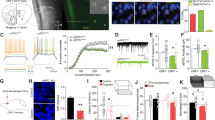
Abstract
Alcoholism is associated with changes in brain reward and control systems, including the prefrontal cortex. In prefrontal areas, the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) has been suggested to have an important role in the development of alcohol-abuse disorders and studies from this laboratory demonstrate that OFC-mediated behaviors are impaired in alcohol-dependent animals. However, it is not known whether chronic alcohol (ethanol) exposure alters the fundamental properties of OFC neurons. In this study, mice were exposed to repeated cycles of chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) exposure to induce dependence and whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology was used to examine the effects of CIE treatment on lateral OFC (lOFC) neuron excitability, synaptic transmission, and plasticity. Repeated cycles of CIE exposure and withdrawal enhanced current-evoked action potential (AP) spiking and this was accompanied by a reduction in the after-hyperpolarization and a decrease in the functional activity of SK channels. CIE mice also showed an increase in the AMPA/NMDA ratio, and this was associated with an increase in GluA1/GluA2 AMPA receptor expression and a decrease in GluN2B NMDA receptor subunits. Following CIE treatment, lOFC neurons displayed a persistent long-term potentiation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission following a spike-timing-dependent protocol. Lastly, CIE treatment diminished the inhibitory effect of acute ethanol on AP spiking of lOFC neurons and reduced expression of the GlyT1 transporter. Taken together, these results suggest that chronic exposure to ethanol leads to enhanced intrinsic excitability and glutamatergic synaptic signaling of lOFC neurons. These alterations may contribute to the impairment of OFC-dependent behaviors in alcohol-dependent individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aldridge GM, Podrebarac DM, Greenough WT, Weiler IJ (2008). The use of total protein stains as loading controls: an alternative to high-abundance single-protein controls in semi-quantitative immunoblotting. J Neurosci Methods 172: 250–254.
Badanich K, Becker H, Woodward J (2011). Effects of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure on orbitofrontal and medial prefrontal cortex-dependent behaviors in mice. Behav Neurosci 125: 879–891.
Badanich K, Mulholland P, Beckley J, Trantham-Davidson H, Woodward J (2013). Ethanol reduces neuronal excitability of lateral orbitofrontal cortex neurons via a glycine receptor dependent mechanism. Neuropsycopharmacology 38: 1176–1188.
Bechara A (2005). Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nat Neurosci 8: 1458–1463.
Bechara A, Van Der Linden M (2005). Decision-making and impulse control after frontal lobe injuries. Curr Opin Neurol 18: 734–739.
Bissonette G, Martins G, Frans T, Harper E, Schoenbaum G, Powell E (2008). Double dissociation of the effects of medial and orbital prefrontal cortical lesions on attentional and affective shifts in mice. J Neurosci 28: 11124–11130.
Bissonette GB, Schoenbaum G, Roesch MR, Powell EM (2015). Interneurons are necessary for coordinated activity during reversal learning in orbitofrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 77: 454–464.
Blank T, Nijholt I, Kye M, Radulovic J, Spiess J (2003). Small-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel SK3 generates age-related memory and LTP deficits. Nat Neurosci 6: 911–912.
Bokura H, Yamaguchi S, Kobayashi S (2001). Electrophysiological correlates for response inhibition in a Go/NoGo task. Clin Neurophysiol 112: 2224–2232.
Brennan A, Dolinsky B, Vu M, Stanley M, Yeckel M, Arnsten A (2008). Blockade of IP3-mediated SK channel signaling in the rat medial prefrontal cortex improves spatial working memory. Learn Mem 15: 93–96.
Brodie M, Appel S (1998). The effects of ethanol on dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area studied with intracellular recording in brain slices. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22: 236–244.
Brodie M, McElvain M, Bunney E, Appel S (1999). Pharmacological reduction of small conductance calcium-activated potassium current (SK) potentiates the excitatory effect of ethanol on ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290: 325–333.
Brown K, Calizo L, Goodlett C, Staton M (2007). Neonatal alcohol exposure impairs acquisition of eyeblink conditioned responses during discrimination learning and reversal in weanling rats. Dev Psychobiol 49: 243–257.
DePoy L, Daut R, Brigman J, MacPherson K, Crowley N, Gunduz-Cinar O et al (2013). Chronic alcohol produces neuroadaptations to prime dorsal striatal learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 14783–14788.
Dias R, Robbins T, Roberts A (1996). Dissociation in prefrontal cortex of affective and attentional shifts. Nature 380: 69–72.
Dittmer A, Dittmer J (2006). Beta-actin is not a reliable loading control in Western blot analysis. Electrophoresis 27: 2844–2845.
Fortier C, Maksimovskiy A, Venne J, Lafleche G, McGlinchey R (2009). Silent trace eliminates differential eyeblink learning in abstinent alcoholics. Int J Environ Res Public Health 6: 2007–2027.
Fortier C, Steffen E, Lafleche G, Venne J, Disterhoft J, McGlinchey R (2008). Delay discrimination and reversal eyeblink classical conditioning in abstinent chronic alcoholics. Neuropsychology 22: 196–208.
Goldstein R, Tomasi D, Rajaram S, Cottone LA, Zhang L, Maloney T et al (2007). Role of the anterior cingulate and medial orbitofrontal cortex in processing drug cues in cocaine addiction. Neuroscience 144: 1153–1159.
Goldstein R, Volkow N (2002). Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry 159: 1642–1652.
Gu N, Vervaeke K, Hu H, Storm J (2005). Kv7/KCNQ/M and HCN/h, but not KCa2/SK channels, contribute to the somatic medium after-hyperpolarization and excitability control in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol 556.3: 689–715.
Hammond R, Bond C, Strassmaier T, Ngo-Anh T, Adelman J, Maylie J et al (2006). Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel type 2 (SK2) modulates hippocampal learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 26: 1844–1853.
Hansen H, Waroux O, Seutin V, Jentsch T, Aznar S, Mikkelsen J (2008). Kv7 channels: interaction with dopaminergic and serotoninergic neurotransmission in the CNS. J Physiol 586.7: 1823–1832.
Holmes A, Fitzgerald PJ, MacPherson KP, DeBrouse L, Colacicco G, Flynn SM et al (2012). Chronic alcohol remodels prefrontal neurons and disrupts NMDAR-mediated fear extinction encoding. Nat Neurosci 15: 1359–1361.
Hopf F, Bowers M, Chang SJ, Chen B, Martin M, Seif T et al (2010). Reduced nucleus accumbens SK channel activity enhances alcohol seeking during abstinence. Neuron 65: 682–694.
Hopf F, Martin M, Chen B, Bowers M, Mohamedi M, Bonci A (2007). Withdrawal from intermittent ethanol exposure increases probability of burst firing in VTA neurons in virto. J Neurophysiol 98: 2297–2310.
Iversen S, Mishkin M (1970). Perseverative interference in monkeys following selecetive lesions of the inferior prefrontal convexity. Exp Brain Res 11: 376–386.
Jedema H, Carter M, Dugan B, Gurnsey K, Olsen A, Bradberry C (2011). Acute impact of ethanol on cognitive performance in rhesus macaques. Cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 21: 1783–1791.
Jentsch J, Olausson P, De La Garza R 2nd, Taylor J (2002). Impairments of reversal learning and response perseveration after repeated, intermittent cocaine administrations to monkeys. Neuropsycopharmacology 26: 183–190.
Kaczorowski CC, Disterhoft J, Spruston N (2007). Stability and plasticity of intrinsic membrane properties in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: effects of internal anions. J Physiol 578: 799–818.
Kay AR (1992). An intracellular medium formulary. J Neurosci Methods 44: 91–100.
Kim A, Zamora-Martinez ER, Edwards S, Mandyam CD (2014). Structural reorganization of pyramidal neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex of alcohol dependent rats is associated with altered glial plasticity. Brain Struct Funct 220: 1705–1720.
Kolb B, Pellis S, Robinson T (2004). Self administration of cocaine modifies neuronal morphology in nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. Brain Cogn 55: 104–115.
Kringelbach M, Rolls E (2004). The functional neuroanatomy of the human orbitofrontal cortex: evidence from neuroimaging and neuropsychology. Prog Neurobiol 72: 341–372.
Kroener S, Mulholland P, New N, Gass J, Becker H, Chandler L (2012). Chronic alcohol exposure alters behavioral and synaptic plasticity of the rodent prefrontal cortex. PLoS One 7: e37541.
Lopez de Armentia M, Sah P (2004). Firing properties and connectivity of neurons in the rat lateral central nucleus of the amygdala. J Neurophysiol 92: 1285–1294.
Lowery-Gionta E, Marcinkiewcz C, Kash TL (2014). Functional alterations in the dorsal raphe nucleus following acute and chronic ethanol exposure. Neuropsycopharmacology 40: 590–600.
Ma Y, Hemley S, Toll J, Jentsch J, Evans C, Levine M et al (2013). Drug-primed reinstatement of cocaine seeking in mice: increased excitability of medium-sized spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens. ASN Neuro 5: 257–271.
Matochik J, London E, Eldreth D, Cadet J, Bolla K (2003). Frontal cortical tissue composition in abstinent cocaine abusers: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroimage 19: 1095–1102.
McAlonan K, Brown V (2003). Orbital prefrontal cortex mediates reversal learning and not attentional set shhifting in the rat. Behav Brain Res 146: 97–103.
McGuier N, Padula A, Lopez M, Woodward J, Mulholland P (2015). Withdrawal from chronic intermittent alcohol exposure increases dendritic spine density in the lateral orbitofrontal cortex in mice. Alcohol 49: 21–27.
Mulholland P, Becker H, Woodward J, Chandler L (2011). SK2 channels regulate alcohol-associated plasticity of glutamatergic synapses. Biol Psychiatry 69: 625–632.
O'Doherty J, Kringelbach M, Rolls E, Hornak J, Andrews C (2001). Abstract reward and punishment representations in the human orbitofrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci 4: 95–102.
Okamoto T, Harnett M, Morikawa H (2006). Hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih) is an ethanol target in midbrain dopamine neurons of mice. J Neurophysiol 95: 619–626.
Padula AE, Griffin WC 3rd, Lopez MF, Nimitvilai S, Cannady R, McGuier NS et al (2015). KCNN genes that encode small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels influence alcohol and drug addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 40: 1928–1939.
Pleil KE, Lowery-Gionta EG, Crowley NA, Li C, Marcinkiewcz CA, Rose JH et al (2015). Effects of chronic ethanol exposure on neuronal function in the prefrontal cortex and extended amygdala. Neuropharmacology (e-pub ahead of print) doi:10.1016.
Ponomarev I, Wang S, Zhang L, Harris RA, Mayfield RD (2012). Gene coexpression networks in human brain identify epigenetic modifications in alcohol dependence. J Neurosci 32: 1884–1897.
Ramus S, Eichenbaum H (2000). Neural correlates of olfactory recognition memory in the rat orbitofrontal cortex. J Neurosci 20: 8199–8208.
Robinson T, Gorny G, Mitton E, Kolb B (2001). Cocaine self-administration alters the morphology of dendrites and dendritic spines in the nucleus accumbens and neocortex. Synapse 39: 257–266.
Robinson T, Kolb B (1999). Alterations in the morphology of dendrites and dendritic spines in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex following repeated treatment with amphetamine or cocaine. Eur J Neurosci 11: 1598–1604.
Roesch M, Calu D, Burke K, Schoenbaum G (2007a). Should I stay or should I go? Transformation of time-discounted rewards in orbitofrontal cortex and associated brain circuits. Ann N Y Aced Sci 1104: 21–34.
Roesch M, Stalnaker T, Schoenbaum G (2007b). Associative encoding in anterior piriformis cortex versus orbitofrontal cortex during odor discrimination and reversal learning. Cereb Cortex 17: 643–652.
Rogers R, Everitt B, Baldacchino A, Blackshaw A, Swaninson R, Wynne K et al (1999a). Dissociable deficits in the decision-making cognition of chronic amphetamine abusers, opiate abusers, patients with focal damage to prefrontal cortex, and tryptophan-depleted normal volunteers: Evidence for monoaminergic mechanisms. Neuropsycopharmacology 20: 322–339.
Rogers R, Owen A, Middleton H, Williams E, Pickard J, Sahakian B et al (1999b). Choosing between small, likely rewards and large, unlikely rewards activates inferior and orbital prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 19: 9029–9038.
Sah P (1996). Ca(2+)-activated K+ currents in neurones: types, physiological roles and modulation. Trends Neurosci 19: 150–154.
Sah P, Faber E (2002). Channels underlying neuronal calcium-activated potassium currents. Prog Neurobiol 66: 345–353.
Sailer C, Hu H, Kaufmann W, Trieb M, Schwarzer C, Storm J et al (2002). Regional differences in distribution and functional expression of small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels in rat brain. J Neurosci 22: 9698–9707.
Sailer C, Kaufmann W, Marksteiner J, Knaus H (2004). Comparative immunohistochemical distribution of three small-conductance Ca2+-activated potassium channel subunits, SK1, SK2, and SK3 in mouse brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 26: 458–469.
Schoenbaum G, Chiba A, Gallagher M (1998). Orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala encode expected outcomes during learning. Nat Neurosci 1: 155–159.
Schoenbaum G, Saddoris M, Ramus S, Shaham Y, Selow B (2004). Cocaine-experienced rats exhibit learning deficits in a task sensitive to orbitofrontal cortex lesions. Eur J Neurosci 19: 1997–2002.
Stackman R, Hammond R, Linardatos E, Gerlach A, Maylie J, Adelman J et al (2002). Small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels modulate synaptic plasticity and memory encoding. J Neurosci 22: 10163–10171.
Thorpe S, Rolls E, Maddison S (1983). The orbitofrontal cortex: neuronal activity in the behaving monkey. Exp Brain Res 49: 93–115.
Trantham-Davidson H, Burnett EJ, Gass JT, Lopez MF, Mulholland PJ, Centanni SW et al (2014). Chronic alcohol disrupts dopamine receptor activity and the cognitive function of the medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 34: 3706–3718.
Traynelis SF, Wollmuth LP, McBain CJ, Menniti FS, Vance KM, Ogden KK et al (2010). Glutamate receptor ion channels: structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol Rev 62: 405–496.
Tremblay L, Schultz W (1999). Relative reward preference in primate orbitofrontal cortex. Nature 398: 704–708.
Velumian A, Zhang L, Pennefather P, Carlen P (1997). Reversible inhibition of IK, IAHP, Ih and ICa currents by internally applied gluconate in rat hippocampal pyramidal neurones. Pflugers Arch 433: 343–350.
Verdejo-Garcia A, Bechara A, Recknor E, Perex-Garcia M (2006). Executive dysfunction in substance dependent individuals during drug use and abstinence: an examination of the behavioral, cognitive and emotional correlates of addiction. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 12: 405–415.
Villalobos C, Shakkottai V, Chandy KG, Michelhaugh S, Andrade R (2004). SKCa channels mediate the medium but not the slow calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in cortical neurons. J Neurosci 24: 3537–3542.
Volkow N, Fowloer J, Wang GJ (2004). The addicted human brain viewed in the light of imaging studies: brain circuits and treatment strategies. Neuropharmacology 47: 3–13.
Zhang L, Weiner J, Valiante T, Velumian A, Watson P, Jahromi S et al (1994). Whole-cell recording of the Ca(2+)-dependent slow afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal neurones: efffects of internally applied anions. Pflugers Arch 426: 247–253.
Acknowledgements
We thank Diana Fulmer for assistance with the western blotting studies and Laura Ralston for coordinating the vapor inhalation treatments. This work was supported by P50AA010761 and R37AA009986 to JJW, UO1 AA020929 to MFL, and U01AA020930 to PJM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nimitvilai, S., Lopez, M., Mulholland, P. et al. Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure Enhances the Excitability and Synaptic Plasticity of Lateral Orbitofrontal Cortex Neurons and Induces a Tolerance to the Acute Inhibitory Actions of Ethanol. Neuropsychopharmacol 41, 1112–1127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.250
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.250
This article is cited by
-
LPA1 receptors in the lateral habenula regulate negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Adaptor protein complex 2 in the orbitofrontal cortex predicts alcohol use disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Acute depletion of dopamine precursors in the human brain: effects on functional connectivity and alcohol attentional bias
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)
-
Neurodevelopmental signatures of narcotic and neuropsychiatric risk factors in 3D human-derived forebrain organoids
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Drug addiction: from bench to bedside
Translational Psychiatry (2021)