Abstract
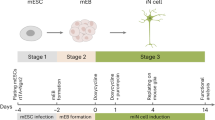
A detailed protocol is described allowing the generation of essentially pure populations of glutamatergic neurons from mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells. It is based on the culture of ES cells that are kept undifferentiated by repeated splitting and subsequently amplified as non-adherent cell aggregates. Treatment with retinoic acid causes these ES cells to essentially become neural progenitors with the characteristics of Pax6-positive radial glial cells. As they do in vivo, these progenitors differentiate in glutamatergic pyramidal neurons that form functional synaptic contacts and can be kept in culture for long periods of time. This protocol does not require the use of ES lines expressing resistance or fluorescent markers and can thus be applied in principle to any wild-type or mutant ES line of interest. At least 2 weeks are required from starting ES cell culture until plating progenitors and differentiating neurons establish synaptic transmission within about 10 days.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greene, L.A. & Tischler, A.S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73, 2424–2428 (1976).
Bain, G., Kitchens, D., Yao, M., Huettner, J.E. & Gottlieb, D.I. Embryonic stem cells express neuronal properties in vitro . Dev. Biol. 168, 342–357 (1995).
Li, M., Pevny, L., Lovell-Badge, R. & Smith, A. Generation of purified neural precursors from embryonic stem cells by lineage selection. Curr. Biol. 8, 971–974 (1998).
Okabe, S., Forsberg-Nilsson, K., Spiro, A.C., Segal, M. & McKay, R.D. Development of neuronal precursor cells and functional postmitotic neurons from embryonic stem cells in vitro . Mech. Dev. 59, 89–102 (1996).
Rathjen, J. & Rathjen, P.D. Mouse ES cells: experimental exploitation of pluripotent differentiation potential. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11, 587–594 (2001).
Smith, A.G. Embryo-derived stem cells: of mice and men. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 435–462 (2001).
Wichterle, H., Lieberam, I., Porter, J.A. & Jessell, T.M. Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into motor neurons. Cell 110, 385–397 (2002).
Kim, J.Y. et al. Dopaminergic neuronal differentiation from rat embryonic neural precursors by Nurr1 overexpression. J. Neurochem. 85, 1443–1454 (2003).
Wobus, A.M. & Boheler, K.R. Embryonic stem cells: prospects for developmental biology and cell therapy. Physiol. Rev. 85, 635–678 (2005).
Conti, L. et al. Niche-independent symmetrical self-renewal of a mammalian tissue stem cell. PLoS Biol. 3, e283 (2005).
Keller, G. Embryonic stem cell differentiation: emergence of a new era in biology and medicine. Genes Dev. 19, 1129–1155 (2005).
Bibel, M. et al. Differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into a defined neuronal lineage. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 1003–1009 (2004).
Malatesta, P. et al. Neuronal or glial progeny: regional differences in radial glia fate. Neuron 37, 751–764 (2003).
Plachta, N., Bibel, M., Tucker, K.L. & Barde, Y.A. Developmental potential of defined neural progenitors derived from mouse embryonic stem cells. Development 131, 5449–5456 (2004).
Pera, M.F. & Trounson, A.O. Human embryonic stem cells: prospects for development. Development 131, 5515–5525 (2004).
Pfaffl, M. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 2002–2007 (2001).
Tucker, K.L., Meyer, M. & Barde, Y.A. Neurotrophins are required for nerve growth during development. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 29–37 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bibel, M., Richter, J., Lacroix, E. et al. Generation of a defined and uniform population of CNS progenitors and neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Protoc 2, 1034–1043 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.147
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.147
This article is cited by
-
Dissecting the roles of MBD2 isoforms and domains in regulating NuRD complex function during cellular differentiation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Transcriptional repression by a secondary DNA binding surface of DNA topoisomerase I safeguards against hypertranscription
Nature Communications (2023)
-
MLL3/MLL4 methyltransferase activities control early embryonic development and embryonic stem cell differentiation in a lineage-selective manner
Nature Genetics (2023)
-
Tissue engineering of the gastrointestinal tract: the historic path to translation
Journal of Biological Engineering (2022)
-
High throughput screening identifies SOX2 as a super pioneer factor that inhibits DNA methylation maintenance at its binding sites
Nature Communications (2021)