Abstract
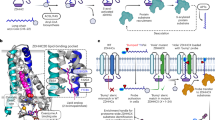
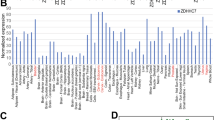
S-palmitoylation mediated by the zinc finger aspartate-histidine-histidine-cysteine (ZDHHC) protein acyltransferases (PATs) modulates protein localization, stability, interactions and signal transduction. In this study, we screened the 23 ZDHHC family members and identified ZDHHC20 as one of the major PATs involved in the DNA damage response (DDR). Inhibition of ZDHHC20 expression impaired cellular DNA damage repair capabilities. Meanwhile, data from ZDHHC20 knock-out mice, human tumor cell lines and xenograft tumor models showed that knock-out of ZDHHC20 significantly enhanced radiosensitivity. Using palmitoylation label-free quantitative proteomics, we found that over 600 proteins were palmitoylated in a ZDHHC20-dependent manner. Via the acyl-biotin exchange (ABE) assay, we revealed that KRAB-associated protein 1 (KAP1), also known as tripartite motif-containing protein 28 (Trim28), was palmitoylated at cysteine 232 by ZDHHC20. Notably, ZDHHC20-dependent KAP1 palmitoylation increased the chromatin binding of phosphorylated KAP1, which facilitated chromatin accessibility and subsequent recruitment of the DDR components BRCA1 and 53BP1. Further, we demonstrated that Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM)-dependent phosphorylation of ZDHHC20 at serine 339 increased KAP1 palmitoylation. Taken together, our findings elucidate the role and mechanism of the ATM-ZDHHC20-KAP1 axis in the DDR and provide a novel sensitizing strategy for radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data generated in this study are available within the article and supplementary files.
References
Groelly FJ, Fawkes M, Dagg RA, Blackford AN, Tarsounas M. Targeting DNA damage response pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023;23:78–94.
Chang HHY, Pannunzio NR, Adachi N, Lieber MR. Non-homologous DNA end joining and alternative pathways to double-strand break repair. Nat Rev Mol cell Biol. 2017;18:495–506.
Pilié PG, Tang C, Mills GB, Yap TA. State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:81–104.
Helleday T, Petermann E, Lundin C, Hodgson B, Sharma RA. DNA repair pathways as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:193–204.
Nickoloff JA. Toward greater precision in cancer radiotherapy. Cancer Res. 2021;81:3156–7.
Xiao M, Fried JS, Ma J, Su Y, Boohaker RJ, Zeng Q, et al. A disease-relevant mutation of SPOP highlights functional significance of ATM-mediated DNA damage response. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:17.
Yang C, Tang X, Guo X, Niikura Y, Kitagawa K, Cui K, et al. Aurora-B mediated ATM serine 1403 phosphorylation is required for mitotic ATM activation and the spindle checkpoint. Mol cell. 2011;44:597–608.
Boohaker RJ, Cui X, Stackhouse M, Xu B. ATM-mediated Snail Serine 100 phosphorylation regulates cellular radiosensitivity. Radiother Oncol. 2013;108:403–8.
Weitering TJ, Takada S, Weemaes CMR, van Schouwenburg PA, van der Burg M. ATM: translating the DNA damage response to adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2021;42:350–65.
Matsuoka S, Ballif BA, Smogorzewska A, McDonald ER 3rd, Hurov KE, Luo J, et al. ATM and ATR substrate analysis reveals extensive protein networks responsive to DNA damage. 2007;316:1160–6.
Dantuma NP, van Attikum H. Spatiotemporal regulation of posttranslational modifications in the DNA damage response. EMBO J. 2016;35:6–23.
Yu F, Wei J, Cui X, Yu C, Ni W, Bungert J, et al. Post-translational modification of RNA m6A demethylase ALKBH5 regulates ROS-induced DNA damage response. Nucleic acids Res. 2021;49:5779–97.
Liu Z, Liu C, Fan C, Li R, Zhang S, Liu J, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX2 fosters ferroptosis resistance via suppressing NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in non-small cell lung cancer. Drug Resistance Updat. 2024;77:101154.
Liu Z, Xiao M, Mo Y, Wang H, Han Y, Zhao X, et al. Emerging roles of protein palmitoylation and its modifying enzymes in cancer cell signal transduction and cancer therapy. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:3447–57.
Wang L, Cai J, Zhao X, Ma L, Zeng P, Zhou L, et al. Palmitoylation prevents sustained inflammation by limiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation through chaperone-mediated autophagy. Mol Cell. 2023;83:281–97.e10.
Zhang M, Zhou L, Xu Y, Yang M, Xu Y, Komaniecki GP, et al. A STAT3 palmitoylation cycle promotes T(H)17 differentiation and colitis. Nature. 2020;586:434–9.
Lu Y, Zheng Y, Coyaud É, Zhang C, Selvabaskaran A, Yu Y, et al. Palmitoylation of NOD1 and NOD2 is required for bacterial sensing. 2019;366:460–7.
Chen S, Zhu B, Yin C, Liu W, Han C, Chen B, et al. Palmitoylation-dependent activation of MC1R prevents melanomagenesis. Nature. 2017;549:399–403.
Runkle KB, Kharbanda A, Stypulkowski E, Cao XJ, Wang W, Garcia BA, et al. Inhibition of DHHC20-mediated EGFR palmitoylation creates a dependence on EGFR signaling. Mol Cell. 2016;62:385–96.
Yao H, Lan J, Li C, Shi H, Brosseau JP, Wang H, et al. Inhibiting PD-L1 palmitoylation enhances T-cell immune responses against tumours. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019;3:306–17.
Fan X, Sun S, Yang H, Ma H, Zhao C, Niu W, et al. SETD2 palmitoylation mediated by ZDHHC16 in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated glioblastoma promotes ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage. Int J Radiat Oncol, Biol, Phys. 2022;113:648–60.
Sudo H, Tsuji AB, Sugyo A, Imai T, Saga T, Harada YN. A loss of function screen identifies nine new radiation susceptibility genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;364:695–701.
Azizi SA, Delalande C, Lan T, Qiu T, Dickinson BC. Charting the chemical space of acrylamide-based inhibitors of zDHHC20. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022;13:1648–54.
F SM, Abrami L, Bracq L, Panyain N, Mercier V, Kunz B, et al. SARS-CoV-2 hijacks a cell damage response, which induces transcription of a more efficient Spike S-acyltransferase. Nat Commun. 2023;14:7302.
Carreras-Sureda A, Abrami L, Ji-Hee K, Wang WA, Henry C, Frieden M, et al. S-acylation by ZDHHC20 targets ORAI1 channels to lipid rafts for efficient Ca(2+) signaling by Jurkat T cell receptors at the immune synapse. eLife. 2021;10:e72051.
Kharbanda A, Walter DM, Gudiel AA, Schek N, Feldser DM, Witze ES. Blocking EGFR palmitoylation suppresses PI3K signaling and mutant KRAS lung tumorigenesis. Sci Signal. 2020;13:eaax2364.
Mo Y, Han Y, Chen Y, Fu C, Li Q, Liu Z, et al. ZDHHC20 mediated S-palmitoylation of fatty acid synthase (FASN) promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol cancer. 2024;23:274.
Bennardo N, Cheng A, Huang N, Stark JM. Alternative-NHEJ is a mechanistically distinct pathway of mammalian chromosome break repair. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000110.
Stark JM, Pierce AJ, Oh J, Pastink A, Jasin M. Genetic steps of mammalian homologous repair with distinct mutagenic consequences. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:9305–16.
Kozar K, Ciemerych MA, Rebel VI, Shigematsu H, Zagozdzon A, Sicinska E, et al. Mouse development and cell proliferation in the absence of D-cyclins. Cell.2004;118:477–91.
Xiao M, Zhang S, Liu Z, Mo Y, Wang H, Zhao X, et al. Dual-functional significance of ATM-mediated phosphorylation of spindle assembly checkpoint component Bub3 in mitosis and the DNA damage response. J Biol Chem. 2022;298:101632.
Xiao M, Li X, Su Y, Liu Z, Han Y, Wang S, et al. Kinetochore protein MAD1 participates in the DNA damage response through ataxia-telangiectasia mutated kinase-mediated phosphorylation and enhanced interaction with KU80. Cancer Biol Med. 2020;17:640–51.
Chen Y, Xiao M, Mo Y, Ma J, Han Y, Li Q, et al. Nuclear porcupine mediates XRCC6/Ku70 S-palmitoylation in the DNA damage response. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024;13:109.
Ziv Y, Bielopolski D, Galanty Y, Lukas C, Taya Y, Schultz DC, et al. Chromatin relaxation in response to DNA double-strand breaks is modulated by a novel ATM- and KAP-1 dependent pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:870–6.
Ma J, Benitez JA, Li J, Miki S, Ponte de Albuquerque C, Galatro T, et al. Inhibition of Nuclear PTEN Tyrosine Phosphorylation Enhances Glioma Radiation Sensitivity through Attenuated DNA Repair. Cancer cell. 2019;36:690–1.
Ning W, Jiang P, Guo Y, Wang C, Tan X, Zhang W, et al. GPS-Palm: a deep learning-based graphic presentation system for the prediction of S-palmitoylation sites in proteins. Brief Bioinforma. 2021;22:1836–47.
Czerwińska P, Mazurek S, Wiznerowicz M. The complexity of TRIM28 contribution to cancer. J Biomed Sci. 2017;24:63.
Noon AT, Shibata A, Rief N, Löbrich M, Stewart GS, Jeggo PA, et al. 53BP1-dependent robust localized KAP-1 phosphorylation is essential for heterochromatic DNA double-strand break repair. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:177–84.
Bacon CW, Challa A, Hyder U, Shukla A, Borkar AN, Bayo J, et al. KAP1 is a chromatin reader that couples steps of RNA polymerase II transcription to sustain oncogenic programs. Mol Cell. 2020;78:1133–51.e14.
Wang D, Zhou J, Liu X, Lu D, Shen C, Du Y, et al. Methylation of SUV39H1 by SET7/9 results in heterochromatin relaxation and genome instability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:5516–21.
Toiber D, Erdel F, Bouazoune K, Silberman DM, Zhong L, Mulligan P, et al. SIRT6 recruits SNF2H to DNA break sites, preventing genomic instability through chromatin remodeling. Mol cell. 2013;51:454–68.
Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46.
Wang Y, Cheng S, Fleishman JS, Chen J, Tang H, Chen ZS, et al. Targeting anoikis resistance as a strategy for cancer therapy. Drug Resistance Updat. 2024;75:101099.
Wei M, Huang X, Liao L, Tian Y, Zheng X. SENP1 decreases RNF168 phase separation to promote DNA damage repair and drug resistance in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83:2908–23.
Lu CT, Huang KY, Su MG, Lee TY, Bretaña NA, Chang WC, et al. DbPTM 3.0: an informative resource for investigating substrate site specificity and functional association of protein post-translational modifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D295–305.
Zhu G, Jin L, Sun W, Wang S, Liu N. Proteomics of post-translational modifications in colorectal cancer: Discovery of new biomarkers. Biochimica et Biophysica acta Rev cancer. 2022;1877:188735.
Miao C, Huang Y, Zhang C, Wang X, Wang B, Zhou X, et al. Post-translational modifications in drug resistance. Drug Resistance updat. 2025;78:101173.
Ocasio CA, Baggelaar MP, Sipthorp J, Losada de la Lastra A, Tavares M, Volaric J, et al. A palmitoyl transferase chemical-genetic system to map ZDHHC-specific S-acylation. Nat Biotechnol. 2024;42:1548–58.
Bayona-Feliu A, Herrera-Moyano E, Badra-Fajardo N, Galván-Femenía I, Soler-Oliva ME, Aguilera A. The chromatin network helps prevent cancer-associated mutagenesis at transcription-replication conflicts. Nat Commun. 2023;14:6890.
Xiao L, Parolia A, Qiao Y, Bawa P, Eyunni S, Mannan R, et al. Targeting SWI/SNF ATPases in enhancer-addicted prostate cancer. Nature. 2022;601:434–9.
Chakraborty R, Ostriker AC, Xie Y, Dave JM, Gamez-Mendez A, Chatterjee P, et al. Histone Acetyltransferases p300 and CBP Coordinate Distinct Chromatin Remodeling Programs in Vascular Smooth Muscle Plasticity. Circulation. 2022;145:1720–37.
Torchy MP, Hamiche A, Klaholz BP. Structure and function insights into the NuRD chromatin remodeling complex. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72:2491–507.
Min JN, Tian Y, Xiao Y, Wu L, Li L, Chang S. The mINO80 chromatin remodeling complex is required for efficient telomere replication and maintenance of genome stability. Cell Res. 2013;23:1396–413.
Lee DH, Goodarzi AA, Adelmant GO, Pan Y, Jeggo PA, Marto JA, et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis reveals that PP4 dephosphorylates KAP-1 impacting the DNA damage response. EMBO J. 2012;31:2403–15.
Fontana GA, Hess D, Reinert JK, Mattarocci S, Falquet B, Klein D, et al. Rif1 S-acylation mediates DNA double-strand break repair at the inner nuclear membrane. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2535.
Kuo CY, Li X, Stark JM, Shih HM, Ann DK. RNF4 regulates DNA double-strand break repair in a cell cycle-dependent manner. Cell Cycle (Georget, Tex). 2016;15:787–98.
Kuo CY, Li X, Kong XQ, Luo C, Chang CC, Chung Y, et al. An arginine-rich motif of ring finger protein 4 (RNF4) oversees the recruitment and degradation of the phosphorylated and SUMOylated Krüppel-associated box domain-associated protein 1 (KAP1)/TRIM28 protein during genotoxic stress. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:20757–72.
Goodarzi AA, Kurka T, Jeggo PA. KAP-1 phosphorylation regulates CHD3 nucleosome remodeling during the DNA double-strand break response. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18:831–9.
Blackford AN, Jackson SP. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: the trinity at the heart of the DNA damage response. Mol cell. 2017;66:801–17.
Stokes MP, Rush J, Macneill J, Ren JM, Sprott K, Nardone J, et al. Profiling of UV-induced ATM/ATR signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:19855–60.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [82272754, 82503164, 82003237]; Chongqing University Educational Reform Research Project [2021Y55]; China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [grant number 2024M752392]; The Scientific Research Project of Tianjin Education Commission [grant number 2022KJ220]; The Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (25ZR1402085); Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital Innovation Fund [grant number B2203]; Tianjin Key Medical Discipline Construction Project [grant number TJYXZDXK-3-004B]. We appreciate Dr. Lei Shi for providing relevant cell lines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL, HW, and YH performed most of the experiments and wrote the manuscript. YC, YW, SZ, YM, CW, and MX performed experiments and analyzed the data. BX and MX conceived the study and experimental design and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Wang, H., Han, Y. et al. ZDHHC20-mediated S-palmitoylation of KAP1/TRIM28 promotes DNA damage repair. Oncogene 44, 4533–4548 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03604-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03604-9