Abstract
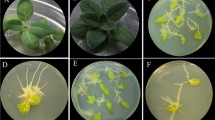
This transformation procedure generates, with high efficiency (70–90%), hairy roots in cultivars, landraces and accessions of Phaseolus vulgaris (common bean) and other Phaseolus spp. Hairy roots rapidly develop after wounding young plantlets with Agrobacterium rhizogenes, at the cotyledon node, and keeping the plants in high-humidity conditions. Callogenesis always precedes hairy-root formation, and after 15 days, when roots develop at wounded sites, the stem with the normal root is cleaved below the hairy root zone. Transgenic roots and nodules co-transformed with a binary vector can be easily identified using a reporter gene. This procedure, in addition to inducing robust transgenic hairy roots that are susceptible to being nodulated by rhizobia and to fixing nitrogen efficiently, sets the foundation for a high-throughput functional genomics approach on the study of root biology and root–microbe interactions. This protocol can be completed within 30 days.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McClean, P., Kami, K. & Gepts, P. Genomic and genetic diversity in common bean. in Legume Crop Genomics (eds. Wilson, R.F., Stalker, H.T. & Brummer, E.C.) 60–82 (AOC Press, Champaign, IL, 2004).
Broughton, W.J. et al. Beans (Phaseolus spp.) model food legumes. Plant Soil 252, 55–128 (2003).
Christou, P. Biotechnology applied to grain legumes. Field Crops Res. 53, 83–97 (1997).
Aragão, F.J.L., Vianna, G.R., Albino, M.M.C. & Rech, E.L. Transgenic dry bean tolerant to the herbicide glufosinate ammonium. Crop Sci. 42, 1298–1302 (2002).
Gepts, P. et al. Genomics of Phaseolus beans, a major source of dietary protein and micronutrients in the tropics. in Genomics of Tropical Crop Plants (eds. Moore, P.H. & Ming, R.) (Springer, Berlin, 2007) (in press).
Zhang, Z., Coyne, D.P. & Mitra, A. Factors affecting Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of common bean. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 122, 300–305 (1997).
Veltcheva, M., Svetleva, D., Petkova, S. & Perl, A. In vitro regeneration and genetic transformation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) problems and progress. Sci. Hortic. 107, 2–10 (2005).
Liu, Z., Park, B.J., Kanno, A. & Kameya, T. The novel use of a combination of sonication and vacuum infiltration in Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) with lea gene. Mol. Breed. 16, 189–197 (2005).
Brasileiro, A.C.M. et al. Suceptibility of common and tepary beans to Agrobacterium spp. Strains and improvement of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation using microprojectile bombardment. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 121, 810–815 (1996).
Zambre, M. et al. A reproductible genetic transformation system for cultivated Phaseolus acutifolius (tepary bean) and its use to asses the role of arcelins in resistence to the Mexican bean weevil. Theor. Appl. Genet. 110, 914–924 (2005).
Oldroyd, G., Harrison, M. & Udvardi, M. Peace talks and trade deals: keys to long-term harmony in legume–microbe symbioses. Plant Physiol. 137, 1205–1210 (2005).
Estrada-Navarrete, G. et al. Agrobacterium rhizogenes-transformation of the Phaseolus spp.: a tool for functional genomics. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 19, 1385–1393 (2006).
Shaner, N.C. et al. Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 12, 1567–1572 (2004).
Ramírez, M. et al. Sequencing and analysis of common bean ESTs: building a foundation for functional genomics. Plant Physiol. 137, 1211–1227 (2005).
Campos, F. et al. Characterization and gene expression of nodulin Npv30 from Common bean. Plant Physiol. 109, 363–370 (1995).
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by CONACYT 42562-Q and by Dirección General de Asuntos del Personal Académico IN-215805-2 grants. We thank Dr. José Luis Reyes and Oswaldo Valdés L. for pTdTRNAi vector construction and Olivia Santana for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Estrada-Navarrete, G., Alvarado-Affantranger, X., Olivares, JE. et al. Fast, efficient and reproducible genetic transformation of Phaseolus spp. by Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Nat Protoc 2, 1819–1824 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.259
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.259
This article is cited by
-
An ex vitro hairy root system from petioles of detached soybean leaves for in planta screening of target genes and CRISPR strategies associated with nematode bioassays
Planta (2024)
-
Development of transgenic composite Stylosanthes plants to study root growth regulated by a β-expansin gene, SgEXPB1, under phosphorus deficiency
Plant Cell Reports (2023)
-
The aquaporin gene PvXIP1;2 conferring drought resistance identified by GWAS at seedling stage in common bean
Theoretical and Applied Genetics (2022)
-
An NADPH oxidase regulates carbon metabolism and the cell cycle during root nodule symbiosis in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris)
BMC Plant Biology (2021)
-
One-step generation of composite soybean plants with transgenic roots by Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation
BMC Plant Biology (2020)