Abstract
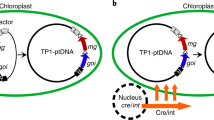
Incorporation of a selectable marker gene in the plastid genome is essential to uniformly alter the thousands of genome copies in a tobacco cell. When transformation is accomplished, however, the marker gene becomes undesirable. Here we describe plastid transformation vectors, the method of plastid transformation using tobacco leaves and alternative protocols for marker gene excision with the P1 bacteriophage Cre-loxP site-specific recombination system. Plastid vectors carry a marker gene flanked with directly oriented loxP sites and a gene of interest, which are introduced into plastids by the biolistic process. The transforming DNA integrates into the plastid genome by homologous recombination via plastid targeting sequences. Marker gene excision is accomplished by a plastid-targeted Cre protein expressed from a nuclear gene. Expression may be from an integrated gene introduced by Agrobacterium transformation (Transformation Protocol), by pollination (Pollination Protocol) or from a transient, non-integrated T-DNA (Transient Protocol). Transplastomic plants are obtained in about 3 months, yielding seed after 2 months. The time required to remove the plastid marker and nuclear genes and to obtain seed takes 10–16 months, depending on which protocol is used.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maliga, P. Plastid transformation in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 55, 289–313 (2004).
Bock, R. Transgenic plastids in basic research and plant biotechnology. J. Mol. Biol. 312, 425–438 (2001).
Corneille, S., Lutz, K., Svab, Z. & Maliga, P. Efficient elimination of selectable marker genes from the plastid genome by the CRE-lox site-specific recombination system. Plant J. 72, 171–178 (2001).
Lutz, K.A., Bosacchi, M.H. & Maliga, P. Plastid marker gene excision by transiently expressed CRE recombinase. Plant J. 45, 447–456 (2006).
Svab, Z. & Maliga, P. High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 913–917 (1993).
Zubko, M.K., Zubko, E.I., van Zuilen, K., Mayer, P. & Day, A. Stable transformation of petunia plastids. Transgenic Res. 13, 523–530 (2004).
Svab, Z., Hajdukiewicz, P. & Maliga, P. Stable transformation of plastids in higher plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 8526–8530 (1990).
Maliga, P. New vectors and marker excision systems mark progress in engineering the plastid genome of higher plants. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 4, 971–976 (2005).
Herz, S., Fussl, M., Steiger, S. & Koop, H.U. Development of novel types of plastid transformation vectors and evaluation of factors controlling expression. Transgenic Res. 14, 969–982 (2005).
Hajdukiewicz, P.T.J., Gilbertson, L. & Staub, J.M. Multiple pathways for Cre/lox-mediated recombination in plastids. Plant J. 27, 161–170 (2001).
Chakrabarti, S.K., Lutz, K.A., Lerwirijawong, B., Svab, Z. & Maliga, P. Expression of the cry9Aa2 B.t. gene in the tobacco chlroplasts confers extreme resistance to potato tuber moth. Transgenic Res. (2006). DOI:10.1007/S11248-006-0018-Z.
Tungsuchat, T., Kuroda, H., Narangajavana, J. & Maliga, P. Gene activation in plastids by the CRE site-specific recombinase. Plant Mol. Biol. 61, 711–718 (2006).
Klaus, S.M.J., Huang, F.C., Golds, T.J. & Koop, H.-U. Generation of marker-free plastid transformants using a transiently cointegrated selection gene. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 225–229 (2004).
Iamtham, S. & Day, A. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from transgenic tobacco plastids. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 1172–1176 (2000).
Kode, V., Mudd, E., Iamtham, S. & Day, A. Isolation of precise plastid deletion mutants by homology-based excision: a resource for site-directed mutagenesis, multi-gene changes and high-throughput plastid transformation. Plant J. 46, 901–909 (2006).
Murashige, T. & Skoog, F. A revised medium for the growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant 15, 473–497 (1962).
Cséplö, A. & Maliga, P. Large scale isolation of maternally inherited lincomycin resistance mutations, in diploid Nicotiana plumbaginifolia protoplast cultures. Mol. Gen. Genet. 196, 407–412 (1984).
Murray, M.G. & Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8, 4321–4325 (1980).
Khan, M.S. & Maliga, P. Fluorescent antibiotic resistance marker to track plastid transformation in higher plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 910–915 (1999).
Kapila, J., De Rycke, R., Van Montagu, M. & Angenon, G. An Agrobacterium-mediated transient gene expression system for intact leaves. Plant Sci. 122, 101–108 (1997).
Kuroda, H. & Maliga, P. The plastid clpP1 gene is essential for plant development. Nature 425, 86–89 (2003).
Klein, T.M., Wolf, E.D., Wu, R. & Sanford, J.C. High-velocity microprojectiles for delivering nucleic acids in living cells. Nature 327, 70–73 (1987).
O'Neill, C., Horvath, G.V., Horvath, E., Dix, P.J. & Medgyesy, P. Chloroplast transformation in plants: polyethylene glycol (PEG) treatment of protoplasts is an alternative to biolistic delivery systems. Plant J. 3, 729–738 (1993).
Golds, T., Maliga, P. & Koop, H.U. Stable plastid transformation in PEG-treated protoplasts of Nicotiana tabacum. Biotechnology 11, 95–97 (1993).
Kofer, W., Eibl, C., Steinmuller, K. & Koop, H.-U. PEG-mediated plastid transformation in higher plants. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol.-Plant 34, 303–309 (1998).
Corneille, S., Lutz, K.A., Azhagiri, A.K. & Maliga, P. Identification of functional lox sites in the plastid genome. Plant J. 35, 753–762 (2003).
Hood, E.E., Helmer, G.L., Fraley, R.T. & Chilton, M.D. The hypervirulance of Agrobacterium tumefaciens A281 is encoded in a region of pTiBo542 outside of T-DNA. J. Bacteriol. 168, 1291–1301 (1986).
Hood, E.E., Gelvin, S.B., Melchers, L.S. & Hoekema, A. New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res. 2, 208–218 (1993).
Maliga, P. & Nixon, P. Judging the homoplastomic state of plastid transformants. Trends Plant Sci. 3, 4–6 (1998).
Ruf, S., Biehler, K. & Bock, R. A small chloroplast-encoded protein as a novel architectural component of the light-harvesting antenna. J. Cell Biol. 149, 369–377 (2000).
Swiatek, M. et al. PCR analysis of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis-purifed plastid DNA, a sensitive tool to judge the hetero-/homoplastomic status of plastid transformants. Curr. Genet. 43, 45–53 (2003).
Maliga, P. Engineering the plastid genome of higher plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 5, 164–172 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Azhagiri for making information about vector pPRV123 available at the prepublication stage. Development of plastid transformation and marker excision systems was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation and the USDA Biotechnology Risk Assessment Research Grant Program to P.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutz, K., Svab, Z. & Maliga, P. Construction of marker-free transplastomic tobacco using the Cre-loxP site-specific recombination system. Nat Protoc 1, 900–910 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.118
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.118
This article is cited by
-
Engineered PPR proteins as inducible switches to activate the expression of chloroplast transgenes
Nature Plants (2019)
-
Selectable marker recycling in the nonconventional yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous by transient expression of Cre on a genetically unstable vector
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2019)
-
Genetic modification of western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) for the phytoremediation of RDX and TNT
Planta (2019)
-
Production and characterization of fungal β-glucosidase and bacterial cellulases by tobacco chloroplast transformation
Plant Biotechnology Reports (2016)
-
The usage of snapdragon Delila (Del) gene as a visible selection marker for the antibiotic-free transformation system
Journal of Plant Biology (2015)