Abstract
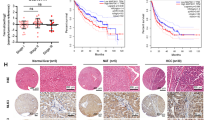
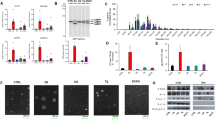
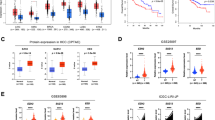
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane protein complex (EMC) is an ER multiprotein complex that affects a wide range of pathophysiological processes. Recently, the function of EMC6, a subunit of EMC, has been attracting attention for its role in cancers. However, research on EMC6 in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unknown. Here, we first observed the decreased EMC6 expression in human HCC tissues, and diminished expression level of EMC6 was associated with poor prognosis of HCC patients. In parallel, the knockdown of EMC6 promoted tumor progression both in HCC cell lines and in tumor-cell bearing nude mice. To delineate the in vivo roles of EMC6, we generated a hepatocyte-specific knockout of Emc6 (Emc6f/f;Alb-Cre, named Emc6 LKO) using a floxed Emc6 line. Emc6 LKO mice exhibited progressive liver dysfunction, fibrosis and spontaneous carcinogenesis phenotypes. Significant lipid metabolic disorder in the Emc6 LKO liver was revealed by combined metabolomic and proteomic analysis. Moreover, drastic elevation of 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 13 (HSD17B13), a lipid droplet-associated enzyme, was identified to be involved in the process of EMC6-induced lipid metabolic disorder and HCC progression. Inhibition of HSD17B13 by a Pharmacological inhibitor BI-3231 effectively mitigated EMC6-driven HCC progression in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, these results unveiled a novel regulatory mechanism of EMC in HCC progression through lipid metabolism and may provide a new biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in the main text or the supplementary materials. Metabolomics data can be found under National Genomics Data Center accession number OMIX010094. Proteomics data can be found under ProteomeXchange accession number PXD067920 (hosting repository: iProX, project ID IPX0013248000).
Code availability
Code used during the study is available from the corresponding authors or first authors by request.
References
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391:1301–14.
Wen N, Cai Y, Li F, Ye H, Tang W, Song P, et al. The clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma worldwide: A concise review and comparison of current guidelines: 2022 update. Biosci Trends. 2022;16:20–30.
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86.
Rumgay H, Ferlay J, de Martel C, Georges D, Ibrahim AS, Zheng R, et al. Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by subtype. Eur J Cancer. 2022;161:108–18.
Dhamija E, Paul SB, Kedia S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with hepatocellular carcinoma: An increasing concern. Indian J Med Res. 2019;149:9–17.
Vogel A, Chan SL, Dawson LA, Kelley RK, Llovet JM, Meyer T, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2025;36:491−506.
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84.
Jemal A, Ward EM, Johnson CJ, Cronin KA, Ma J, Ryerson B, et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975-2014, Featuring Survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109: djx030.
Lebeaupin C, Vallee D, Hazari Y, Hetz C, Chevet E, Bailly-Maitre B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2018;69:927–47.
Ajoolabady A, Kaplowitz N, Lebeaupin C, Kroemer G, Kaufman RJ, Malhi H, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases. Hepatology. 2023;77:619–39.
Hetz C, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:421–38.
Luna-Marco C, Ubink A, Kopsida M, Heindryckx F. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Metabolism in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 2023;193:1377–88.
Wang M, Kaufman RJ. Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature. 2016;529:326–35.
Rohrig F, Schulze A. The multifaceted roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:732–49.
Bai L, You Q, Feng X, Kovach A, Li H. Structure of the ER membrane complex, a transmembrane-domain insertase. Nature. 2020;584:475–8.
Pleiner T, Tomaleri GP, Januszyk K, Inglis AJ, Hazu M, Voorhees RM. Structural basis for membrane insertion by the human ER membrane protein complex. Science. 2020;369:433–6.
Couto-Lima CA, Machado MCR, Anhezini L, Oliveira MT, Molina R, da Silva RR, et al. EMC1 is required for the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial functions in the drosophila muscle. Biomolecules. 2024;14:1258.
Richard M, Boulin T, Robert VJ, Richmond JE, Bessereau JL. Biosynthesis of ionotropic acetylcholine receptors requires the evolutionarily conserved ER membrane complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:E1055–63.
Satoh T, Ohba A, Liu Z, Inagaki T, Satoh AK dPob/EMC is essential for biosynthesis of rhodopsin and other multi-pass membrane proteins in Drosophila photoreceptors. Elife. 2015;4.
Tang X, Snowball JM, Xu Y, Na CL, Weaver TE, Clair G, et al. EMC3 coordinates surfactant protein and lipid homeostasis required for respiration. J Clin Invest. 2017;127:4314–25.
Zhu Q, Zhu X, Zhang L. ER membrane complex (EMC): Structure, functions, and roles in diseases. FASEB J. 2024;38:e23539.
Volkmar N, Thezenas ML, Louie SM, Juszkiewicz S, Nomura DK, Hegde RS, et al. The ER membrane protein complex promotes biogenesis of sterol-related enzymes maintaining cholesterol homeostasis. J Cell Sci. 2019;132: jcs223453.
Lahiri S, Chao JT, Tavassoli S, Wong AK, Choudhary V, Young BP, et al. A conserved endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex (EMC) facilitates phospholipid transfer from the ER to mitochondria. PLoS Biol. 2014;12:e1001969.
Janer A, Prudent J, Paupe V, Fahiminiya S, Majewski J, Sgarioto N, et al. SLC25A46 is required for mitochondrial lipid homeostasis and cristae maintenance and is responsible for Leigh syndrome. EMBO Mol Med. 2016;8:1019–38.
Guna A, Volkmar N, Christianson JC, Hegde RS. The ER membrane protein complex is a transmembrane domain insertase. Science. 2018;359:470–3.
Jonikas MC, Collins SR, Denic V, Oh E, Quan EM, Schmid V, et al. Comprehensive characterization of genes required for protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science. 2009;323:1693–7.
Shen X, Kan S, Hu J, Li M, Lu G, Zhang M, et al. EMC6/TMEM93 suppresses glioblastoma proliferation by modulating autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2043.
Wang X, Xia Y, Xu C, Lin X, Xue P, Zhu S, et al. ER membrane protein complex subunit 6 (EMC6) is a novel tumor suppressor in gastric cancer. BMB Rep. 2017;50:411–6.
Xiao W, Cao RC, Yang WJ, Tan JH, Liu RQ, Kan HP, et al. Roles and clinical significances of ATF6, EMC6, and APAF1 in prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Front Genet. 2021;12:730847.
Zhou X, Xiao B, Jiang M, Rui J. Pan-cancer analysis identifies EMC6 as a potential target for lung adenocarcinoma. iScience. 2024;27:108648.
He W, Wang M, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhao D, Li W, et al. Estrogen induces LCAT to maintain cholesterol homeostasis and suppress hepatocellular carcinoma development. Cancer Res. 2024;84:2417–31.
Toh MR, Wong EYT, Wong SH, Ng AWT, Loo LH, Chow PK, et al. Global epidemiology and genetics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2023;164:766–82.
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:589–604.
Calvisi DF, Wang C, Ho C, Ladu S, Lee SA, Mattu S, et al. Increased lipogenesis, induced by AKT-mTORC1-RPS6 signaling, promotes development of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1071–83.
Li K, Shi W, Song Y, Qin L, Zang C, Mei T, et al. Reprogramming of lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma resulting in downregulation of phosphatidylcholines used as potential markers for diagnosis and prediction. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023;23:1015–26.
Du A, Wang Z, Huang T, Xue S, Jiang C, Qiu G, et al. Fatty acids in cancer: metabolic functions and potential treatment. MedComm Oncol. 2023;2:e25.
Chitwood PJ, Juszkiewicz S, Guna A, Shao S, Hegde RS. EMC is required to initiate accurate membrane protein topogenesis. Cell. 2018;175:1507–19 e16.
Li Y, Zhao Y, Hu J, Xiao J, Qu L, Wang Z, et al. A novel ER-localized transmembrane protein, EMC6, interacts with RAB5A and regulates cell autophagy. Autophagy. 2013;9:150–63.
Tong L, Zheng X, Wang T, Gu W, Shen T, Yuan W, et al. Inhibition of UBA52 induces autophagy via EMC6 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28:e18164.
Li R, Wang X, Zhang X, Yu J, Feng J, Lv P, et al. Ad5-EMC6 mediates antitumor activity in gastric cancer cells through the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513:663–8.
Hall Z, Chiarugi D, Charidemou E, Leslie J, Scott E, Pellegrinet L, et al. Lipid Remodeling in Hepatocyte Proliferation and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology. 2021;73:1028–44.
Broadfield LA, Pane AA, Talebi A, Swinnen JV, Fendt SM. Lipid metabolism in cancer: New perspectives and emerging mechanisms. Dev Cell. 2021;56:1363–93.
Phoolchund AGS, Khakoo SI. MASLD and the Development of HCC: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Challenges. Cancers. 2024;16:259.
Peng P, Qin S, Li L, He Z, Li B, Nice EC, et al. Epigenetic remodeling under oxidative stress: Mechanisms driving tumor metastasis. MedComm Oncol. 2024;3:e70000.
Chen D, Zhang Y, Wang W, Chen H, Ling T, Yang R, et al. Identification and characterization of robust hepatocellular carcinoma prognostic subtypes based on an integrative metabolite-protein interaction network. Adv Sci. 2021;8:e2100311.
Chen H, Cai W, Chu ESH, Tang J, Wong CC, Wong SH, et al. Hepatic cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression induced spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma formation in mice. Oncogene. 2017;36:4415–26.
Wang B, Liu J, Lei R, Xue B, Li Y, Tian X, et al. Cold exposure, gut microbiota, and hypertension: a mechanistic study. Sci Total Environ. 2022;833:155199.
Janneh AH, Kassir MF, Atilgan FC, Lee HG, Sheridan M, Oleinik N, et al. Crosstalk between pro-survival sphingolipid metabolism and complement signaling induces inflammasome-mediated tumor metastasis. Cell Rep. 2022;41:111742.
Lee M, Lee SY, Bae YS. Functional roles of sphingolipids in immunity and their implication in disease. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55:1110–30.
Bocher V, Chinetti G, Fruchart JC, Staels B. [Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARS) in the regulation of lipids and inflammation control]. J Soc Biol. 2002;196:47–52.
Wei X, Zhang J, Tang M, Wang X, Fan N, Peng Y. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein promotes liver steatosis by targeting PPARalpha. Lipids Health Dis. 2022;21:29.
Chen X, Cubillos-Ruiz JR. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:71–88.
Li Y, Xu K, Zhou A, Xu Z, Wu J, Peng X, et al. Integrative Transcriptomics and proteomics analysis reveals THRSP’s role in lipid metabolism. Genes. 2024;15:1562.
Innes H, Morgan MY, Hampe J, Stickel F, Buch S. The rs72613567:TA polymorphism in HSD17B13 is associated with survival benefit after development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023;58:623–31.
Abul-Husn NS, Cheng X, Li AH, Xin Y, Schurmann C, Stevis P, et al. A protein-truncating HSD17B13 Variant and Protection from Chronic Liver Disease. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1096–106.
Kogiso T, Ogasawara Y, Horiuchi K, Taniai M, Tokushige K. Analysis of genetic factors associated with fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2023;12:17798–807.
Vilar-Gomez E, Pirola CJ, Sookoian S, Wilson LA, Liang T, Chalasani N. The protection conferred by HSD17B13 rs72613567 polymorphism on risk of steatohepatitis and fibrosis may be limited to selected subgroups of patients with NAFLD. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12:e00400.
Ma Y, Brown PM, Lin DD, Ma J, Feng D, Belyaeva OV, et al. 17-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 13 deficiency does not protect mice from obesogenic diet injury. Hepatology. 2021;73:1701–16.
Alcober-Boquet L, Kraus N, Huber LS, Vutukuri R, Fuhrmann DC, Stross C, et al. BI-3231, an enzymatic inhibitor of HSD17B13, reduces lipotoxic effects induced by palmitic acid in murine and human hepatocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024;326:C880–C92.
Thamm S, Willwacher MK, Aspnes GE, Bretschneider T, Brown NF, Buschbom-Helmke S, et al. Discovery of a novel potent and selective HSD17B13 inhibitor, BI-3231, a well-characterized chemical probe available for open science. J Med Chem. 2023;66:2832–50.
Stender S, Romeo S. HSD17B13 as a promising therapeutic target against chronic liver disease. Liver Int. 2020;40:756–7.
Caddeo A, Romeo S. Precision medicine and nucleotide-based therapeutics to treat steatotic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025;31:S76–S93.
Mak LY, Gane E, Schwabe C, Yoon KT, Heo J, Scott R, et al. A phase I/II study of ARO-HSD, an RNA interference therapeutic, for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2023;78:684–92.
Pharmaceuticals R A study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ALN-HSD in adult participants with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) with fibrosis with genetic risk factors. Clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 13 July 2023. https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05519475
IAP Ltd. A study of INI-822 in healthy volunteers and participants with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or presumed NASH. Clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 6 Aug 2023. https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05945537
AstraZeneca. Knockdown of HSD17B13 mRNA, pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability, of AZD7503 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 15 Nov 2023. https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05560607
AstraZeneca. A study to assess the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of AZD7503 in healthy participants. Clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed 23 Nov 2023. https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05143905
Li D, Zhao YG, Li D, Zhao H, Huang J, Miao G, et al. The ER-Localized Protein DFCP1 Modulates ER-Lipid Droplet Contact Formation. Cell Rep. 2019;27:343–58 e5.
Estes RE, Lin B, Khera A, Davis MY. Lipid Metabolism Influence on Neurodegenerative Disease Progression: Is the Vehicle as Important as the Cargo?. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:788695.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients who agreed to provide their tissue for research purposes.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81970825 to YuZ); the Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (No. 2023ZYD0172 to XZ, No. 2024NSFSC0744 to SZ, and No. 2022JDJQ0062 to YuZ); the Chengdu Science and Technology Program (No. 2024-YF05-01868-SN); the Sichuan Returned Overseas Talent Funding (YuZ and SZ); the Human Resources and Social Security Department of Sichuan Province (2021) and research grant from Jinfeng Laboratory (JFLKYXM202403AZ-101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YuZ, XZ and SZ was responsible for Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YunZ, CX and ZJ was responsible for Investigation, Visualization, and Writing – original draft. YL contributed to Methodology. XW, ZW, JC, XY contributed to Investigation. QL contributed to Visualization. CC contributed to Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xiong, C., Jiang, Z. et al. Unveiling EMC6 as a novel pathogenic determinant in hepatocellular carcinoma: orchestration of lipid metabolism through regulation of lipid droplet-associated enzyme HSD17B13. Oncogene 45, 322–338 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03649-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03649-w