Abstract
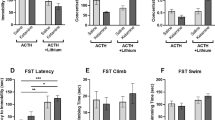
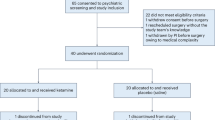
The N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist ketamine is associated with rapid but transient antidepressant effects in patients with treatment resistant unipolar depression (TRD). Based on work suggesting that ketamine and lithium may share overlapping mechanisms of action, we tested lithium compared to placebo as a continuation strategy following ketamine in subjects with TRD. Participants who met all eligibility criteria and showed at least an initial partial response to a single intravenous infusion of ketamine 0.5 mg/kg were randomized under double-blind conditions to lithium or matching placebo before receiving an additional three infusions of ketamine. Subsequent to the ketamine treatments, participants remained on lithium or placebo during a double-blind continuation phase. The primary study outcome was depression severity as measured by the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale compared between the two groups at Study Day 28, which occurred ~2 weeks following the final ketamine of four infusions. Forty-seven participants with TRD were enrolled in the study and underwent an initial ketamine infusion, of whom 34 participants were deemed to have at least a partial antidepressant response and were eligible for randomization. Comparison between treatment with daily oral lithium (n = 18) or matching placebo (n = 16) at the primary outcome showed no difference in depression severity between groups (t32 = 0.11, p = 0.91, 95% CI [−7.87, 8.76]). There was no difference between lithium and placebo in continuing the acute antidepressant response to ketamine. The identification of a safe and effective strategy for preventing depression relapse following an acute course of ketamine treatment remains an important goal for future studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ferrari AJ, Charlson FJ, Norman RE, Patten SB, Freedman G, Murray CJL, et al. Burden of depressive disorders by country, sex, age, and year: findings from the global burden of disease study 2010. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001547.
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1905–17.
Cipriani A, Geddes JR, Furukawa TA, Barbui C. Metareview on short-term effectiveness and safety of antidepressants for depression: an evidence-based approach to inform clinical practice. Can J Psychiatry. 2007;52:553–62.
Cuffel BJ, Azocar F, Tomlin M, Greenfield SF, Busch AB, Croghan TW. Remission, residual symptoms, and nonresponse in the usual treatment of major depression in managed clinical practice. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64:397–402.
Greenberg PE, Fournier A-A, Sisitsky T, Pike CT, Kessler RC. The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2005 and 2010). J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:155–62.
Insel TR, Scolnick EM. Cure therapeutics and strategic prevention: raising the bar for mental health research. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11:11–17.
Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, et al. Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;47:351–4.
Mathew SJ, Shah A, Lapidus K, Clark C, Jarun N, Ostermeyer B, et al. Ketamine for treatment-resistant unipolar depression: current evidence. CNS Drugs. 2012;26:189–204.
Caddy C, Amit BH, McCloud TL, Rendell JM, Furukawa TA, McShane R, et al. Ketamine and other glutamate receptor modulators for depression in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015;9:CD011612.
Zarate CA, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA, et al. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:856–64.
Murrough JW, Iosifescu DV, Chang LC, Al Jurdi RK, Green CE, Perez AM, et al. Antidepressant efficacy of ketamine in treatment-resistant major depression: a two-site randomized controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170:1134–42.
Murrough JW, Perez AM, Pillemer S, Stern J, Parides MK, aan het Rot M, et al. Rapid and longer-term antidepressant effects of repeated ketamine infusions in treatment-resistant major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;74:250–6.
Bschor T. Lithium in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Drugs. 2014;74:855–62.
Klein PS, Melton DA. A molecular mechanism for the effect of lithium on development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:8455–9.
Beurel E, Grieco SF, Jope RS. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;148:114–31.
Li N, Lee B, Liu R-J, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M, et al. mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science. 2010;329:959–64.
Beurel E, Song L, Jope RS. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 is necessary for the rapid antidepressant effect of ketamine in mice. Mol Psychiatry. 2011;16:1068–70.
Liu R-J, Fuchikami M, Dwyer JM, Lepack AE, Duman RS, Aghajanian GK. GSK-3 inhibition potentiates the synaptogenic and antidepressant-like effects of subthreshold doses of ketamine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38:2268–77.
Levin B. The futility study—progress over the last decade. Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;45:69–75.
Lam RW, Kennedy SH, Grigoriadis S, McIntyre RS, Milev R, Ramasubbu R, et al. Canadian network for mood and anxiety treatments (CANMAT) clinical guidelines for the management of major depressive disorder in adults. III. Pharmacotherapy. J Affect Disord. 2009;117 Suppl 1:S26–43.
Kellner CH, Knapp RG, Petrides G, Rummans TA, Husain MM, Rasmussen K, et al. Continuation electroconvulsive therapy vs pharmacotherapy for relapse prevention in major depression: a multisite study from the Consortium for Research in Electroconvulsive Therapy (CORE). Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:1337–44.
Sackeim HA, Haskett RF, Mulsant BH, Thase ME, Mann JJ, Pettinati HM, et al. Continuation pharmacotherapy in the prevention of relapse following electroconvulsive therapy: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc. 2001;285:1299–307.
Kantrowitz JT, Halberstam B, Gangwisch J. Single-dose ketamine followed by daily D-Cycloserine in treatment-resistant bipolar depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76:737–8.
Wilkinson ST, Wright D, Fasula MK, Fenton L, Griepp M, Ostroff RB, et al. Cognitive behavior therapy may sustain antidepressant effects of intravenous ketamine in treatment-resistant depression. Psychother Psychosom. 2017;86:162–7.
Mathew SJ, Murrough JW, aan het Rot M, Collins KA, Reich DL, Charney DS. Riluzole for relapse prevention following intravenous ketamine in treatment-resistant depression: a pilot randomized, placebo-controlled continuation trial. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13:71–82.
Ibrahim L, Diazgranados N, Franco-Chaves J, Brutsche N, Henter ID, Kronstein P, et al. Course of improvement in depressive symptoms to a single intravenous infusion of ketamine vs add-on riluzole: results from a 4-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37:1526–33.
Daly EJ, Singh JB, Fedgchin M, Cooper K, Lim P, Shelton RC, et al. Efficacy and safety of intranasal esketamine adjunctive to oral antidepressant therapy in treatment-resistant depression: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:139–48.
Bauer M, Dopfmer S. Lithium augmentation in treatment-resistant depression: meta-analysis of placebo-controlled studies. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1999;19:427–34.
Nierenberg AA, Fava M, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Thase ME, McGrath PJ, et al. A comparison of lithium and T(3) augmentation following two failed medication treatments for depression: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1519–30. quiz 1665
Gelenberg A, Freeman C, Markowitz J, Rosenbaum J, Thase M, Trivedi M, et al. Treatment of Patients With Major Depressive Disorder. Practice Guideline. 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costi, S., Soleimani, L., Glasgow, A. et al. Lithium continuation therapy following ketamine in patients with treatment resistant unipolar depression: a randomized controlled trial. Neuropsychopharmacol. 44, 1812–1819 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0365-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-019-0365-0
This article is cited by
-
The why, when, where, how, and so what of so-called rapidly acting antidepressants
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Non-improvement predicts subsequent non-response to repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for depression: a re-analysis of a 2-week open-label study in patients with unipolar and bipolar depression
Translational Psychiatry (2024)
-
Lithium augmentation of ketamine increases insulin signaling and antidepressant-like active stress coping in a rodent model of treatment-resistant depression
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Strategies to Prolong Ketamine’s Efficacy in Adults with Treatment-Resistant Depression
Advances in Therapy (2021)
-
Efficacy of ketamine for major depressive episodes at 2, 4, and 6-weeks post-treatment: A meta-analysis
Psychopharmacology (2021)