Abstract
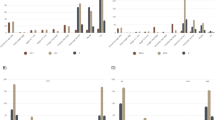
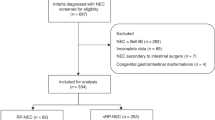
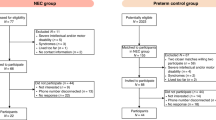
The study objective was to determine whether Ureaplasma respiratory tract colonization of preterm infants <33 wk gestation is associated with an increased risk for necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). One or more tracheal or nasopharyngeal aspirates for Ureaplasma culture and PCR were obtained during the first week of life from 368 infants <33 wk gestation enrolled from 1999 to 2003 or from 2007 to 2009. NEC Bell stage ≥2 was confirmed by radiological criteria, and pathology, if available. Cord serum samples were analyzed for IL-6 and IL-1β concentrations, and placentas were reviewed for histological chorioamnionitis in the first cohort. NEC was confirmed in 29 of 368 (7.9%) of the combined cohorts. The incidence of NEC was 2.2-fold higher in Ureaplasma-positive (12.3%) than Ureaplasma-negative (5.5%) infants <33 wk (OR, 2.43; 95% CI, 1.13–5.2; p = 0.023) and 3.3-fold higher in Ureaplasma-positive (14.6%) than Ureaplasma-negative (4.4%) infants ≤28 wk (OR, 3.67; 95% CI, 1.36–9.93; p = 0.01). Age of onset, hematologic parameters at onset, and NEC severity were similar between Ureaplasma-positive and negative infants. Cord serum IL-6 and IL-1β concentrations were significantly higher in Ureaplasma-positive than in Ureaplasma-negative NEC-affected infants. Ureaplasma may be a factor in NEC pathogenesis in preterm infants by contributing to intestinal mucosal injury and/or altering systemic or local immune responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BPD:
-
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- NEC:
-
necrotizing enterocolitis
- VLBW:
-
very LBW
REFERENCES
Uauy RD, Fanaroff AA, Korones SB, Phillips EA, Phillips JB, Wright LL 1991 Necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants: biodemographic and clinical correlates. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J Pediatr 119: 630–638
Fitzgibbons SC, Ching Y, Yu D, Carpenter J, Kenny M, Weldon C, Lillehei C, Valim C, Horbar JD, Jaksic T 2009 Mortality of necrotizing enterocolitis expressed by birth weight categories. J Pediatr Surg 44: 1072–1075; discussion 1075–1076.
Viscardi RM, Lyon NH, Sun C-C, Hebel JR, Hasday JD 1997 Inflammatory cytokine mRNAs in surgical specimens of necrotizing enterocolitis and normal newborn intestine. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med 17: 547–559
Caplan MS, Lickerman M, Adler L, Dietsch GN, Yu A 1997 The role of recombinant platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in a neonatal rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Res 42: 779–783
Edelson MB, Bagwell CE, Rozycki HJ 1999 Circulating pro- and counterinflammatory cytokine levels and severity in necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics 103: 766–771
Halpern MD, Holubec H, Dominguez JA, Williams CS, Meza YG, McWilliam DL, Payne CM, McCuskey RS, Besselsen DG, Dvorak B 2002 Up-regulation of IL-18 and IL-12 in the ileum of neonatal rats with necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Res 51: 733–739
Harris MC, D'Angio CT, Gallagher PR, Kaufman D, Evans J, Kilpatrick L 2005 Cytokine elaboration in critically ill infants with bacterial sepsis, necrotizing entercolitis, or sepsis syndrome: correlation with clinical parameters of inflammation and mortality. J Pediatr 147: 462–468
Seitz G, Warmann SW, Guglielmetti A, Heitmann H, Ruck P, Kreis ME, Fuchs J 2005 Protective effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody on experimental necrotizing enterocolitis in the rat. J Pediatr Surg 40: 1440–1445
van Waarde WM, Brus F, Okken A, Kimpen JL 1997 Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization, prematurity and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur Respir J 10: 886–890
Waites KB, Katz B, Schelonka RL 2005 Mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas as neonatal pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev 18: 757–789
Goldenberg RL, Andrews WW, Goepfert AR, Faye-Petersen O, Cliver SP, Carlo WA, Hauth JC 2008 The Alabama Preterm Birth Study: umbilical cord blood Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis cultures in very preterm newborn infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198: 43.e1–43.e5
Viscardi RM, Hasday JD 2009 Role of Ureaplasma species in neonatal chronic lung disease: epidemiologic and experimental evidence. Pediatr Res 65: 84R–90R
Patterson AM, Taciak V, Lovchik J, Fox RE, Campbell AB, Viscardi RM 1998 Ureaplasma urealyticum respiratory tract colonization is associated with an increase in interleukin 1-beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha relative to interleukin 6 in tracheal aspirates of preterm infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17: 321–328
Viscardi RM, Manimtim WM, Sun CC, Duffy L, Cassell GH 2002 Lung pathology in premature infants with Ureaplasma urealyticum infection. Pediatr Dev Pathol 5: 141–150
Manimtim WM, Hasday JD, Hester L, Fairchild KD, Lovchik JC, Viscardi RM 2001 Ureaplasma urealyticum modulates endotoxin-induced cytokine release by human monocytes derived from preterm and term newborns and adults. Infect Immun 69: 3906–3915
Viscardi RM, Kaplan J, Lovchik JC, He JR, Hester L, Rao S, Hasday JD 2002 Characterization of a murine model of Ureaplasma urealyticum pneumonia. Infect Immun 70: 5721–5729
Yoder BA, Coalson JJ, Winter VT, Siler-Khodr T, Duffy LB, Cassell GH 2003 Effects of antenatal colonization with Ureaplasma urealyticum on pulmonary disease in the immature baboon. Pediatr Res 54: 797–807
Viscardi RM, Atamas SP, Luzina IG, Hasday JD, He JR, Sime PJ, Coalson JJ, Yoder BA 2006 Antenatal Ureaplasma urealyticum respiratory tract infection stimulates proinflammatory, profibrotic responses in the preterm baboon lung. Pediatr Res 60: 141–146
Wang EE, Frayha H, Watts J, Hammerberg O, Chernesky MA, Mahony JB, Cassell GH 1988 Role of Ureaplasma urealyticum and other pathogens in the development of chronic lung disease of prematurity. Pediatr Infect Dis J 7: 547–551
Taylor-Robinson D, Furr PM, Liberman MM 1984 The occurrence of genital mycoplasmas in babies with and without respiratory distress. Acta Paediatr Scand 73: 383–386
Sánchez PJ, Regan JA 1990 Vertical transmission of Ureaplasma urealyticum from mothers to preterm infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 9: 398–401
Jones V, Wilks M, Johnson G, Warwick S, Hennessey E, Kempley S, Millar M 2010 The use of molecular techniques for bacterial detection in the analysis of gastric aspirates collected from infants on the first day of life. Early Hum Dev 86: 167–170
Viscardi RM, Muhumuza CK, Rodriguez A, Fairchild KD, Sun CC, Gross GW, Campbell AB, Wilson PD, Hester L, Hasday JD 2004 Inflammatory markers in intrauterine and fetal blood and cerebrospinal fluid compartments are associated with adverse pulmonary and neurologic outcomes in preterm infants. Pediatr Res 55: 1009–1017
Viscardi RM, Hashmi N, Gross GW, Sun CC, Rodriguez A, Fairchild KD 2008 Incidence of invasive ureaplasma in VLBW infants: relationship to severe intraventricular hemorrhage. J Perinatol 28: 759–765
Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, Brotherton T 1978 Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 187: 1–7
Shepard MC 1983 Culture media for Ureaplasmas. In: Razin S, Tully JG (eds) Methods in Mycoplasmology. Vol 1 Academic Press, New York, pp 137–146
Xiao L, Glass JI, Paralanov V, Yooseph S, Cassell GH, Duffy LB, Waites KB 2010 Detection and characterization of human Ureaplasma species and serovars by real-time PCR. J Clin Microbiol 48: 2715–2723
Redline RW, Wilson-Costello D, Borawski E, Fanaroff AA, Hack M 1998 Placental lesions associated with neurologic impairment and cerebral palsy in very low-birth-weight infants. Arch Pathol Lab Med 122: 1091–1098
Morowitz MJ, Poroyko V, Caplan M, Alverdy J, Liu DC 2010 Redefining the role of intestinal microbes in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics 125: 777–785
Sánchez PJ, Regan JA 1988 Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization and chronic lung disease in low birth weight infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 7: 542–546
Waites KB, Crouse DT, Cassell GH 1993 Systemic neonatal infection due to Ureaplasma urealyticum. Clin Infect Dis 17: S131–S135
Ollikainen J, Hiekkaniemi H, Korppi M, Katila ML, Heinonen K 1993 Ureaplasma urealyticum cultured from brain tissue of preterm twins who died of intraventricular hemorrhage. Scand J Infect Dis 25: 529–531
Ollikainen J, Hiekkaniemi H, Korppi M, Sarkkinen H, Heinonen K 1993 Ureaplasma urealyticum infection associated with acute respiratory insufficiency and death in premature infants. J Pediatr 122: 756–760
Schelonka RL, Katz B, Waites KB, Benjamin DK Jr 2005 Critical appraisal of the role of Ureaplasma in the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia with metaanalytic techniques. Pediatr Infect Dis J 24: 1033–1039
Normann E, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, Eaton F, Schwendimann L, Gressens P, Thebaud B 2009 A novel mouse model of Ureaplasma-induced perinatal inflammation: effects on lung and brain injury. Pediatr Res 65: 430–436
Moss TJ, Knox CL, Kallapur SG, Nitsos I, Theodoropoulos C, Newnham JP, Ikegami M, Jobe AH 2008 Experimental amniotic fluid infection in sheep: effects of Ureaplasma parvum serovars 3 and 6 on preterm or term fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198: 122.e1–122.e8
Novy MJ, Duffy L, Axthelm MK, Sadowsky DW, Witkin SS, Gravett MG, Cassell GH, Waites KB 2009 Ureaplasma parvum or Mycoplasma hominis as sole pathogens cause chorioamnionitis, preterm delivery, and fetal pneumonia in rhesus macaques. Reprod Sci 16: 56–70
Oh KJ, Lee KA, Sohn YK, Park CW, Hong JS, Romero R, Yoon BH 2010 Intraamniotic infection with genital mycoplasmas exhibits a more intense inflammatory response than intraamniotic infection with other microorganisms in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 203: 211.e1–211.e8
Hitti J, Tarczy-Hornoch P, Murphy J, Hillier SL, Aura J, Eschenbach DA 2001 Amniotic fluid infection, cytokines, and adverse outcome among infants at 34 weeks' gestation or less. Obstet Gynecol 98: 1080–1088
Weeks JW, Reynolds L, Taylor D, Lewis J, Wan T, Gall SA 1997 Umbilical cord blood interleukin-6 levels and neonatal morbidity. Obstet Gynecol 90: 815–818
Goepfert AR, Andrews WW, Carlo W, Ramsey PS, Cliver SP, Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC 2004 Umbilical cord plasma interleukin-6 concentrations in preterm infants and risk of neonatal morbidity. Am J Obstet Gynecol 191: 1375–1381
Andrews WW, Goldenberg RL, Faye-Petersen O, Cliver S, Goepfert AR, Hauth JC 2006 The Alabama Preterm Birth study: polymorphonuclear and mononuclear cell placental infiltrations, other markers of inflammation, and outcomes in 23- to 32-week preterm newborn infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 195: 803–808
Giannone PJ, Nankervis CA, Richter JM, Schanbacher BL, Reber KM 2009 Prenatal lipopolysaccharide increases postnatal intestinal injury in a rat model of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 48: 276–282
Cotten CM, Taylor S, Stoll B, Goldberg RN, Hansen NI, Sanchez PJ, Ambalavanan N, Benjamin DK Jr 2009 Prolonged duration of initial empirical antibiotic treatment is associated with increased rates of necrotizing enterocolitis and death for extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 123: 58–66
Guillet R, Stoll BJ, Cotten CM, Gantz M, McDonald S, Poole WK, Phelps DL 2006 Association of H2-blocker therapy and higher incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 117: e137–e142
Onderdonk AB, Hecht JL, McElrath TF, Delaney ML, Allred EN, Leviton A 2008 Colonization of second-trimester placenta parenchyma. Am J Obstet Gynecol 199: 52.e1–52.e10
Jacobsson B, Aaltonen R, Rantakokko-Jalava K, Morken NH, Alanen A 2009 Quantification of Ureaplasma urealyticum DNA in the amniotic fluid from patients in PTL and pPROM and its relation to inflammatory cytokine levels. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 88: 63–70
Kasper DC, Mechtler TP, Reischer GH, Witt A, Langgartner M, Pollak A, Herkner KR, Berger A 2010 The bacterial load of Ureaplasma parvum in amniotic fluid is correlated with an increased intrauterine inflammatory response. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 67: 117–121
Acknowledgements
We thank Elise Janofsky and Mary Spence for their technical assistance and data abstraction, and Lynn Duffy, Department of Pathology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by grants HL71113, HL087166, and 5RO1A1072577 from the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okogbule-Wonodi, A., Gross, G., Sun, CC. et al. Necrotizing Enterocolitis Is Associated With Ureaplasma Colonization in Preterm Infants. Pediatr Res 69, 442–447 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182111827
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e3182111827
This article is cited by
-
Randomized trial of azithromycin to eradicate Ureaplasma respiratory colonization in preterm infants: 2-year outcomes
Pediatric Research (2022)
-
Neonatal Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization increases pulmonary and cerebral morbidity despite treatment with macrolide antibiotics
Infection (2016)
-
Clinical significance of FABP2 expression in newborns with necrotizing enterocolitis
World Journal of Pediatrics (2016)
-
Gut microbiota, the immune system, and diet influence the neonatal gut–brain axis
Pediatric Research (2015)
-
Maternal influences on fetal microbial colonization and immune development
Pediatric Research (2015)