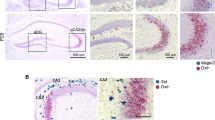
Abstract
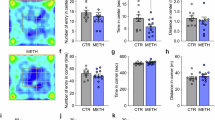
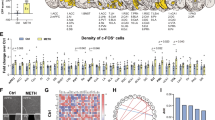
The present study was designated to investigate the effect of oxytocin (OXT) on the retrieval of methamphetamine (METH)-associated reward memories induced by drugs in mice and its underlying mechanisms related to adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) and memory engrams. The data showed that repeated hippocampal microinjections of OXT (1.25 and 2.5 μg) for 8 consecutive days significantly prevented the retrieval of METH-associated reward memories induced by drugs in a time-, dose- and receptor-dependent manner in mice. At the meanwhile, OXT was found to markedly elevate AHN levels, enhancing the proliferation, survival and maturation of newborn neurons by using NestinCreERT2::Rosa26-tdTomato mice and BrdU labeling. Notably, reduction or depletion of AHN by temozolomide (TMZ) or NestinCreERT2 mice combined with adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) (AAV-CAG-DIO-rtTA-EGFP and AAV-TRE-DTA) could attenuate the inhibition of OXT on the retrieval of METH-associated reward memories in mice. By using activity-dependent labeling strategy in mice, it was observed that the retrieval of METH-associated reward memories was mediated by activation of METH-associated memory engrams in the dentate gyrus (DG) region of the hippocampus. Repeated hippocampal microinjections of OXT effectively prevented the activation of these memory engrams, which could be abolished after reducing AHN by TMZ. In summary, this study revealed that OXT effectively prevented the retrieval of METH-associated reward memories induced by drugs in mice, which may be related to its enhancement on AHN as well as inhibition on METH-associated memory engrams in DG.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data needed for the conclusion in the present study were presented in the manuscript and Supplementary Materials. Additional data to this paper may be requested from the corresponding authors.
References
Morley KC, Cornish JL, Faingold A, Wood K, Haber PS. Pharmacotherapeutic agents in the treatment of methamphetamine dependence. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017;26:563–78.
Bauml KT, Trissl L. Selective memory retrieval can revive forgotten memories. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119:e2114377119.
Keyes PC, Adams EL, Chen Z, Bi L, Nachtrab G, Wang VJ, et al. Orchestrating opiate-associated memories in thalamic circuits. Neuron. 2020;107:1113–23 e1114.
Tsai ST, Liew HK, Li HM, Lin SZ, Chen SY. Harnessing neurogenesis and neuroplasticity with stem cell treatment for addictive disorders. Cell Transpl. 2019;28:1127–31.
Che X, Bai Y, Cai J, Liu Y, Li Y, Yin M, et al. Hippocampal neurogenesis interferes with extinction and reinstatement of methamphetamine-associated reward memory in mice. Neuropharmacology. 2021;196:108717.
Toni N, Schinder AF. Maturation and functional integration of new granule cells into the adult hippocampus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;8:a018903.
Toni N, Teng EM, Bushong EA, Aimone JB, Zhao C, Consiglio A, et al. Synapse formation on neurons born in the adult hippocampus. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:727–34.
Toni N, Laplagne DA, Zhao C, Lombardi G, Ribak CE, Gage FH, et al. Neurons born in the adult dentate gyrus form functional synapses with target cells. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:901–7.
Josselyn SA, Tonegawa S. Memory engrams: recalling the past and imagining the future. Science. 2020;367:eaaw4325.
Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, De Cristofaro A, Hsiang HL, et al. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science. 2014;344:598–602.
Roy DS, Muralidhar S, Smith LM, Tonegawa S. Silent memory engrams as the basis for retrograde amnesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:E9972–E9979.
Wang C, Yue H, Hu Z, Shen Y, Ma J, Li J, et al. Microglia mediate forgetting via complement-dependent synaptic elimination. Science. 2020;367:688–94.
Ko SY, Frankland PW. Neurogenesis-dependent transformation of hippocampal engrams. Neurosci Lett. 2021;762:136176.
Guskjolen A, Kenney JW, de la Parra J, Yeung BA, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW. Recovery of “Lost” infant memories in mice. Curr Biol. 2018;28:2283–90.e2283.
Lopez-Oropeza G, Duran P, Martinez-Canabal A. Maternal enrichment increases infantile spatial amnesia mediated by postnatal neurogenesis modulation. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022;16:971359.
Vasudevan K, Hassell JE Jr, Maren S. Hippocampal engrams and contextual memory. Adv Neurobiol. 2024;38:45–66.
Zhou Y, Zhu H, Liu Z, Chen X, Su X, Ma C, et al. A ventral CA1 to nucleus accumbens core engram circuit mediates conditioned place preference for cocaine. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:1986–99.
Trouche S, Perestenko PV, van de Ven GM, Bratley CT, McNamara CG, Campo-Urriza N, et al. Recoding a cocaine-place memory engram to a neutral engram in the hippocampus. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19:564–7.
Qi S, Tan SM, Wang R, Higginbotham JA, Ritchie JL, Ibarra CK, et al. Optogenetic inhibition of the dorsal hippocampus CA3 region during early-stage cocaine-memory reconsolidation disrupts subsequent context-induced cocaine seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47:1473–83.
Xia L, Nygard SK, Sobczak GG, Hourguettes NJ, Bruchas MR. Dorsal-CA1 hippocampal neuronal ensembles encode nicotine-reward contextual associations. Cell Rep. 2017;19:2143–56.
Dai Z, Liu Y, Nie L, Chen W, Xu X, Li Y, et al. Locus coeruleus input-modulated reactivation of dentate gyrus opioid-withdrawal engrams promotes extinction. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023;48:327–40.
Cincotta C, Ruesch E, Senne R, Ramirez S. Hippocampal fear engrams modulate ethanol-induced maladaptive contextual generalization in mice. Hippocampus. 2022;32:707–15.
Sharma SR, Gonda X, Dome P, Tarazi FI. What’s love got to do with it: role of oxytocin in trauma, attachment and resilience. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;214:107602.
Gulliver D, Werry E, Reekie TA, Katte TA, Jorgensen W, Kassiou M. Targeting the oxytocin system: new pharmacotherapeutic approaches. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019;40:22–37.
Yoon S, Kim YK. The Role of the oxytocin system in anxiety disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1191:103–20.
Georgiou P, Zanos P, Garcia-Carmona JA, Hourani S, Kitchen I, Laorden ML, et al. Methamphetamine abstinence induces changes in mu-opioid receptor, oxytocin and CRF systems: association with an anxiogenic phenotype. Neuropharmacology. 2016;105:520–32.
Zanos P, Wright SR, Georgiou P, Yoo JH, Ledent C, Hourani SM, et al. Chronic methamphetamine treatment induces oxytocin receptor up-regulation in the amygdala and hypothalamus via an adenosine A2A receptor-independent mechanism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014;119:72–79.
Everett N, Baracz S, Cornish J. Oxytocin treatment in the prelimbic cortex reduces relapse to methamphetamine-seeking and is associated with reduced activity in the rostral nucleus accumbens core. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2019;183:64–71.
Everett NA, McGregor IS, Baracz SJ, Cornish JL. The role of the vasopressin V1A receptor in oxytocin modulation of methamphetamine primed reinstatement. Neuropharmacology. 2018;133:1–11.
Everett NA, Baracz SJ, Cornish JL. The effect of chronic oxytocin treatment during abstinence from methamphetamine self-administration on incubation of craving, reinstatement, and anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020;45:597–605.
Hicks C, Cornish JL, Baracz SJ, Suraev A, McGregor IS. Adolescent pre-treatment with oxytocin protects against adult methamphetamine-seeking behavior in female rats. Addict Biol. 2016;21:304–15.
Cox BM, Bentzley BS, Regen-Tuero H, See RE, Reichel CM, Aston-Jones G. Oxytocin acts in nucleus accumbens to attenuate methamphetamine seeking and demand. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;81:949–58.
Han WY, Du P, Fu SY, Wang F, Song M, Wu CF, et al. Oxytocin via its receptor affects restraint stress-induced methamphetamine CPP reinstatement in mice: Involvement of the medial prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus glutamatergic system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014;119:80–87.
Baracz SJ, Rourke PI, Pardey MC, Hunt GE, McGregor IS, Cornish JL. Oxytocin directly administered into the nucleus accumbens core or subthalamic nucleus attenuates methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res. 2012;228:185–93.
Cai J, Che X, Xu T, Luo Y, Yin M, Lu X, et al. Repeated oxytocin treatment during abstinence inhibited context- or restraint stress-induced reinstatement of methamphetamine-conditioned place preference and promoted adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Exp Neurol. 2022;347:113907.
Che X, Cai J, Liu Y, Xu T, Yang J, Wu C. Oxytocin signaling in the treatment of drug addiction: therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;223:107820.
Fan XY, Yang JY, Dong YX, Hou Y, Liu S, Wu CF. Oxytocin inhibits methamphetamine-associated learning and memory alterations by regulating DNA methylation at the synaptophysin promoter. Addict Biol. 2020;25:e12697.
Qi J, Han WY, Yang JY, Wang LH, Dong YX, Wang F, et al. Oxytocin regulates changes of extracellular glutamate and GABA levels induced by methamphetamine in the mouse brain. Addict Biol. 2012;17:758–69.
Yang JY, Qi J, Han WY, Wang F, Wu CF. Inhibitory role of oxytocin in psychostimulant-induced psychological dependence and its effects on dopaminergic and glutaminergic transmission. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31:1071–4.
Qi J, Yang JY, Wang F, Zhao YN, Song M, Wu CF. Effects of oxytocin on methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference and the possible role of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex of mice in reinstatement. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56:856–65.
Qi J, Yang JY, Song M, Li Y, Wang F, Wu CF. Inhibition by oxytocin of methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity related to dopamine turnover in the mesolimbic region in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008;376:441–8.
Wang G, Wang W, Zhang Y, Gou X, Zhang Q, Huang Y, et al. Ethanol changes Nestin-promoter induced neural stem cells to disturb newborn dendritic spine remodeling in the hippocampus of mice. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19:416–24.
Han W, Wang F, Qi J, Wang F, Zhang L, Zhao S, et al. NMDA receptors in the medial prefrontal cortex and the dorsal hippocampus regulate methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity and extracellular amino acid release in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2012;232:44–52.
Leng H, Zhang X, Wang Q, Luan X, Sun X, Guo F, et al. Regulation of stress-induced gastric ulcers via central oxytocin and a potential mechanism through the VTA-NAc dopamine pathway. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019;31:e13655.
Zhang RR, Cui QY, Murai K, Lim YC, Smith ZD, Jin S, et al. Tet1 regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognition. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13:237–45.
Ladron de Guevara-Miranda D, Moreno-Fernandez RD, Gil-Rodriguez S, Rosell-Valle C, Estivill-Torrus G, Serrano A, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid-induced increase in adult hippocampal neurogenesis facilitates the forgetting of cocaine-contextual memory. Addict Biol. 2019;24:458–70.
Dogbevia GK, Robetamanith M, Sprengel R, Hasan MT. Flexible, AAV-equipped genetic modules for inducible control of gene expression in mammalian brain. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016;5:e309.
Hasan MT, Althammer F, Silva da Gouveia M, Goyon S, Eliava M, Lefevre A, et al. A fear memory engram and its plasticity in the hypothalamic oxytocin system. Neuron. 2019;103:133–46 e138.
Rotheneichner P, Romanelli P, Bieler L, Pagitsch S, Zaunmair P, Kreutzer C, et al. Tamoxifen activation of cre-recombinase has no persisting effects on adult neurogenesis or learning and anxiety. Front Neurosci. 2017;11:27.
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ. Paxinos and Franklin’s the mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 5th Edition. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press; 2019.
Zhang Z, Yang J, Liu C, Xie J, Qiu S, Yang X, et al. Pseudoginsenoside-F11 alleviates cognitive deficits and Alzheimer’s disease-type pathologies in SAMP8 mice. Pharmacol Res. 2019;139:512–23.
Zhu H, Pleil KE, Urban DJ, Moy SS, Kash TL, Roth BL. Chemogenetic inactivation of ventral hippocampal glutamatergic neurons disrupts consolidation of contextual fear memory. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39:1880–92.
Cuartero MI, de la Parra J, Perez-Ruiz A, Bravo-Ferrer I, Duran-Laforet V, Garcia-Culebras A, et al. Abolition of aberrant neurogenesis ameliorates cognitive impairment after stroke in mice. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:1536–50.
Chen BK, Murawski NJ, Cincotta C, McKissick O, Finkelstein A, Hamidi AB, et al. Artificially enhancing and suppressing hippocampus-mediated memories. Curr Biol. 2019;29:1885–94.e1884.
Yuan L, Sun S, Pan X, Zheng L, Li Y, Yang J, et al. Pseudoginsenoside-F11 improves long-term neurological function and promotes neurogenesis after transient cerebral ischemia in mice. Neurochem Int. 2020;133:104586.
Marco A, Meharena HS, Dileep V, Raju RM, Davila-Velderrain J, Zhang AL, et al. Mapping the epigenomic and transcriptomic interplay during memory formation and recall in the hippocampal engram ensemble. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:1606–17.
Lin YT, Chen CC, Huang CC, Nishimori K, Hsu KS. Oxytocin stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis via oxytocin receptor expressed in CA3 pyramidal neurons. Nat Commun. 2017;8:537.
Kempermann G, Song H, Gage FH. Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Hippocampus. 2023;33:269–70.
Mishra R, Phan T, Kumar P, Morrissey Z, Gupta M, Hollands C, et al. Augmenting neurogenesis rescues memory impairments in Alzheimer’s disease by restoring the memory-storing neurons. J Exp Med. 2022;219:e20220391.
Chen R, Wang Z, Lin Q, Hou X, Jiang Y, Le Q, et al. Destabilization of fear memory by Rac1-driven engram-microglia communication in hippocampus. Brain Behav Immun. 2024;119:621–36.
Ramirez S, Liu X, MacDonald CJ, Moffa A, Zhou J, Redondo RL, et al. Activating positive memory engrams suppresses depression-like behaviour. Nature. 2015;522:335–9.
Galinato MH, Takashima Y, Fannon MJ, Quach LW, Morales Silva RJ, Mysore KK, et al. Neurogenesis during abstinence is necessary for context-driven methamphetamine-related memory. J Neurosci. 2018;38:2029–42.
Calpe-Lopez C, Garcia-Pardo MP, Aguilar MA. Cannabidiol treatment might promote resilience to cocaine and methamphetamine use disorders: a review of possible mechanisms. Molecules. 2019;24:2583.
Jiang C, Xu Y, Zhong J, Wu J, He J, Xu W, et al. Chloral hydrate alters brain activation induced by methamphetamine-associated cue and prevents relapse. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:934167.
Xue YX, Luo YX, Wu P, Shi HS, Xue LF, Chen C, et al. A memory retrieval-extinction procedure to prevent drug craving and relapse. Science. 2012;336:241–5.
Cox BM, Young AB, See RE, Reichel CM. Sex differences in methamphetamine seeking in rats: impact of oxytocin. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013;38:2343–53.
Qian H, Shang Q, Liang M, Gao B, Xiao J, Wang J, et al. MicroRNA-31-3p/RhoA signaling in the dorsal hippocampus modulates methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology. 2021;238:3207–19.
Mohammadi M, Eskandari K, Azizbeigi R, Haghparast A. The inhibitory effect of cannabidiol on the rewarding properties of methamphetamine in part mediates by interacting with the hippocampal D1-like dopamine receptors. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2023;126:110778.
Epp JR, Silva Mera R, Kohler S, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW. Neurogenesis-mediated forgetting minimizes proactive interference. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10838.
Mandyam CD, Wee S, Crawford EF, Eisch AJ, Richardson HN, Koob GF. Varied access to intravenous methamphetamine self-administration differentially alters adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64:958–65.
Razavi Y, Keyhanfar F, Haghparast A, Shabani R, Mehdizadeh M. Cannabidiol promotes neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus during an abstinence period in rats following chronic exposure to methamphetamine. Metab Brain Dis. 2021;36:1381–90.
Castilla-Ortega E, Blanco E, Serrano A, Ladron de Guevara-Miranda D, Pedraz M, Estivill-Torrus G, et al. Pharmacological reduction of adult hippocampal neurogenesis modifies functional brain circuits in mice exposed to a cocaine conditioned place preference paradigm. Addict Biol. 2016;21:575–88.
Ishikawa R, Fukushima H, Frankland PW, Kida S. Hippocampal neurogenesis enhancers promote forgetting of remote fear memory after hippocampal reactivation by retrieval. Elife. 2016;5:e17464.
Raj B, Farrell JA, Liu J, El Kholtei J, Carte AN, Navajas Acedo J, et al. Emergence of neuronal diversity during vertebrate brain development. Neuron. 2020;108:1058–74.e1056.
Leuner B, Caponiti JM, Gould E. Oxytocin stimulates adult neurogenesis even under conditions of stress and elevated glucocorticoids. Hippocampus. 2012;22:861–8.
Kee N, Teixeira CM, Wang AH, Frankland PW. Preferential incorporation of adult-generated granule cells into spatial memory networks in the dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:355–62.
Piatti VC, Davies-Sala MG, Esposito MS, Mongiat LA, Trinchero MF, Schinder AF. The timing for neuronal maturation in the adult hippocampus is modulated by local network activity. J Neurosci. 2011;31:7715–28.
Song J, Sun J, Moss J, Wen Z, Sun GJ, Hsu D, et al. Parvalbumin interneurons mediate neuronal circuitry-neurogenesis coupling in the adult hippocampus. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16:1728–30.
Matos MR, Visser E, Kramvis I, van der Loo RJ, Gebuis T, Zalm R, et al. Memory strength gates the involvement of a CREB-dependent cortical fear engram in remote memory. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2315.
Mu Y, Gage FH. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2011;6:85.
Frankland PW, Kohler S, Josselyn SA. Hippocampal neurogenesis and forgetting. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36:497–503.
Zhou Y, Yan E, Cheng D, Zhu H, Liu Z, Chen X, et al. The projection from ventral CA1, not prefrontal cortex, to nucleus accumbens core mediates recent memory retrieval of cocaine-conditioned place preference. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020;14:558074.
Legault M, Rompre PP, Wise RA. Chemical stimulation of the ventral hippocampus elevates nucleus accumbens dopamine by activating dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci. 2000;20:1635–42.
Todd CL, Grace AA. Modulation of ventral tegmental area dopamine cell activity by the ventral subiculum and entorhinal cortex. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;877:688–90.
Acknowledgements
The present research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82273916) from Jingyu Yang, the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Fund Project (82204373), the Youth Scientific Research Project of Educational Commission of Liaoning Province (JYTQN2023320), the General Project of Liaoning Provincial Department of Science and Technology (2024-MSLH-427) and the Youqing Support Project of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University (YQ202201) from Xiaohang Che. The graphic abstract was created with the help of Adobe Illustrator CS6 software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CJL and CXH contributed equally to this work. CJL, CXH, LYT, YJY and WCF contributed to the conception and design of the present study. CJL, CXH, DYL, GZK, YMX, LXC, ZWZ, ANN and BYJ performed the experiment. LXL, LYC and XTY performed the statistical analysis of the experimental data. CJL and CXH wrote the first draft of the manuscript. DYL and YMX wrote the sections of the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods performed in this study were conducted in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Ethical approval was obtained from the Experimental Animal Research Committee of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University and performed in accordance to the Guidelines for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Registration no. SYPU-IACUC-GZR2020-04.13-110). The study does not include human participants. The study does not include data from humans.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, J., Che, X., Deng, Y. et al. Oxytocin attenuates the retrieval of methamphetamine-associated reward memories by enhancing adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Mol Psychiatry 30, 5664–5679 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03222-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03222-7