Abstract
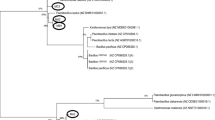
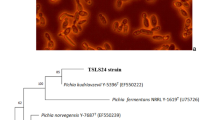
The production of poly(hydroxyalkanoate)s (PHAs) as ecofriendly bioplastics by various deep-sea bacteria (4 types of Colwellia spp., 11 types of Moritella spp., and 18 types of Shewanella spp.) from glucose, fructose, gluconate, or from one of the several plant oils as the sole source of carbon was examined at atmospheric pressure. Some of the deep-sea bacteria successfully accumulated PHAs that had a wide range of molecular weights and contained 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, and the other hydroxyalkanoate units. Furthermore, with a plant oil as its sole source of carbon, Shewanella surugensis produced low-molecular weight oligomeric PHAs. These results provide important and basic information regarding the production of PHAs by deep-sea bacteria and on the diversity of PHA synthase enzymes in nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Okuyama, H., Orikasa, Y., Nishida, T., Watanabe, K. & Morita, N. Bacterial genes responsible for the biosynthesis of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids and their heterologous expression. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 665–670 (2007).
Wada, M., Fukunaga, N. & Sasaki, S. Aerobic synthesis of unsaturated fatty-acids in a psychrotrophic bacterium, Pseudomonas sp. strain E-3, having two mechanisms for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 37, 355–362 (1991).
Lee, T. H., Hoover, R. L., Williams, J. D., Sperling, R. I., Ravalese, J., Spur, B. W., Robinson, D. R., Corey, E. J., Lewis, R. A. & Austen, K. F. Effect of dietary enrichment with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on in vitro neutrophil and monocyte leukotriene generation and neutrophil function. N. Engl. J. Med. 312, 1217–1224 (1985).
Pereira, S. L., Leonard, A. E. & Mukerji, P. Recent advances in the study of fatty acid desaturases from animals and lower eukaryotes. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 68, 97–106 (2003).
Krembs, C., Eicken, H., Junge, K. & Deming, J. W. High concentrations of exopolymeric substances in Arctic winter sea ice: implications for the polar ocean carbon cycle and cryoprotection of diatoms. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 49, 2163–2181 (2002).
Methe, B. A., Nelson, K. E., Deming, J. W., Momen, B., Melamud, E., Zhang, X., Moult, J., Madupu, R., Nelson, W. C., Dodson, R. J., Brinkac, L. M., Daugherty, S. C., Durkin, A. S., DeBoy, R. T., Kolonay, J. F., Sullivan, S. A., Zhou, L., Davidsen, T. M., Wu, M., Huston, A. L., Lewis, M., Weaver, B., Weidman, J. F., Khouri, H., Utterback, T. R., Feldblyum, T. V. & Fraser, C. M. The psychrophilic lifestyle as revealed by the genome sequence of Colwellia psychrerythraea 34H through genomic and proteomic analyses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10913–10918 (2005).
Sukovich, D. J., Seffernick, J. L., Richman, J. E., Hunt, K. A., Gralnick, J. A. & Wackett, L. P. Structure, function, and insights into the biosynthesis of a head-to-head hydrocarbon in Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 3842–3849 (2010).
Doi, Y. Microbial Polyesters, (VCH, New York, USA, 1990).
Marchessault, R.H. & Yu, G. in Biopolymers, Volume 3b, Polyesters II: Properties and Chemical Synthesis (eds Doi Y., Steinbüchel A.) (Wiley-VCH, Weinhelm, Germany, 2001).
Lenz, R. W. & Marchessault, R. H. Bacterial polyesters: biosynthesis, biodegradable plastics and biotechnology. Biomacromolecules 6, 1–8 (2005).
Iwata, T., Aoyagi, Y., Fujita, M., Yamane, H., Doi, Y., Suzuki, Y., Takeuchi, A. & Uesugi, K. Processing of a strong biodegradable poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] fiber and a new fiber structure revealed by micro-beam X-ray diffraction with synchrotron radiation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 25, 1100–1104 (2004).
Pohlmann, A., Fricke, W. F., Reinecke, F., Kusian, B., Liesegang, H., Cramm, R., Eitinger, T., Ewering, C., Pötter, M., Schwartz, E., Strittmatter, A., Voß, I., Gottschalk, G., Steinbüchel, A., Friedrich, B. & Bowien, B. Genome sequence of the bioplastic-producing ‘Knallgas’ bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 1257–1262 (2006).
Fiedler, S., Steinbuchel, A. & Rehm, B. H. The role of the fatty acid beta-oxidation multienzyme complex from Pseudomonas oleovorans in polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis: molecular characterization of the Fadba operon from P. oleovorans and of the enoyl-CoA hydratase genes PhaJ from P. oleovorans and Pseudomonas putida. Arch. Microbiol. 178, 149–160 (2002).
Tsuge, T., Fukui, T., Matsusaki, H., Taguchi, S., Kobayashi, G., Ishizaki, A. & Doi, Y. Molecular cloning of two (R)-specific enoyl-CoA hydratase genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their use for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 184, 193–198 (2000).
Rehm, B. H. Polyester synthases: natural catalysts for plastics. Biochem. J. 376, 15–33 (2003).
Numata, K. & Doi, Y. Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanaotes by a novel facultatively anaerobic Vibrio sp. under marine conditions. Mar. Biotechnol. 14, 323–331 (2012).
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W. & Lipman, D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410 (1990).
Chuah, J.-A., Yamada, M., Taguchi, S., Sudesh, K., Doi, Y. & Numata, K. Biosynthesis and characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoate containing 5-hydroxyvalerate units: effects of 5HV units on biodegradability, cytotoxicity, mechanical and thermal properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 98, 331–338 (2013).
Doi, Y., Tamaki, A., Kunioka, M. & Soga, K. Biosynthesis of terpolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, and 5-hydroxyvalerate in Alcaligenes eutrophus from 5-chloropentanoic and pentanoic acids. Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun 8, 631–635 (1987).
Fukui, T. & Doi, Y. Cloning and analysis of the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) biosynthesis genes of Aeromonas caviae. J. Bacteriol. 179, 4821–4830 (1997).
Yamanaka, K., Kimura, Y., Aoki, T. & Kudo, T. End-group analysis of bacterially produced poly(3-hydroxybutyrate): discovery of succinate as the polymerization starter. Macromolecules 42, 4038–4046 (2009).
Li, J., Uzawa, J. & Doi, Y. Conformational behavior of methyl (3R)-3-22butanoate in solutions: effect of intramolecular hydrogen bond. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 70, 1887–1893 (1997).
Tsuge, T., Watanabe, S., Sato, S., Hiraishi, T., Abe, H., Doi, Y. & Taguchi, S. Variation in copolymer composition and molecular weight of polyhydroxyalkanoate generated by saturation mutagenesis of Aeromonas caviae PHA synthase. Macromol. Biosci. 7, 846–854 (2007).
Tsuge, T., Yano, K., Imazu, S., Numata, K., Kikkawa, Y., Abe, H., Taguchi, S. & Doi, Y. Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) copolymer from fructose using wild-type and laboratory-evolved PHA synthases. Macromol. Biosci. 5, 112–117 (2005).
Pawan, G. L. & Semple, S. J. Effect of 3-hydroxybutyrate in obese subjects on very-low-energy diets and during therapeutic starvation. Lancet 321, 15–17 (1983).
Metz, J. G., Roessler, P., Facciotti, D., Levering, C., Dittrich, F., Lassner, M., Valentine, R., Lardizabal, K., Domergue, F., Yamada, A., Yazawa, K., Knauf, V. & Browse, J. Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by polyketide synthases in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Science 293, 290–293 (2001).
Yano, Y., Nakayama, A. & Yoshida, K. Distribution of polyunsaturated fatty acids in bacteria present in intestines of deep-sea fish and shallow-sea poikilothermic animals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 2572–2577 (1997).
Fukui, T., Yokomizo, S., Kobayashi, G. & Doi, Y. Co-expression of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and (R)-enoyl-CoA hydratase genes of Aeromonas caviae establishes copolyester biosynthesis pathway in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 170, 69–75 (1999).
Numata, K., Motoda, Y., Watanabe, S., Tochio, N., Kigawa, T. & Doi, Y. Active intermediates of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase from Aeromonas caviae in polymerization reaction. Biomacromolecules 13, 3450–3455 (2012).
Steinbüchel, A., Hustede, E., Liebergesell, M., Pieper, U., Timm, A. & Valentin, H. Molecular basis for biosynthesis and accumulation of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 9, 217–230 (1992) corrigendum ibid. 10, 347–350 (1993).
Liebergesell, M. & Steinbüchel, A. Cloning and molecular analysis of the poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid) biosynthetic genes of Thiocystis violacea. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38, 493–501 (1993).
Jia, Y., Yuan, W., Wodzinska, J., Park, C., Sinskey, A. J. & Stubbe, J. Mechanistic studies on Class I polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthase from Ralstonia eutropha: Class I and III synthases share a similar catalytic mechanism. Biochemistry 40, 1011–1019 (2001).
Kichise, T., Taguchi, S. & Doi, Y. Enhanced accumulation and changed monomer composition in polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) copolyester by in vitro evolution of Aeromonas caviae PHA synthase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 2411–2419 (2002).
Li, P., Chakraborty, S. & Stubbe, J. Detection of covalent and noncovalent intermediates in the polymerization reaction catalyzed by a C149S Class III polyhydroxybutyrate synthase. Biochemistry 48, 9202–9211 (2009).
Normi, Y. M., Hiraishi, T., Taguchi, S., Abe, H., Sudesh, K., Najimudin, N. & Doi, Y. Characterization and properties of G4X mutants of Ralstonia eutropha PHA synthase for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Macromol. Biosci. 5, 197–206 (2005).
Tian, J., Sinskey, A. J. & Stubbe, J. Detection of intermediates from the polymerization reaction catalyzed by a D302A mutant of Class III polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase. Biochemistry 44, 1495–1503 (2005).
Tsuge, T., Watanabe, S., Shimada, D., Abe, H., Doi, Y. & Taguchi, S. Combination of N149S and D171G mutations in Aeromonas caviae polyhydroxyalanoate synthase and impact on polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 277, 217–222 (2007).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant for the RIKEN Biomass Engineering Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Polymer Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Numata, K., Morisaki, K., Tomizawa, S. et al. Synthesis of poly- and oligo(hydroxyalkanoate)s by deep-sea bacteria, Colwellia spp., Moritella spp., and Shewanella spp. Polym J 45, 1094–1100 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2013.25
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2013.25
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Microbial decomposition of biodegradable plastics on the deep-sea floor
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Microbial accumulation of bioplastics from waste stream: recent advancements and applications
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2024)
-
Biodegradability of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate) and poly(ε-caprolactone) via biological carbon cycles in marine environments
Polymer Journal (2021)
-
Poly(amino acid)s/polypeptides as potential functional and structural materials
Polymer Journal (2015)
-
Whole genome amplification approach reveals novel polyhydroxyalkanoate synthases (PhaCs) from Japan Trench and Nankai Trough seawater
BMC Microbiology (2014)