Abstract
Introduction
There is an increasing use of biodegradable peri-rectal spacer prior to radiation therapy for prostate cancer to reduce treatment-associated rectal toxicity. While data from individual trials and cohorts is maturing, there is a lack of an updated quantitative analysis that includes outcomes following peri-rectal spacer. We aim to delineate the clinical impact of peri-rectal spacer in localised prostate cancer patients treated with radiotherapy.
Methods
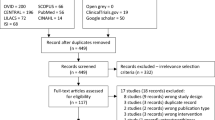
In March 2024, a systematic search was performed on MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Central Register of controlled trials for publications since the year 2010. Prospective and retrospective studies reporting comparative outcomes of patients with and without peri-rectal spacer prior to radiotherapy were considered. Outcomes are reported in binary fashion. Random effect meta-analysis with the use of weighted mean difference was adopted. Early (≤3 months) and late rectal toxicity stratified according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) criteria, early and late genitourinary toxicity, quality of life in bowel, sexual and urinary domains (in terms of minimal clinically important difference) were assessed.
Results
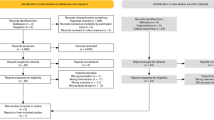
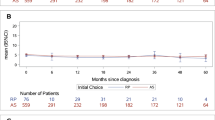
The systematic review included 17 studies. There are 3 RCTs, 3 prospective cohorts, and 11 retrospective cohorts. Three thousand two hundred patients were included, with 1471 patients who received peri-rectal spacer and 1729 without. The use of spacer is associated with lower likelihood of late (1.62% vs. 9.35%, RR = 0.25, 95% CI = 0.15–0.42, P < 0.001) and early grade 2 or above late rectal toxicity (3.07% vs. 6.05%, RR = 0.53, 95% CI = 0.33–0.86, P < 0.001). No difference is observed in significant grade 3 or above GI (acute or late) events. There is no statistical difference in bowel-related bowel QoL (risk difference = −0.16, 95% CI = −0.38–0.06, P = 0.15). The perirectal spacer is not associated with negative impact to urinary or sexual domains of QoL either.
Conclusion
In localised prostate cancer patients treated with radiation therapy, the use of peri-rectal spacer is associated with reduced rectal toxicities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zelefsky MJ, Levin EJ, Hunt M, Yamada Y, Shippy AM, Jackson A, et al. Incidence of late rectal and urinary toxicities after three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:1124–9.
Mariados N, Sylvester J, Shah D, Karsh L, Hudes R, Beyer D, et al. Hydrogel spacer prospective multicenter randomized controlled pivotal trial: dosimetric and clinical effects of perirectal spacer application in men undergoing prostate image-guided intensity modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92:971–7.
Hamstra DA, Mariados N, Sylvester J, Shah D, Karsh L, Hudes R, et al. Continued benefit to rectal separation for prostate radiation therapy: final results of a phase III trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;97:976–85.
Karsh LI, Gross ET, Pieczonka CM, Aliotta PJ, Skomra CJ, Ponsky LE, et al. Absorbable hydrogel spacer use in prostate radiotherapy: a comprehensive review of phase 3 clinical trial published data. Urology. 2018;115:39–44.
Song DY, Herfarth KK, Uhl M, Eble MJ, Pinkawa M, van Triest B, et al. A multi-institutional clinical trial of rectal dose reduction via injected polyethylene-glycol hydrogel during intensity modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer: analysis of dosimetric outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;87:81–7.
Seymour ZA, Pinkawa M, Daignault-Newton S, Bosch W, Michalski JM, Gay H, et al. A pooled long-term follow-up after radiotherapy for prostate cancer with and without a rectal hydrogel spacer: impact of hydrogel on decline in sexual quality of life. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1239104.
Mariados NF, Orio PF, Schiffman Z, Van TJ, Engelman A, Nurani R, et al. Hyaluronic acid spacer for hypofractionated prostate radiation therapy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023;9:511–8.
Ogita M, Yamashita H, Nozawa Y, Ozaki S, Sawayanagi S, Ohta T, et al. Phase II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy with hydrogel spacer for prostate cancer: acute toxicity and propensity score-matched comparison. Radiat Oncol. 2021;16:107.
Pinkawa M, Berneking V, König L, Frank D, Bretgeld M, Eble MJ. Hydrogel injection reduces rectal toxicity after radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017;193:22–8.
Whalley D, Hruby G, Alfieri F, Kneebone A, Eade T. SpaceOAR hydrogel in dose-escalated prostate cancer radiotherapy: rectal dosimetry and late toxicity. Clin Oncol. 2016;28:e148–e54.
Abdelhakiem MK, Keller A, Bajpai RR, Smith RP, Beriwal S, Benoit R. Cs-131 prostate brachytherapy boost and effect of hydrogel rectal spacer on long-term patient-reported rectal bleeding and bowel quality of life. Brachytherapy. 2023;22:808–21.
Taniguchi T, Iinuma K, Nakano M, Kawase M, Takeuchi S, Kato D, et al. Chronological changes of lower urinary tract symptoms after low-dose-rate brachytherapy for prostate cancer using SpaceOAR system. Prostate Int. 2022;10:207–12.
Kundu P, Lin EY, Yoon SM, Parikh NR, Ruan D, Kishan AU, et al. Rectal radiation dose and clinical outcomes in prostate cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy with and without hydrogel. Front Oncol. 2022;12:853246.
Teyateeti A, Grossman C, Kollmeier MA, Fiasconaro M, Hopkins M, McBride S, et al. Influence of hydrogel spacer placement with prostate brachytherapy on rectal and urinary toxicity. BJU Int. 2022;129:337–44.
Alshak MN, Eidelberg A, Diaz SM, Stoddard MD, Formenti S, Nagar H, et al. Natural history of lower urinary tract symptoms among men undergoing stereotactic body radiation therapy for prostate cancer with and without a rectal hydrogel spacer. World J Urol. 2022;40:1143–50.
Lin Y, Ong W, Tacey M, Bolton D, Tan A, Chan Y, et al. Effect of hydrogel and hyaluronic acid rectal spacer on rectal dosimetry and toxicity in low-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021;65:266.
Kobayashi H, Eriguchi T, Tanaka T, Ogata T, Ishida M, Nakajima Y, et al. Distribution analysis of hydrogel spacer and evaluation of rectal dose reduction in Japanese prostate cancer patients undergoing stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Clin Oncol. 2021;26:736–43.
Navaratnam A, Cumsky J, Abdul-Muhsin H, Gagneur J, Shen J, Kosiorek H, et al. Assessment of polyethylene glycol hydrogel spacer and its effect on rectal radiation dose in prostate cancer patients receiving proton beam radiation therapy. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020;5:92–100.
te Velde BL, Westhuyzen J, Awad N, Wood M, Shakespeare TP. Late toxicities of prostate cancer radiotherapy with and without hydrogel SpaceAOR insertion. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2019;63:836–41.
Chao M, Ow D, Ho H, Chan Y, Joon DL, Spencer S, et al. Improving rectal dosimetry for patients with intermediate and high-risk prostate cancer undergoing combined high-dose-rate brachytherapy and external beam radiotherapy with hydrogel space. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2019;11:8–13.
Taggar AS, Charas T, Cohen GN, Boonyawan K, Kollmeier M, McBride S, et al. Placement of an absorbable rectal hydrogel spacer in patients undergoing low-dose-rate brachytherapy with palladium-103. Brachytherapy. 2018;17:251–8.
Cornford P, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E, Van den Broeck T, Brunckhorst O, Darraugh J, et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-ISUP-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer-2024 update. part I: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2024;86:148–63.
Miller LE, Efstathiou JA, Bhattacharyya SK, Payne HA, Woodward E, Pinkawa M. Association of the placement of a perirectal hydrogel spacer with the clinical outcomes of men receiving radiotherapy for prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e208221.
Yamaguchi H, Kato T, Ishikawa Y, Takemasa K, Narita Y, Takagawa Y, et al. Safety of hydrogel spacers for rectal wall protection in patients with prostate cancer: a retrospective analysis of 200 consecutive cases. Int J Urol. 2023;30:401–7.
Pieczonka CM, Mariados N, Sylvester JE, Karsh LI, Hudes RS, Beyer DC, et al. Hydrogel spacer application technique, patient tolerance and impact on prostate intensity modulated radiation therapy: results from a prospective, multicenter, pivotal randomized controlled trial. Urol Pract. 2016;3:141–6.
Freites-Martinez A, Santana N, Arias-Santiago S, Viera A. Using the common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE - version 5.0) to evaluate the severity of adverse events of anticancer therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:90–2.
Payne HA, Pinkawa M, Peedell C, Bhattacharyya SK, Woodward E, Miller LE. SpaceOAR hydrogel spacer injection prior to stereotactic body radiation therapy for men with localized prostate cancer: a systematic review. Medecine. 2021;100:e28111.
Babar M, Katz A, Ciatto M. Dosimetric and clinical outcomes of SpaceOAR in men undergoing external beam radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer: a systematic review. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021;65:384–97.
Armstrong N, Bahl A, Pinkawa M, Ryder S, Ahmadu C, Ross J, et al. SpaceOAR hydrogel spacer for reducing radiation toxicity during radiotherapy for prostate cancer. a systematic review. Urology. 2021:156:e74–85.
Afkhami Ardekani M, Ghaffari H. Optimization of prostate brachytherapy techniques with polyethylene glycol-based hydrogel spacers: a systematic review. Brachytherapy. 2020;19:13–23.
Aluwini S, Pos F, Schimmel E, Krol S, van der Toorn PP, de Jager H, et al. Hypofractionated versus conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for patients with prostate cancer (HYPRO): late toxicity results from a randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:464–74.
Dearnaley D, Syndikus I, Mossop H, Khoo V, Birtle A, Bloomfield D, et al. Conventional versus hypofractionated high-dose intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: 5-year outcomes of the randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 CHHiP trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1047–60.
Pinkawa M, Berneking V, Schlenter M, Krenkel B, Eble MJ. Quality of life after radiation therapy for prostate cancer with a hydrogel spacer: 5-year results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;99:374–7.
Gomez-Aparicio MA, Valero J, Caballero B, Garcia R, Hernando-Requejo O, Montero A, et al. Extreme hypofractionation with SBRT in localized prostate cancer. Curr Oncol. 2021;28:2933–49.
Datta NR, Stutz E, Rogers S, Bodis S. Conventional versus hypofractionated radiation therapy for localized or locally advanced prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis along with therapeutic implications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;99:573–89.
Corkum MT, Achard V, Morton G, Zilli T. Ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy for localised prostate cancer: how far can we go? Clin Oncol. 2022;34:340–9.
Cuccia F, Mazzola R, Nicosia L, Figlia V, Giaj-Levra N, Ricchetti F, et al. Impact of hydrogel peri-rectal spacer insertion on prostate gland intra-fraction motion during 1.5 T MR-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. 2020;15:178.
Mazzola R, Sicignano G, Cuccia F, Vitale C, Rigo M, Giaj-Levra N, et al. Impact of hydrogel peri-rectal spacer insertion on seminal vesicles intrafraction motion during 1.5 T-MRI-guided adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Br J Radiol. 2021;94:20210521.
Applewhite J, Barker J Jr, Vestal JC. Successful use of absorbable hydrogel rectal spacers (SpaceOAR) before salvage radiation therapy after previous prostate cryotherapy. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2021;6:100647.
Pinkawa M, Schubert C, Escobar-Corral N, Holy R, Eble MJ. Application of a hydrogel spacer for postoperative salvage radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol. 2015;191:375–9.
Opbroek T, Cobussen A, Van Limbergen EJ, Vanneste BGL. Focal salvage high-dose-rate brachytherapy with implantable rectum spacer for locally recurrent prostate cancer after initial low-dose-rate with grade 3 rectal toxicity. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2023;15:154–8.
McDonough MJ, Feldmeier JJ, Parsai I, Dobelbower RR Jr, Selman SH. Salvage external beam radiotherapy for clinical failure after cryosurgery for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:624–7.
Vestal JC. Critical review of the efficacy and safety of cryotherapy of the prostate. Curr Urol Rep. 2005;6:190–3.
Nguyen PL, Devlin PM, Beard CJ, Orio PF 3rd, O’Leary MP, Wolfsberger LD, et al. High-dose-rate brachytherapy for prostate cancer in a previously radiated patient with polyethylene glycol hydrogel spacing to reduce rectal dose: case report and review of the literature. Brachytherapy. 2013;12:77–83.
Poon DMC, Yuan J, Wong OL, Yang B, Tse MY, Lau KK, et al. One-year clinical outcomes of MR-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy with rectal spacer for patients with localized prostate cancer. World J Urol. 2024;42:97.
Fredman E, Moore A, Icht O, Tschernichovsky R, Shemesh D, Bragilovski D, et al. Acute toxicity and early prostate specific antigen response after two-fraction stereotactic radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer using peri-rectal spacing - initial report of the SABR-dual trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024;120:1404–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chris Ho-Ming Wong was responsible for the conceptualisation of the study, methodology design, and writing of the manuscript. Ivan Ching-Ho Ko was responsible for the data collection, analysis, and draughting of the manuscript. David Ka-Wai Leung was responsible for the data analysis, interpretation, and critical revision of the manuscript. Steffi Kar-Kei Yuen was responsible for the data validation and contributed to manuscript preparation. Brian Siu assisted in manuscript screening and extraction. Cathy Yuan provided resources and contributed to methodology, analysis, and the review of the manuscript. Jeremy Yuen-Chun Teoh was responsible for the supervision, funding acquisition, project administration, and final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval is waived for the study did not involve the use data from individual patient.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, C.HM., Ko, I.CH., Leung, D.KW. et al. Does biodegradable peri-rectal spacer mitigate treatment toxicities in radiation therapy for localised prostate cancer—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 28, 927–937 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-025-00961-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-025-00961-0
This article is cited by
-
“Re: does biodegradable peri-rectal spacer mitigate treatment toxicities in radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer—a systematic review and meta-analysis.”
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2025)