnormalities in first-episode schizophrenia and first-episode affective psychosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65: 746–760.
Kubicki M, Westin CF, Maier SE, Frumin M, Nestor PG, Salisbury DF et al (2002). Uncinate fasciculus findings in schizophrenia: a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging study. Am J Psychiatry 159: 813–820.
Kubicki M, Westin CF, Nestor PG, Wible CG, Frumin M, Maier SE et al (2003). Cingulate fasciculus integrity disruption in schizophrenia: a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 54: 1171–1180.
Lahiri DK, Bye S, Nurnberger Jr JI, Hodes ME, Crisp M (1992). A non-organic and non-enzymatic extraction method gives higher yields of genomic DNA from whole-blood samples than do nine other methods tested. J Biochem Biophys Methods 25: 193–205.
Lencz T, Szeszko PR, DeRosse P, Burdick KE, Bromet EJ, Bilder RM et al (2010). A schizophrenia risk gene, ZNF804A, influences neuroanatomical and neurocognitive phenotypes. Neuropsychopharmacology 35: 2284–2291.
Lerch JP, Evans AC (2005). Cortical thickness analysis examined through power analysis and a population simulation. Neuroimage 24: 163–173.
Lichtenstein P, Yip BH, Bjork C, Pawitan Y, Cannon TD, Sullivan PF et al (2009). Common genetic determinants of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in Swedish families: a population-based study. Lancet 373: 234–239.
Liu SK, Chiu CH, Chang CJ, Hwang TJ, Hwu HG, Chen WJ (2002). Deficits in sustained attention in schizophrenia and affective disorders: stable versus state-dependent markers. Am J Psychiatry 159: 975–982.
MacDonald D, Kabani N, Avis D, Evans AC (2000). Automated 3-D extraction of inner and outer surfaces of cerebral cortex from MRI. Neuroimage 12: 340–356.
McIntosh AM, Maniega SM, Lymer GK, McKirdy J, Hall J, Sussmann JE et al (2008). White matter tractography in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 64: 1088–1092.
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR (2006). Intermediate phenotypes and genetic mechanisms of psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 818–827.
Narr KL, Toga AW, Szeszko P, Thompson PM, Woods RP, Robinson D et al (2005). Cortical thinning in cingulate and occipital cortices in first episode schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 58: 32–40.
O’Donnell LJ, Kubicki M, Shenton ME, Dreusicke MH, Grimson WE, Westin CF (2006). A method for clustering white matter fiber tracts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27: 1032–1036.
O’Donovan MC, Craddock N, Norton N, Williams H, Peirce T, Moskvina V et al (2008). Identification of loci associated with schizophrenia by genome-wide association and follow-up. Nat Genet 40: 1053–1055.
Oldfield RC (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9: 97–113.
Ongur D, Lundy M, Greenhouse I, Shinn AK, Menon V, Cohen BM et al (2010). Default mode network abnormalities in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 183: 59–68.
Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O’Donovan MC, Sullivan PF et al (2009). Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 460: 748–752.
Quraishi S, Frangou S (2002). Neuropsychology of bipolar disorder: a review. J Affect Disord 72: 209–226.
Riley B, Thiselton D, Maher BS, Bigdeli T, Wormley B, McMichael GO et al (2010). Replication of association between schizophrenia and ZNF804A in the Irish Case-Control Study of Schizophrenia sample. Mol Psychiatry 15: 29–37.
Rimol LM, Hartberg CB, Nesvag R, Fennema-Notestine C, Hagler Jr DJ, Pung CJ et al (2010). Cortical thickness and subcortical volumes in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 68: 41–50.
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC (1998). A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17: 87–97.
Song SK, Yoshino J, Le TQ, Lin SJ, Sun SW, Cross AH et al (2005). Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. Neuroimage 26: 132–140.
Szeszko PR, Bilder RM, Lencz T, Ashtari M, Goldman RS, Reiter G et al (2000). Reduced anterior cingulate gyrus volume correlates with executive dysfunction in men with first-episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 43: 97–108.
Takahashi T, Wood SJ, Yung AR, Soulsby B, McGorry PD, Suzuki M et al (2009). Progressive gray matter reduction of the superior temporal gyrus during transition to psychosis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66: 366–376.
Tkachev D, Mimmack ML, Ryan MM, Wayland M, Freeman T, Jones PB et al (2003). Oligodendrocyte dysfunction in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Lancet 362: 798–805.
Tohka J, Zijdenbos A, Evans A (2004). Fast and robust parameter estimation for statistical partial volume models in brain MRI. Neuroimage 23: 84–97.
Voineskos AN, Farzan F, Barr MS, Lobaugh NJ, Mulsant BH, Chen R et al (2010a). The role of the corpus callosum in transcranial magnetic stimulation induced interhemispheric signal propagation. Biol Psychiatry 68: 825–831.
Voineskos AN, Lobaugh NJ, Bouix S, Rajji TK, Miranda D, Kennedy JL et al (2010b). Diffusion tensor tractography findings in schizophrenia across the adult lifespan. Brain 133 (Part 5): 1494–1504.
Voineskos AN, O’Donnell LJ, Lobaugh NJ, Markant D, Ameis SH, Niethammer M et al (2009). Quantitative examination of a novel clustering method using magnetic resonance diffusion tensor tractography. Neuroimage 45: 370–376.
Walter H, Schnell K, Erk S, Arnold C, Kirsch P, Esslinger C et al (2010). Effects of a genome-wide supported psychosis risk variant on neural activation during a theory-of-mind task. Mol Psychiatry 4: 462–470.
Walters JT, Corvin A, Owen MJ, Williams H, Dragovic M, Quinn EM et al (2010). Psychosis susceptibility gene ZNF804A and cognitive performance in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67: 692–700.
Westin CF, Maier SE, Mamata H, Nabavi A, Jolesz FA, Kikinis R (2002). Processing and visualization for diffusion tensor MRI. Med Image Anal 6: 93–108.
Whitford TJ, Kubicki M, Schneiderman JS, O’Donnell LJ, King R, Alvarado JL et al (2010). Corpus callosum abnormalities and their association with psychotic symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 68: 70–77.
Williams HJ, Craddock N, Russo G, Hamshere ML, Moskvina V, Dwyer S et al (2011). Most genome-wide significant susceptibility loci for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder reported to date cross-traditional diagnostic boundaries. Hum Mol Genet 20: 387–391.
Williams HJ, Norton N, Dwyer S, Moskvina V, Nikolov I, Carroll L et al (2010). Fine mapping of ZNF804A and genome-wide significant evidence for its involvement in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 4: 429–441.
Yatham LN, Lyoo IK, Liddle P, Renshaw PF, Wan D, Lam RW et al (2007). A magnetic resonance imaging study of mood stabilizer- and neuroleptic-naive first-episode mania. Bipolar Disord 9: 693–697.
Zijdenbos AP, Forghani R, Evans AC (2002). Automatic ‘pipeline’ analysis of 3-D MRI data for clinical trials: application to multiple sclerosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21: 1280–1291.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Clinician Scientist Award (ANV), APA/APIRE Astra-Zeneca Young Minds in Psychiatry Award (ANV), and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (AT). Dr Aristotle N Voineskos had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Bruce G Pollock receives research support from the National Institute of Health and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Within the past 5 years, he has been a member of the advisory board of Lundbeck Canada (final meeting was in May 2009) and Forest Laboratories (final meeting was in March 2008). Dr Pollock has served one time as a consultant for Wyeth (October 2008) and Takeda (July 2007). He was also a faculty member of the Lundbeck International Neuroscience Foundation (LINF) (final meeting was in April 2010). Dr Benoit H Mulsant currently receives research support from the US National Institute of Mental Health, the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Wyeth. During the past five years, he has also received research support or honoraria from Astra-Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Forest Laboratories, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Pfizer. Dr James L Kennedy received speaker fees from Eli Lilly in 2010. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voineskos, A., Lerch, J., Felsky, D. et al. The ZNF804A Gene: Characterization of a Novel Neural Risk Mechanism for the Major Psychoses. Neuropsychopharmacol 36, 1871–1878 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.72
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.72
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The schizophrenia risk gene ZNF804A: clinical associations, biological mechanisms and neuronal functions
Molecular Psychiatry (2017)
-
Genetics of structural connectivity and information processing in the brain
Brain Structure and Function (2016)
-
Analysis of schizophrenia-related genes and electrophysiological measures reveals ZNF804A association with amplitude of P300b elicited by novel sounds
Translational Psychiatry (2014)
-
Genetic Modifiers and Subtypes in Schizophrenia
Current Behavioral Neuroscience Reports (2014)
-
Schizophrenia risk gene ZNF804A does not influence macroscopic brain structure: an MRI study in 892 volunteers
Molecular Psychiatry (2012)