Abstract
Background
Bariatric surgery (BS) improves long-term glycemic control more effectively than medical treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The objective of this study was to explore the dynamic changes on inflammatory and metabolic-related circulating proteins in a large cohort of overweight patients and patients with class I to III obesity undergoing bariatric surgery (BS).
Subjects/methods
We performed quantitative proteomic analysis (399 inflammatory/metabolic proteins, Olink Proteomics) in plasma samples collected before (n = 114) and 1 month (n = 67), 3 months (n = 64), 6 months (n = 60), 12 months (n = 48) and 24 months (n = 18) after either Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) or vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG).
Results
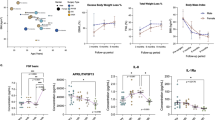
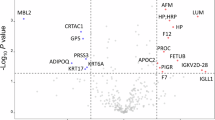
Circulating proteins primarily expressed in the liver markedly changed after BS including IGFBP-1/2 (upregulated at all time points post-surgery) and the peroxisomal enzyme HAOX1 (downregulated at all time points post-surgery). Regression analysis revealed a strong association between the changes in HAOX1 and improvements in liver enzymes. In addition, a soluble broad-spectrum pattern recognition receptor, scavenger receptor cysteine rich family member with 4 domains (SSC4D), exhibited the highest decrease among all proteins at 24 months post-surgery. Finally, we detected that inflammatory markers were transiently increased after RYGB compared to VSG as well as in patients with severe obesity compared to patients with overweight and patients with obesity at 1-month post-surgery.
Conclusions
This study identified novel inflammatory and metabolic proteins possibly implicated in the systemic metabolic response to BS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Olink raw proteomics data is provided in Table S1. Olink proteomics data (mean and SD) for all the proteins at different time points is provided in Table S2. This study reports original code deposited at (https://github.com/Cclarrisacheung/ijo-candeladiazcanestro-bariatric-surgery-2025). Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this work paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
References
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14:88–98.
Hu FB. Globalization of diabetes: the role of diet, lifestyle, and genes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1249–57.
Lear SA, Humphries KH, Kohli S, Birmingham CL. The use of BMI and waist circumference as surrogates of body fat differs by ethnicity. Obesity. 2007;15:2817–24.
Simonson DC, Halperin F, Foster K, Vernon A, Goldfine AB. Clinical and Patient-centered outcomes in obese patients with type 2 diabetes 3 years after randomization to roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery versus intensive lifestyle management: the SLIMM-T2D study. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:670–9.
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Nanni G, et al. Bariatric-metabolic surgery versus conventional medical treatment in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: 5 year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;386:964–73.
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Aminian A, Brethauer SA, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes - 5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:641–51.
Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg. 2013;23:427–36.
Dixon JB, le Roux CW, Rubino F, Zimmet P. Bariatric surgery for type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2012;379:2300–11.
Yoshino M, Kayser BD, Yoshino J, Stein RI, Reeds D, Eagon JC, et al. Effects of diet versus gastric bypass on metabolic function in diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:721–32.
Jackness C, Karmally W, Febres G, Conwell IM, Ahmed L, Bessler M, et al. Very low-calorie diet mimics the early beneficial effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on insulin sensitivity and beta-cell Function in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2013;62:3027–32.
Albaugh VL, Flynn CR, Cai S, Xiao Y, Tamboli RA, Abumrad NN. Early Increases in Bile Acids Post Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Are Driven by Insulin-Sensitizing, Secondary Bile Acids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100:E1225–33.
Wewer Albrechtsen NJ, Geyer PE, Doll S, Treit PV, Bojsen-Moller KN, Martinussen C, et al. Plasma proteome profiling reveals dynamics of inflammatory and lipid homeostasis markers after Roux-En-Y gastric bypass surgery. Cell Syst. 2018;7:601–12.e3.
Dreyfuss JM, Yuchi Y, Dong X, Efthymiou V, Pan H, Simonson DC, et al. High-throughput mediation analysis of human proteome and metabolome identifies mediators of post-bariatric surgical diabetes control. Nat Commun. 2021;12:6951.
Petrera A, von Toerne C, Behler J, Huth C, Thorand B, Hilgendorff A, et al. Multiplatform approach for plasma proteomics: complementarity of olink proximity extension assay technology to mass spectrometry-based protein profiling. J Proteome Res. 2021;20:751–62.
Shah RV, Hwang SJ, Yeri A, Tanriverdi K, Pico AR, Yao C, et al. Proteins altered by surgical weight loss highlight biomarkers of insulin resistance in the community. Arter Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39:107–15.
Katz DH, Robbins JM, Deng S, Tahir UA, Bick AG, Pampana A, et al. Proteomic profiling platforms head to head: Leveraging genetics and clinical traits to compare aptamer- and antibody-based methods. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabm5164.
Wang H, Hanash S. Mass spectrometry based proteomics for absolute quantification of proteins from tumor cells. Methods. 2015;81:34–40.
Wang Y, Wang C, Zhu S, Zhang P, Liang H. Chinese surgical guidelines for obesity and type 2 diabetes (2019). Chin J Pract Surg. 2019;39:301–6.
Yang W, Wang C. Metabolic surgery needs stronger endorsement in Asian T2DM patients with low BMI. Obes Surg. 2022;32:212–3.
Diaz-Canestro C, Chen J, Liu Y, Han H, Wang Y, Honore E, et al. A machine-learning algorithm integrating baseline serum proteomic signatures predicts exercise responsiveness in overweight males with prediabetes. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4:100944.
Jones JM, Morrell JC, Gould SJ. Identification and characterization of HAOX1, HAOX2, and HAOX3, three human peroxisomal 2-hydroxy acid oxidases. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12590–7.
Howard TA, Misra DN, Grove M, Becich MJ, Shao JS, Gordon M, et al. Human gastric intrinsic factor expression is not restricted to parietal cells. J Anat. 1996;189:303–13.
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Leip EP, Wilson PW, et al. Impact of obesity on plasma natriuretic peptide levels. Circulation. 2004;109:594–600.
Reddy ST, Wadleigh DJ, Grijalva V, Ng C, Hama S, Gangopadhyay A, et al. Human paraoxonase-3 is an HDL-associated enzyme with biological activity similar to paraoxonase-1 protein but is not regulated by oxidized lipids. Arter Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:542–7.
Slunt HH, Thinakaran G, Von Koch C, Lo AC, Tanzi RE, Sisodia SS. Expression of a ubiquitous, cross-reactive homologue of the mouse beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP). J Biol Chem. 1994;269:2637–44.
Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao GX, Ding XS, Gautron L, Parameswara V, et al. Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPAR alpha-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab. 2007;5:415–25.
Jin L, Lin Z, Xu A. Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against atherosclerosis via fine-tuning the multiorgan crosstalk. Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40:22–31.
Enyindah-Asonye G, Li Y, Ruth JH, Spassov DS, Hebron KE, Zijlstra A, et al. CD318 is a ligand for CD6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:E6912–E6921.
Cardoso MS, Santos RF, Almeida S, Sa M, Perez-Cabezas B, Oliveira L, et al. Physical interactions with bacteria and protozoan parasites establish the scavenger receptor SSC4D as a broad-spectrum pattern recognition receptor. Front Immunol. 2021;12:760770.
Gu L, Zhu Y, Watari K, Lee M, Liu J, Perez S, et al. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is a nonenzymatic safety valve that curtails AKT activation to prevent insulin hyperresponsiveness. Cell Metab. 2023;35:1009–1021.e9.
Diaz-Canestro C, Xu A. Impact of different adipose depots on cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021;78:S30–S39.
Guilmeau S, Niot I, Laigneau JP, Devaud H, Petit V, Brousse N, et al. Decreased expression of Intestinal I- and L-FABP levels in rare human genetic lipid malabsorption syndromes. Histochem Cell Biol. 2007;128:115–23.
Kaplan LM, Spindel ER, Isselbacher KJ, Chin WW. Tissue-specific expression of the rat galanin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:1065–9.
Pan X, Lu T, Wu F, Jin L, Zhang Y, Shi L, et al. Circulating complement-C1q TNF-related protein 1 levels are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and are associated with insulin sensitivity in Chinese subjects. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e94478.
Juiz-Valina P, Pena-Bello L, Cordido M, Outeirino-Blanco E, Pertega S, Varela-Rodriguez B, et al. Altered GH-IGF-1 Axis in severe obese subjects is reversed after bariatric surgery-induced weight loss and related with low-grade chronic inflammation. J Clin Med 2020;9:2614.
Yau SW, Harcourt BE, Kao KT, Alexander EJ, Russo VC, Werther GA, et al. Serum IGFBP-2 levels are associated with reduced insulin sensitivity in obese children. Clin Obes. 2018;8:184–90.
Rahman A, Hammad MM, Al Khairi I, Cherian P, Al-Sabah R, Al-Mulla F, et al. Profiling of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) in Obesity and Their Association With Ox-LDL and Hs-CRP in Adolescents. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:727004.
Pratt DS, Kaplan MM. Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1266–71.
Chen H, Li X, Sun Y, Du Y, Wu S, Wu Y, et al. HAO1 negatively regulates liver macrophage activation via the NF-kappaB pathway in alcohol-associated liver disease. Cell Signal. 2022;99:110436.
Khan T, Kryza T, Lyons NJ, He Y, Hooper JD. The CDCP1 Signaling Hub: A Target for Cancer Detection and Therapeutic Intervention. Cancer Res. 2021;81:2259–69.
Magnusson L, Espes D, Casas R, Carlsson PO. Increased Plasma Levels of the Co-stimulatory Proteins CDCP1 and SLAMF1 in Patients With Autoimmune Endocrine Diseases. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1916.
Jia X, Song E, Liu Y, Chen J, Wan P, Hu Y, et al. Identification and multicentric validation of soluble CDCP1 as a robust serological biomarker for risk stratification of NASH in obese Chinese. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4:101257.
Padilla O, Pujana MA, Lopez-de la Iglesia A, Gimferrer I, Arman M, Vila JM, et al. Cloning of S4D-SRCRB, a new soluble member of the group B scavenger receptor cysteine-rich family (SRCR-SF) mapping to human chromosome 7q11.23. Immunogenetics. 2002;54:621–34.
Abbatini F, Rizzello M, Casella G, Alessandri G, Capoccia D, Leonetti F, et al. Long-term effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, and adjustable gastric banding on type 2 diabetes. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:1005–10.
Singhal R, Cardoso VR, Wiggins T, Super J, Ludwig C, Gkoutos GV, et al. 30-day morbidity and mortality of sleeve gastrectomy, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and one anastomosis gastric bypass: a propensity score-matched analysis of the GENEVA data. Int J Obes. 2022;46:750–7.
Funding
This work was supported by Hong Kong Research Grants Council/Area of Excellence (AoE/M/707-18) and General Research Fund (17117320 and 17121523); Shenzhen-Hong Kong-Macau Science and Technology Program (Category C, SGDX20210823103537031); Hong Kong Health and Medical Research Fund (08192316), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (82161138026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CD-C performed bioinformatics analysis, interpreted results, and wrote the manuscript. WY collected patients’ data. JC and KC performed bioinformatics analysis. HH, DL and JX performed Olink proteomics. CW and ES contributed to the acquisition of data. AX conceived and supervised the study and wrote and edited the manuscript. CD-C, and AX revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual contents.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Diaz-Canestro, C., Yang, W., Chen, J. et al. Association between plasma proteomic dynamic changes and metabolic outcomes in patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Int J Obes 49, 1745–1754 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01812-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-025-01812-7