Abstract
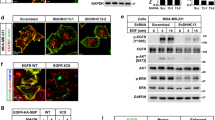
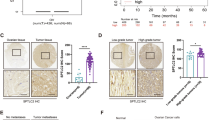
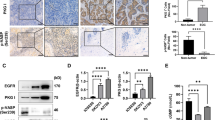
Many cancers are dependent on inappropriate activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and drugs targeting this receptor can improve patient survival, although benefits are generally short-lived. We reveal a novel mechanism linking EGFR and the membrane-spanning, cancer-promoting protein CDCP1 (CUB domain-containing protein 1). Under basal conditions, cell surface CDCP1 constitutively internalizes and undergoes palmitoylation-dependent degradation by a mechanism in which it is palmitoylated in at least one of its four cytoplasmic cysteines. This mechanism is functional in vivo as CDCP1 is elevated and palmitoylated in high-grade serous ovarian tumors. Interestingly, activation of the EGFR system with EGF inhibits proteasome-mediated, palmitoylation-dependent degradation of CDCP1, promoting recycling of CDCP1 to the cell surface where it is available to mediate its procancer effects. We also show that mechanisms inducing relocalization of CDCP1 to the cell surface, including disruption of its palmitoylation and EGF treatment, promote cell migration. Our data provide the first evidence that the EGFR system can function to increase the lifespan of a protein and also promote its recycling to the cell surface. This information may be useful for understanding mechanisms of resistance to EGFR therapies and assist in the design of treatments for EGFR-dependent cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciardiello F, Tortora G . EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. New Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1160–1174.
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG . Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13: 714–726.
Wheeler DL, Dunn EF, Harari PM . Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors—impact on future treatment strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2010; 7: 493–507.
He Y, Wortmann A, Burke LJ, Reid JC, Adams MN, Abdul-Jabbar I et al. Proteolysis-induced N-terminal ectodomain shedding of the integral membrane glycoprotein CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) is accompanied by tyrosine phosphorylation of its C-terminal domain and recruitment of Src and PKCδ. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 26162–26173.
Uekita T, Sakai R . Roles of CUB domain-containing protein 1 signaling in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Sci 2011; 102: 1943–1948.
Wortmann A, He Y, Deryugina EI, Quigley JP, Hooper JD . The cell surface glycoprotein CDCP1 in cancer—insights, opportunities, and challenges. IUBMB Life 2009; 61: 723–730.
Hooper JD, Zijlstra A, Aimes RT, Liang H, Claassen GF, Tarin D et al. Subtractive immunization using highly metastatic human tumor cells identifies SIMA135/CDCP1, a 135 kDa cell surface phosphorylated glycoprotein antigen. Oncogene 2003; 22: 1783–1794.
Awakura Y, Nakamura E, Takahashi T, Kotani H, Mikami Y, Kadowaki T et al. Microarray-based identification of CUB-domain containing protein 1 as a potential prognostic marker in conventional renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2008; 134: 1363–1369.
Emerling BM, Benes CH, Poulogiannis G, Bell EL, Courtney K, Liu H et al. Identification of CDCP1 as a hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha (HIF-2alpha) target gene that is associated with survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 3483–3488.
Razorenova OV, Finger EC, Colavitti R, Chernikova SB, Boiko AD, Chan CK et al. VHL loss in renal cell carcinoma leads to up-regulation of CUB domain-containing protein 1 to stimulate PKCδ-driven migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 1931–1936.
Miyazawa Y, Uekita T, Hiraoka N, Fujii S, Kosuge T, Kanai Y et al. CUB domain-containing protein 1, a prognostic factor for human pancreatic cancers, promotes cell migration and extracellular matrix degradation. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 5136–5146.
Ikeda J, Oda T, Inoue M, Uekita T, Sakai R, Okumura M et al. Expression of CUB domain containing protein (CDCP1) is correlated with prognosis and survival of patients with adenocarcinoma of lung. Cancer Sci 2009; 100: 429–433.
Gao W, Chen L, Ma Z, Du Z, Zhao Z, Hu Z et al. Isolation and phenotypic characterization of colorectal cancer stem cells with organ-specific metastatic potential. Gastroenterology 2013; 145: 636–646, e5.
Uekita T, Jia L, Narisawa-Saito M, Yokota J, Kiyono T, Sakai R . CUB domain-containing protein 1 is a novel regulator of anoikis resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 7649–7660.
Liu H, Ong SE, Badu-Nkansah K, Schindler J, White FM, Hynes RO . CUB-domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) activates Src to promote melanoma metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 1379–1384.
Uekita T, Tanaka M, Takigahira M, Miyazawa Y, Nakanishi Y, Kanai Y et al. CUB-domain-containing protein 1 regulates peritoneal dissemination of gastric scirrhous carcinoma. Am J Pathol 2008; 172: 1729–1739.
Deryugina EI, Conn EM, Wortmann A, Partridge JJ, Kupriyanova TA, Ardi VC et al. Functional role of cell surface CUB domain-containing protein 1 in tumor cell dissemination. Mol Cancer Res 2009; 7: 1197–1211.
Casar B, He Y, Iconomou M, Hooper JD, Quigley JP, Deryugina EI . Blocking of CDCP1 cleavage in vivo prevents Akt-dependent survival and inhibits metastatic colonization through PARP1-mediated apoptosis of cancer cells. Oncogene 2012; 31: 3924–3938.
Casar B, Rimann I, Kato H, Shattil SJ, Quigley JP, Deryugina EI . In vivo cleaved CDCP1 promotes early tumor dissemination via complexing with activated beta1 integrin and induction of FAK/PI3K/Akt motility signaling. Oncogene 2013; 33: 255–268.
Fukuchi K, Steiniger SC, Deryugina E, Liu Y, Lowery CA, Gloeckner C et al. Inhibition of tumor metastasis: functional immune modulation of the CUB domain containing protein 1. Mol Pharm 2010; 7: 245–253.
Kollmorgen G, Niederfellner G, Lifke A, Spohn GJ, Rieder N, Vega Harring S et al. Antibody mediated CDCP1 degradation as mode of action for cancer targeted therapy. Mol Oncol 2013; 7: 1142–1151.
Siva AC, Wild MA, Kirkland RE, Nolan MJ, Lin B, Maruyama T et al. Targeting CUB domain-containing protein 1 with a monoclonal antibody inhibits metastasis in a prostate cancer model. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 3759–3766.
Dong Y, He Y, de Boer L, Stack MS, Lumley JW, Clements JA et al. The cell surface glycoprotein CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) contributes to epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated cell migration. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 9792–9803.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX . Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 127–137.
Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, Leinster DA, Charles KA, Kwong J, Thompson RG et al. A dynamic inflammatory cytokine network in the human ovarian cancer microenvironment. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 66–75.
Blaskovic S, Blanc M, van der Goot FG . What does S-palmitoylation do to membrane proteins? FEBS J 2013; 280: 2766–2774.
Adams MN, Christensen ME, He Y, Waterhouse NJ, Hooper JD . The role of palmitoylation in signalling, cellular trafficking and plasma membrane localization of protease-activated receptor-2. PLoS One 2011; 6: e28018.
Adams MN, Pagel CN, Mackie EJ, Hooper JD . Evaluation of antibodies directed against human protease-activated receptor-2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2012; 385: 861–873.
Dietzen DJ, Hastings WR, Lublin DM . Caveolin is palmitoylated on multiple cysteine residues. Palmitoylation is not necessary for localization of caveolin to caveolae. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 6838–6842.
Joffre C, Barrow R, Menard L, Calleja V, Hart IR, Kermorgant S . A direct role for Met endocytosis in tumorigenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 827–837.
Miyazawa Y, Uekita T, Ito Y, Seiki M, Yamaguchi H, Sakai R . CDCP1 regulates the function of MT1-MMP and invadopodia-mediated invasion of cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 2013; 11: 628–637.
Benes CH, Wu N, Elia AE, Dharia T, Cantley LC, Soltoff SP . The C2 domain of PKCδ is a phosphotyrosine binding domain. Cell 2005; 121: 271–280.
Sandilands E, Frame MC . Endosomal trafficking of Src tyrosine kinase. Trends Cell Biol 2008; 18: 322–329.
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13: 239–246.
Macdonald JL, Pike LJ . A simplified method for the preparation of detergent-free lipid rafts. J Lipid Res 2005; 46: 1061–1067.
Morris DP, Lei B, Wu YX, Michelotti GA, Schwinn DA . The alpha1a-adrenergic receptor occupies membrane rafts with its G protein effectors but internalizes via clathrin-coated pits. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 2973–2985.
Wortmann A, He Y, Christensen ME, Linn M, Lumley JW, Pollock PM et al. Cellular settings mediating Src Substrate switching between focal adhesion kinase tyrosine 861 and CUB-domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) tyrosine 734. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 42303–42315.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Jon Whitehead for helpful discussions. This work was supported by Cancer Council Queensland Grants 614205 and 1021827 and Wesley Research Institute Grant 2008/06 to JDH. MNA and BSH received Australian Post-Graduate Awards. JDH holds Australian Research Council Future Fellowship FT120100917.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
JDH is an inventor on a patent describing CDCP1 as an anticancer target. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adams, M., Harrington, B., He, Y. et al. EGF inhibits constitutive internalization and palmitoylation-dependent degradation of membrane-spanning procancer CDCP1 promoting its availability on the cell surface. Oncogene 34, 1375–1383 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.88
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.88
This article is cited by
-
An oncogenic viral interferon regulatory factor upregulates CUB domain-containing protein 1 to promote angiogenesis by hijacking transcription factor lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 and metastasis suppressor CD82
Cell Death & Differentiation (2020)
-
CDCP1 enhances Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer promoting nuclear localization of β-catenin and E-cadherin
Oncogene (2020)
-
The PDGFRβ/ERK1/2 pathway regulates CDCP1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer
BMC Cancer (2018)
-
Casein Kinase 1 Epsilon Regulates Glioblastoma Cell Survival
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
CDCP1 cleavage is necessary for homodimerization-induced migration of triple-negative breast cancer
Oncogene (2016)