Abstract
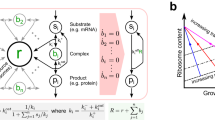
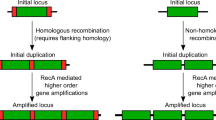
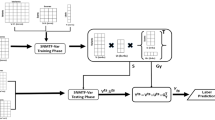
At present, all methods in Evolutionary Computation are bioinspired in the fundamental principles of neo-Darwinism as well as on a vertical gene transfer. Thus, on a mechanism in which an organism receives genetic material from its ancestor. Horizontal, lateral or cross-population gene transfer is any process in which an organism transfers a genetic segment to another one that is not its offspring. Virus transduction is one of the key mechanisms of horizontal gene propagation in microorganism (e.g. bacteria). In the present paper, we model and simulate a transduction operator, exploring a possible role and usefulness of transduction in a genetic algorithm. The genetic algorithm including transduction has been named PETRI (abbreviation of Promoting Evolution Through Reiterated Infection). The efficiency and performance of this algorithm was evaluated using a benchmark function and the 0/1 knapsack problem. The utility was illustrated designing an AM radio receiver, optimizing the main features of the electronic components of the AM radio circuit as well as those of the radio enclosure. Our results shown how PETRI approaches to higher fitness values as transduction probability comes near to 100%. The conclusion is that transduction improves the performance of a genetic algorithm, assuming a population divided among several sub-populations or ‘bacterial colonies’.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perales-Gravan, C., de Vicente Buendia, J. & Lahoz-Beltra, R. Modeling, Simulation and Application of Bacterial Transduction in Genetic Algorithms. Nat Prec (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.3732.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.3732.1