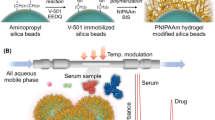
Abstract
Thermosensitive hybrid hydrogels were prepared by chemical crosslinking using poly[N-isopropylacrylamide-co-(3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane)] (pNS) copolymer chains as the backbone and silica nanoparticles (SiP) as crosslinkers. The preparation of these hybrid hydrogels involved mixing a reactive side chain-branched copolymer (pNS) solution with a SiP suspension at 25 °C. During the mixing of these components, caffeine was added as a model drug to form a thermo-responsive drug delivery system. The as-prepared caffeine-loaded hydrogels do not require any further processing. The effects of temperature on the equilibrium swelling ratios and on the release of caffeine from these hybrid hydrogels at different temperatures and with different hydrogel compositions were thoroughly investigated. We found that this novel system provides controllable drug loading and a positive drug-release pattern. More than 90% of the loaded drugs were released at both high and low temperatures, with a faster release rate at higher temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Peppas, N. A., Bures, P., Leobandung, W. & Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50, 27–46 (2000).
Liu, X. M., Wang, L. S., Wang, L., Huang, J. C. & He, C. B. The effect of salt and pH on the phase-transition behaviors of temperature-sensitive copolymers based on N-isopropylacrylamide. Biomaterials 25, 5659–5666 (2004).
Hirokawa, Y. & Tanaka, T. Volume phase transition in a non-ionic gel. J. Chem. Phys. 81, 6379–6380 (1984).
Kim, S. J., Shin, S. R., Lee, J. H., Lee, S. H. & Kim, S. I. Electrical response characterization of chitosan/polyacrylonitrile hydrogel in NaCl solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 90, 91–96 (2003).
Khare, A. R. & Peppas, N. A. Swelling/deswelling of anionic copolymer gels. Biomaterials 16, 559–567 (1995).
Zhang, X. Z., Zhuo, R. X., Cui, J. Z. & Zhang, J. T. A novel thermo-responsive drug delivery system with positive controlled release. Int. J. Pharm. 235, 43–50 (2002).
Zhang, X. Z., Wu, D. Q. & Chu, C. C. Synthesis, characterization and controlled drug release of thermosensitive IPN–PNIPAAm hydrogels. Biomaterials 25, 3793–3805 (2004).
Deng, K., Tian, H., Zhang, P., Zhong, H., Ren, X. & Wang, H. pH–temperature responsive poly(HPA-Co-AMHS) hydrogel as a potential drug-release carrier. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 114, 176–184 (2009).
Wang, K., Fu, Q., Chen, X., Gao, Y. & Dong, K. Preparation and characterization of pH-sensitive hydrogel for drug delivery system. RSC Adv 2, 7772–7780 (2012).
Osada, Y., Okuzaki, H. & Hori, H. A polymer gel with electrically driven motility. Nature 355, 242–244 (1992).
Kurisawa, M., Yokoyama, M. & Okano, T. Gene expression control by temperature with thermo-responsive polymeric gene carriers. J. Controlled Release 69, 127–137 (2000).
Okano, T., Bae, Y. H., Jacobs, H. & Kim, S. W. Thermally on–off switching polymers for drug permeation and release. J. Controlled Release 11, 255–265 (1990).
Zhang, N., Liu, M., Shen, Y., Chen, J., Dai, L. & Gao, C. Preparation, properties, and drug release of thermo- and pH-sensitive poly((2-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate)/poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) semi-IPN hydrogels. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 1523–1534 (2011).
Okahata, Y., Noguchi, H. & Seki, T. Thermoselective permeation from a polymer-grafted capsule membrane. Macromolecules 19, 493–494 (1986).
Tanaka, Y., Kagamin, Y., Matsuda, A. & Osada, Y. Thermoreversible transition of tensile modulus of hydrogel with ordered aggregates. Macromolecules 28, 2574–2576 (1995).
Zhang, J. & Peppas, N. A. Morphology of poly(methacrylic acid)/poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) interpenetrating polymeric networks. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 5, 511–525 (2002).
de Sousa, A., Maria, D. A., de Sousa, R. G. & de Sousa, E. M. B. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous silica/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) functional hybrid useful for drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 1478–1486 (2010).
Geever, L. M., Nugent, M. J. D. & Higginbotham, C. L. The effect of salts and pH buffer solutions on the phase transition temperature and swelling of thermoresponsive pseudogels based on N-isopropylacrylamide. J. Mater. Sci 42, 9845–9854 (2007).
Anseth, K. S., Metters, A. T., Bryant, S. J., Martens, P. J., Elisseeff, J. H. & Bowman, C. N. In situ forming degradable networks and their application in tissue engineering and drug delivery. J. Controlled Release 78, 199–209 (2002).
Bravo, S. A., Lamas, M. C. & Salomon, C. J. In-vitro studies of diclofenac sodium controlled-release from biopolymeric hydrophilic matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 5, 213–219 (2002).
Kim, S. W., Bae, Y. H. & Okano, T. Hydrogels: swelling, drug loading and release. Pharm. Res. 9, 283–290 (1992).
Zhang, J. T., Keller, T. F., Bhat, R., Garipcan, B. & Jandt, K. D. A novel two-level microstructured poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel for controlled release. Acta. Biomater. 6, 3890–3898 (2010).
Ng, L. T. & Swami, S. IPNs based on chitosan with NVP and NVP/HEMA synthesised through photoinitiator-free photopolymerisation technique for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym 60, 523–528 (2005).
Mathews, A. S., Cho, W. J., Kim, I. & Ha, C. S. Thermally responsive poly[N-isopropylacrylamide-co-2- hydroxyethylacrylate] colloidal crystals included in β-cyclodextrin for controlled drug delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 113, 1680–1689 (2009).
Geever, L., Cooney, C., Devine, D., Devery, S., Nugent, M. & Higginbotham, C. Negative temperature sensitive hydrogels in controlled drug delivery. Macromol. Symp. 266, 53–58 (2008).
Takafuji, M., Yamada, S. & Ihara, H. Strategy for preparation of hybrid polymer hydrogels using silica nanoparticles as multifunctional crosslinking points. Chem. Commun 47, 1024–1026 (2011).
Alam, M. A., Takafuji, M. & Ihara, H. Thermosensitive hybrid hydrogels with silica nanoparticle-cross-linked polymer networks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 405, 109–117 (2013).
Makino, K., Hiyoshi, J. & Ohshima, H. Kinetics of swelling and shrinking of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels at different temperatures. Colloids Surf. B 19, 197–204 (2000).
Zhang, X. Z., Yang, Y. Y., Chung, T. S. & Ma, K. X. Preparation and characterization of fast response macroporous poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Langmuir. 17, 6094–6099 (2001).
Ham, M. J. & Kim, Y. H. Property modulation of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels by Incorporation of Modified Silica. Polym. Eng. Sci. 48, 2439–2445 (2008).
Huang, W. J. & Lee, W. F. Effect of silane coupling agent on swelling behaviors and mechanical properties of thermosensitive hybrid gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 111, 2025–2034 (2009).
Ngadaonye, J. I., Geever, L. M., Cloonan, M. O. & Higginbotham, C. L. Photopolymerised thermo-responsive poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide)-based copolymer hydrogels for potential drug delivery applications. J. Polym. Res. 19, 9822–9836 (2012).
Mohapatra, R., Ray, D., Swain, A. K., Pal, T. K. & Sahoo, P. K. Release study of alfuzosin hydrochloride loaded to novel hydrogel P(HEMA-co-AA). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 108, 380–386 (2008).
Hoffman, A. S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 54, 3–12 (2002).
Lee, W. F. & Lin, Y. H. Thermoreversible hydrogels. XIX. Synthesis and swelling behavior and drug release behavior for the N-isopropylacrylamide/poly(ethylene glycol) methylether acrylate copolymeric hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 90, 1683–1691 (2003).
Brazel, C. S. & Peppas, N. A. Mechanisms of solute and drug transport in relaxing, swellable, hydrophilic glassy polymers. Polymer (Guildf). 40, 3383–3398 (1999).
Shi, J., Alves, N. M. & Mano, J. F. Drug release of pH/temperature-responsive calcium alginate/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) semi-IPN beads. Macromol. Biosci. 6, 358–363 (2006).
Guo, B.-L. & Gao, Q.-Y. Preparation and properties of a pH/temperature-responsive carboxymethyl chitosan/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)semi-IPN hydrogel for oral delivery of drugs. Carbohydr. Res. 342, 2416–2422 (2007).
Peppas, N. A. & Franson, N. M. The swelling interphase number as a criterion for prediction of diffusional solute release mechanisms in swellable polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Phys. Ed. 21, 983–997 (1983).
Haraguchi, K., Takehisa, T. & Fan, S. Effects of clay content on the properties of nanocomposite hydrogels composed of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and clay. Macromolecules 35, 10162–10171 (2002).
Zhang, X. Z. & Zhuo, R. X. Dynamic properties of temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel cross-linked through siloxane linkage. Langmuir 17, 12–16 (2001).
Kaneko, Y., Sakai, K., Kikuchi, A., Yoshida, R., Sakurai, Y. & Okano, T. Influence of freely mobile grafted chain length on dynamic properties of comb-type grafted poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Macromolecules 28, 7717–7723 (1995).
Zhang, J. T., Xue, Y. N., Gao, F. Z., Huang, S. W. & Zhuo, R. X. Preparation of temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/β-cyclodextrin-grafted polyethylenimine hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 108, 3031–3037 (2008).
Zhao, S., Cao, M., Li, H., Li, L. & Xu, W. Synthesis and characterization of thermo-sensitive semi-IPN hydrogels based on poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(e-caprolactone) macromer, N-isopropylacrylamide, and sodium alginate. Carbohydr. Res. 345, 425–431 (2010).
Ritger, P. L. & Peppas, N. A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-Fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Controlled Release 5, 23–26 (1987).
Miao, Z. M., Cheng, S. X., Zhang, X. Z. & Zhuo, R. X. Study on drug release behaviors of poly-α,β-[N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-L-aspartamide]-g-poly(3-caprolactone) nano- and microparticles. Biomacromolecules 7, 2020–2026 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Polymer Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, M., Takafuji, M. & Ihara, H. Silica nanoparticle-crosslinked thermosensitive hybrid hydrogels as potential drug-release carriers. Polym J 46, 293–300 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2014.2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2014.2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enhancing the performance of styrene–butadiene rubber with nanoceramic powder for wear-resistant lining sheets
Polymer Bulletin (2024)
-
Synthesis and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/water-hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) based hydrogel by applying gamma radiation
Journal of Polymer Research (2021)
-
Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene oxide (PEO)—N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMA) hydrogel by gamma radiation
Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials (2019)
-
Magnetic nanoparticle-crosslinked ferrohydrogel as a novel class of forward osmosis draw agent
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2018)