Abstract
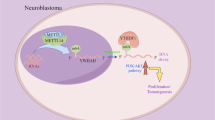
Hepatoblastoma (HB) is a rare but predominant liver cancer in children, with few treatment choices in advanced stages. YWHAE is closely related to several human diseases and acts as a molecular scaffold for malignant transformation. However, whether YWHAE promotes HB development remains unknown. Conducting RNA and m6A sequencing on HB tissues, we found that YWHAE was upregulated and modified by N6-methyadenosine. Functionally, YWHAE promoted proliferation and inhibited cell death in HB by in vitro and in vivo studies. Mechanistically, METTL3-dependent m6A modification activated YWHAE mRNA expression, and the m6A reader IGF2BP2 recognized and bound to the m6A site on YWHAE mRNA, thereby enhancing the mRNA stability of YWHAE. Interestingly, RNA sequencing revealed that YWHAE knockdown was involved in regulating ferroptosis of HB cells by mediating SLC7A11 expression. Moreover, knockdown of YWHAE significantly increased the levels of lipid ROS and peroxides in HB cells, promoting the susceptibility of HB cells to ferroptosis. In summary, these findings illuminated the role of YWHAE in HB progression and uncovered its relevance to ferroptosis as a new therapeutic target for HB.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Czauderna P, Lopez-Terrada D, Hiyama E, Haberle B, Malogolowkin MH, Meyers RL. Hepatoblastoma state of the art: pathology, genetics, risk stratification, and chemotherapy. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014;26:19–28.
Trobaugh-Lotrario AD, Katzenstein HM. Chemotherapeutic approaches for newly diagnosed hepatoblastoma: past, present, and future strategies. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;59:809–12.
Zhang Y, Solinas A, Cairo S, Evert M, Chen X, Calvisi DF. Molecular Mechanisms of Hepatoblastoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2021;41:28–41.
Mhawech P. 14-3-3 proteins-an update. Cell Res. 2005;15:228–36.
Obsil T, Obsilova V. Structural basis of 14-3-3 protein functions. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011;22:663–72.
Morrison DK. The 14-3-3 proteins: integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and cancer development. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19:16–23.
Liu J, Cao S, Ding G, Wang B, Li Y, Zhao Y, et al. The role of 14-3-3 proteins in cell signalling pathways and virus infection. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:4173–82.
Li X, Wang C, Wang S, Hu Y, Jin S, Liu O, et al. YWHAE as an HE4 interacting protein can influence the malignant behaviour of ovarian cancer by regulating the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:302.
Xu Y, Fulciniti M, Samur MK, Ho M, Deng S, Liu L, et al. YWHAE/14-3-3epsilon expression impacts the protein load, contributing to proteasome inhibitor sensitivity in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2020;136:468–79.
Margariti A, Zampetaki A, Xiao Q, Zhou B, Karamariti E, Martin D, et al. Histone deacetylase 7 controls endothelial cell growth through modulation of beta-catenin. Circ Res. 2010;106:1202–11.
Ko BS, Chang TC, Hsu C, Chen YC, Shen TL, Chen SC, et al. Overexpression of 14-3-3epsilon predicts tumour metastasis and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Histopathology. 2011;58:705–11.
Fu Y, Dominissini D, Rechavi G, He C. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m(6)A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:293–306.
Jiang X, Liu B, Nie Z, Duan L, Xiong Q, Jin Z, et al. The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:74.
Zaccara S, Ries RJ, Jaffrey SR. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:608–24.
Wang T, Kong S, Tao M, Ju S. The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in Cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:88.
Li B, Jiang J, Assaraf YG, Xiao H, Chen ZS, Huang C. Surmounting cancer drug resistance: New insights from the perspective of N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modification. Drug Resist Updat. 2020;53:100720.
Song P, Tayier S, Cai Z, Jia G. RNA methylation in mammalian development and cancer. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37:811–31.
Liu L, Wang J, Sun G, Wu Q, Ma J, Zhang X, et al. m(6)A mRNA methylation regulates CTNNB1 to promote the proliferation of hepatoblastoma. Mol cancer. 2019;18:188.
Liu L, He J, Sun G, Huang N, Bian Z, Xu C, et al. The N6-methyladenosine modification enhances ferroptosis resistance through inhibiting SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation in hepatoblastoma. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12:e778.
Cui X, Wang Z, Li J, Zhu J, Ren Z, Zhang D, et al. Cross talk between RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 and miR-186 regulates hepatoblastoma progression through Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2020;53:e12768.
Koppula P, Zhang Y, Zhuang L, Gan B. Amino acid transporter SLC7A11/xCT at the crossroads of regulating redox homeostasis and nutrient dependency of cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018;38:12.
Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhang R, Wang F, Wang T, Jiao Y. The role of erastin in ferroptosis and its prospects in cancer therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:5429–41.
Cao JY, Dixon SJ. Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:2195–209.
Litten JB, Tomlinson GE. Liver tumors in children. Oncologist. 2008;13:812–20.
Tomlinson GE, Kappler R. Genetics and epigenetics of hepatoblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;59:785–92.
Fu H, Subramanian RR, Masters SC. 14-3-3 proteins: structure, function, and regulation. Annu Rev Pharm Toxicol. 2000;40:617–47.
Obsil T. 14-3-3 proteins-a family of universal scaffolds and regulators. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011;22:661–2.
Eichenmuller M, Trippel F, Kreuder M, Beck A, Schwarzmayr T, Haberle B, et al. The genomic landscape of hepatoblastoma and their progenies with HCC-like features. J Hepatol. 2014;61:1312–20.
Zhao Z, Meng J, Su R, Zhang J, Chen J, Ma X, et al. Epitranscriptomics in liver disease: Basic concepts and therapeutic potential. J Hepatol. 2020;73:664–79.
Sun T, Wu R, Ming L. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108613.
Wang J, Chen L, Qiang P. The role of IGF2BP2, an m6A reader gene, in human metabolic diseases and cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:99.
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol cell Biol. 2021;22:266–82.
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D. Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 2021;17:2054–81.
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao N, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:88.
Koppula P, Zhuang L, Gan B. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein cell. 2021;12:599–620.
Wang X, Chen Y, Wang X, Tian H, Wang Y, Jin J, et al. Stem Cell Factor SOX2 Confers Ferroptosis Resistance in Lung Cancer via Upregulation of SLC7A11. Cancer Res. 2021;81:5217–29.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Clinical Specialty Project (the construction of multidisciplinary cooperative diagnosis and treatment system for children’s cancer guided by improving clinical service capacity, 2021), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81871727, 82072375, 82172357, 82293662, 82300037), Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (grant number 23Y11907300). We acknowledge the support of all other involved investigators and participating practitioners for their valued contributions. We are indebted to all the patients and their parents and/or guardians who participated in this study. We would like to express our gratitude to EditSprings (www.editsprings.cn) for the expert linguistic services provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ and JW drafted the initial manuscript and performed most of the experiments. LY and TF assisted with the experiment and critical reagent preparation. HL, JM, HF, and LL provided technical help with tissue array analysis. MZ performed the bioinformatics analysis. QP and SG contributed to the experimental design, guidance, and quality control. YS, HG, CX and LZ conceived the project, analyzed the data, and finalized the figures. DJ, MX, QP and SG critically reviewed and revised the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Animal studies were conducted under the institutional animal care and use committee of Shanghai Children’s Medical Center (SCMC-LAWEC-2022-041). Research involving human subjects received approval from the Institutional Review Board of Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, which is affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in China (SCMCIRB-K2023006-1). Prior to enrolling in the study, informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wang, J., Yang, L. et al. N6-methyadenosine-modified YWHAE mRNA promotes proliferation and inhibits ferroptosis in hepatoblastoma by mediating SLC7A11 expression. Oncogene 44, 1634–1645 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03334-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03334-y