Abstract
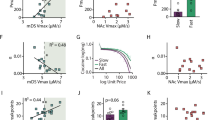
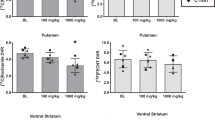
Poor decision making and elevated risk taking, particularly during adolescence, have been strongly linked to drug use; however the causal relationships among these factors are not well understood. To address these relationships, a rat model (the Risky Decision-making Task; RDT) was used to determine whether individual differences in risk taking during adolescence predict later propensity for cocaine self-administration and/or whether cocaine self-administration causes alterations in risk taking. In addition, the RDT was used to determine how risk taking is modulated by dopamine signaling, particularly in the striatum. Results from these experiments indicated that greater risk taking during adolescence predicted greater intake of cocaine during acquisition of self-administration in adulthood, and that adult cocaine self-administration in turn caused elevated risk taking that was present following 6 weeks of abstinence. Greater adolescent risk taking was associated with lower striatal D2 receptor mRNA expression, and pharmacological activation of D2/3 receptors in the ventral, but not dorsal, striatum induced a decrease in risk taking. These findings indicate that the relationship between elevated risk taking and cocaine self-administration is bi-directional, and that low striatal D2 receptor expression may represent a predisposing factor for both maladaptive decision making and cocaine use. Furthermore, these findings suggest that striatal D2 receptors represent a therapeutic target for attenuating maladaptive decision making when choices include risk of adverse consequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Anker JJ, Perry JL, Gliddon LA, Carroll ME (2009). Impulsivity predicts the escalation of cocaine self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93: 343–348.
Bechara A, Dolan S, Denburg N, Hindes A, Anderson SW, Nathan PE (2001). Decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 39: 376–389.
Belin D, Mar AC, Dalley JW, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2008). High impulsivity predicts the switch to compulsive cocaine-taking. Science 320: 1352–1355.
Besson M, Belin D, McNamara R, Theobald DE, Castel A, Beckett VL et al (2010). Dissociable control of impulsivity in rats by dopamine d2/3 receptors in the core and shell subregions of the nucleus accumbens. Neuropsychopharmacology 35: 560–569.
Besson M, Pelloux Y, Dilleen R, Theobald DE, Lyon A, Belin-Rauscent A et al (2013). Cocaine modulation of fronto-striatal expression of zif268, D2 and 5-HT2c receptors in high and low impulsive rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 38: 1963–1973.
Bolla KI, Eldreth DA, London ED, Kiehl KA, Mouratidis M, Contoreggi C et al (2003). Orbitofrontal cortex dysfunction in abstinent cocaine abusers performing a decision-making task. Neuroimage 19: 1085–1094.
Bornovalova MA, Daughters SB, Hernandez GD, Richards JB, Lejuez CW (2005). Differences in impulsivity and risk-taking propensity between primary users of crack cocaine and primary users of heroin in a residential substance-use program. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 13: 311–318.
Broos N, Diergaarde L, Schoffelmeer AN, Pattij T, De Vries TJ (2012). Trait impulsive choice predicts resistance to extinction and propensity to relapse to cocaine seeking: a bidirectional investigation. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 1377–1386.
Caine SB, Negus SS, Mello NK, Patel S, Bristow L, Kulagowski J et al (2002). Role of dopamine D2-like receptors in cocaine self-administration: studies with D2 receptor mutant mice and novel D2 receptor antagonists. J Neurosci 22: 2977–2988.
Chambers RA, Taylor JR, Potenza MN (2003). Developmental neurocircuitry of motivation in adolescence: a critical period of addiction vulnerability. Am J Psychiatry 160: 1041–1052.
Chartier KG, Hesselbrock MN, Hesselbrock VM (2010). Development and vulnerability factors in adolescent alcohol use. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 19: 493–504.
Coffey SF, Gudleski GD, Saladin ME, Brady KT (2003). Impulsivity and rapid discounting of delayed hypothetical rewards in cocaine-dependent individuals. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 11: 18–25.
Dalley JW, Fryer TD, Brichard L, Robinson ES, Theobald DE, Laane K et al (2007). Nucleus accumbens D2/3 receptors predict trait impulsivity and cocaine reinforcement. Science 315: 1267–1270.
Dandy KL, Gatch MB (2009). The effects of chronic cocaine exposure on impulsivity in rats. Behav Pharmacol 20: 400–405.
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004). Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305: 1014–1017.
Ersche KD, Barnes A, Jones PS, Morein-Zamir S, Robbins TW, Bullmore ET (2011). Abnormal structure of frontostriatal brain systems is associated with aspects of impulsivity and compulsivity in cocaine dependence. Brain 134 (Pt 7): 2013–2024.
Ghahremani DG, Lee B, Robertson CL, Tabibnia G, Morgan AT, De Shetler N et al (2012). Striatal dopamine D(2)/D(3) receptors mediate response inhibition and related activity in frontostriatal neural circuitry in humans. J Neurosci 32: 7316–7324.
Haluk DM, Floresco SB (2009). Ventral striatal dopamine modulation of different forms of behavioral flexibility. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 2041–2052.
Johnson PM, Kenny PJ (2010). Dopamine D2 receptors in addiction-like reward dysfunction and compulsive eating in obese rats. Nat Neurosci 13: 635–641.
Lee B, London ED, Poldrack RA, Farahi J, Nacca A, Monterosso JR et al (2009). Striatal dopamine d2/d3 receptor availability is reduced in methamphetamine dependence and is linked to impulsivity. J Neurosci 29: 14734–14740.
Linnet J, Moller A, Peterson E, Gjedde A, Doudet D (2011a). Dopamine release in ventral striatum during Iowa Gambling Task performance is associated with increased excitement levels in pathological gambling. Addiction 106: 383–390.
Linnet J, Moller A, Peterson E, Gjedde A, Doudet D (2011b). Inverse association between dopaminergic neurotransmission and Iowa Gambling Task performance in pathological gamblers and healthy controls. Scand J Psychol 52: 28–34.
Mendez IA, Montgomery KS, LaSarge CL, Simon NW, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2008). Long-term effects of prior cocaine exposure on Morris water maze performance. Neurobiol Learn Mem 89: 185–191.
Mendez IA, Simon NW, Hart N, Mitchell MR, Nation JR, Wellman PJ et al (2010). Self-administered cocaine causes long-lasting increases in impulsive choice in a delay discounting task. Behav Neurosci 124: 470–477.
Mitchell MR, Vokes CM, Blankenship AL, Simon NW, Setlow B (2011). Effects of acute administration of nicotine, amphetamine, diazepam, morphine, and ethanol on risky decision-making in rats. Psychopharmacology 218: 703–712.
Mitchell MR, Weiss VG, Ouimet DJ, Fuchs RA, Morgan D, Setlow B . Intake-dependent effects of cocaine self-administration on impulsive choice in a delay discounting task (submitted).
Morgan D, Grant KA, Gage HD, Mach RH, Kaplan JR, Prioleau O et al (2002). Social dominance in monkeys: dopamine D2 receptors and cocaine self-administration. Nat Neurosci 5: 169–174.
Nader MA, Morgan D, Gage HD, Nader SH, Calhoun TL, Buchheimer N et al (2006). PET imaging of dopamine D2 receptors during chronic cocaine self-administration in monkeys. Nat Neurosci 9: 1050–1056.
Paxinos G, Watson C (2008) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Corrdinates: Compact 6th edn Academic Press.
Perry JL, Larson EB, German JP, Madden GJ, Carroll ME (2005). Impulsivity (delay discounting) as a predictor of acquisition of IV cocaine self-administration in female rats. Psychopharmacology 178: 193–201.
Perry JL, Nelson SE, Carroll ME (2008). Impulsive choice as a predictor of acquisition of IV cocaine self- administration and reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in male and female rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 16: 165–177.
Saddoris MP, Stamatakis A, Carelli RM (2011). Neural correlates of Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer in the nucleus accumbens shell are selectively potentiated following cocaine self-administration. Eur J Neurosci 33: 2274–2287.
Saunders BT, Robinson TE (2010). A cocaine cue acts as an incentive stimulus in some but not others: implications for addiction. Biol Psychiatry 67: 730–736.
Saunders BT, Robinson TE (2011). Individual variation in the motivational properties of cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 36: 1668–1676.
Schoenbaum G, Setlow B (2005). Cocaine makes actions insensitive to outcomes but not extinction: implications for altered orbitofrontal-amygdalar function. Cereb Cortex 15: 1162–1169.
Setlow B, Mendez IA, Mitchell MR, Simon NW (2009). Effects of chronic administration of drugs of abuse on impulsive choice (delay discounting) in animal models. Behavioural pharmacology 20: 380–389.
Shimp KS, Mitchell MR, Beas BS, Bizon JL, Setlow B . Characterization of risky decision making: sensitivity to reward and punishment and relationships with executive functions and impulsivity (submitted).
Simon NW, Gilbert RJ, Mayse JD, Bizon JL, Setlow B (2009). Balancing risk and reward: a rat model of risky decision making. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 2208–2217.
Simon NW, LaSarge CL, Montgomery KS, Williams MT, Mendez IA, Setlow B et al (2010). Good things come to those who wait: attenuated discounting of delayed rewards in aged Fischer 344 rats. Neurobiol Aging 31: 853–862.
Simon NW, Mendez IA, Setlow B (2007). Cocaine exposure causes long-term increases in impulsive choice. Behav Neurosci 121: 543–549.
Simon NW, Montgomery KS, Beas BS, Mitchell MR, LaSarge CL, Mendez IA et al (2011). Dopaminergic modulation of risky decision-making. J Neurosci 31: 17460–17470.
Spear LP (2000). The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24: 417–463.
St Onge JR, Floresco SB (2009). Dopaminergic modulation of risk-based decision making. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 681–697.
Stalnaker TA, Roesch MR, Franz TM, Burke KA, Schoenbaum G (2006). Abnormal associative encoding in orbitofrontal neurons in cocaine-experienced rats during decision-making. Eur J Neurosci 24: 2643–2653.
Stansfield KH, Philpot RM, Kirstein CL (2004). An animal model of sensation seeking: the adolescent rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1021: 453–458.
Stopper CM, Khayambashi S, Floresco SB (2013). Receptor-specific modulation of risk-based decision making by nucleus accumbens dopamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 38: 715–728.
Vaidya JG, Grippo AJ, Johnson AK, Watson D (2004). A comparative developmental study of impulsivity in rats and humans: the role of reward sensitivity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1021: 395–398.
Vanderschuren LJ, Everitt BJ (2004). Drug seeking becomes compulsive after prolonged cocaine self-administration. Science 305: 1017–1019.
Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Ding YS, Sedler M et al (2001). Low level of brain dopamine D2 receptors in methamphetamine abusers: association with metabolism in the orbitofrontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry 158: 2015–2021.
Winstanley CA, Eagle DM, Robbins TW (2006). Behavioral models of impulsivity in relation to ADHD: translation between clinical and preclinical studies. Clin Psychol Rev 26: 379–395.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dominique Ouimet, Colin Vokes, and Jonathan Williams for support in completing these experiments. We also thank Dr Rebecca Haberman for providing us with dopamine receptor probes for in situ hybridization procedures, and the Drug Supply Program at the National Institute on Drug Abuse for kindly providing cocaine HCl.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, M., Weiss, V., Beas, B. et al. Adolescent Risk Taking, Cocaine Self-Administration, and Striatal Dopamine Signaling. Neuropsychopharmacol 39, 955–962 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.295
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.295
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Alcohol Consumption During Adolescence Alters the Cognitive Function in Adult Male Mice by Persistently Increasing Levels of DUSP6
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Effects of fentanyl self-administration on risk-taking behavior in male rats
Psychopharmacology (2023)
-
Adolescent reinforcement-learning trajectories predict cocaine-taking behaviors in adult male and female rats
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
Regulation of risky decision making by gonadal hormones in males and females
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)
-
Differential effects of glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists on risky choice as assessed in the risky decision task
Psychopharmacology (2021)