Abstract
Altered functioning of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) may play a critical role in the etiology of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Chronic stressors such as racial discrimination and lifetime trauma are associated with an increased risk for PTSD, but it is unknown whether they influence the relationship between BNST functioning and PTSD. We investigated acute post-trauma BNST resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) as a predictor of future PTSD symptoms in Black trauma survivors. We also examined whether racial discrimination and lifetime trauma moderated the relationship between BNST rsFC and PTSD symptoms. Black adults (N = 95; 54.7% female; mean age = 34.04) were recruited from an emergency department after experiencing a traumatic injury (72.6% were motor vehicle accidents). Two-weeks post-injury, participants underwent a resting-state fMRI scan and completed questionnaires evaluating their PTSD symptoms as well as lifetime exposure to racial discrimination and trauma. Six-months post-injury, PTSD symptoms were reassessed. Whole brain seed-to-voxel analyses were conducted to examine BNST rsFC patterns. Greater rsFC between the BNST and the posterior cingulate cortex, precuneus, left angular gyrus, and hippocampus prospectively predicted six-month PTSD symptoms after adjusting for sex, age, education, and baseline PTSD symptoms. Acute BNST rsFC was a stronger predictor of PTSD symptoms in individuals who experienced more racial discrimination and lifetime trauma. Thus, in the acute aftermath of a traumatic event, the BNST could be a key biomarker of risk for PTSD in Black Americans, particularly for individuals with a greater history of racial discrimination or previous trauma exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a pervasive mental illness that impacts up to 14% of Black Americans in their lifetime [1]. PTSD is a heterogenous disorder that is broadly characterized by recurring intrusive memories of a traumatic event, hyperarousal, avoidance of trauma-related stimuli, and negative alterations in cognition and mood [2]. Identifying early markers of risk for PTSD is crucial for enhancing early intervention efforts that attempt to thwart PTSD development [3]. While psychosocial factors such as racial discrimination and other forms of stress/trauma exposure (e.g., events that qualify as “criterion A” stressors within the Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th edition [DSM-5] definition of PTSD2) confer risk for PTSD [1, 4], recent research utilizing machine learning techniques indicate the strongest predictive models of PTSD include both neurobiological and psychosocial markers of risk [5]. Thus, it is imperative to investigate the neural underpinnings of PTSD development in the context of psychosocial risk factors. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have identified key markers of risk for PTSD within threat processing neurocircuitry [6], and growing research suggests altered functioning of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) may play a critical role in the etiology of PTSD [7,8,9].
Resting-State BNST connectivity and PTSD
The BNST is a subcortical structure located in the medial basal forebrain, and it has dense structural and functional connections with the limbic system, basal ganglia, and hypothalamus [10,11,12,13]. The BNST is also composed of a high volume of neuropeptide receptors that modulate the stress response [14, 15]. Functionally, the BNST is responsible for detecting environmental cues that signal uncertain threat, as well as initiating and prolonging states of anxiety (i.e. tonic arousal) in response to the ambiguous threat [16, 17]. When there is potential to encounter a threat, BNST activation is essential for early initiation of the fear response, which allows one to proactively cope with the threat. However, when BNST activity is consistently heightened in contextually safe situations (i.e., no threat present), it can lead to persistent states of hyperarousal and hypervigilance [17,18,19], which may increase risk for PTSD by interfering with processes that help individuals cope with posttraumatic stress (e.g., fear extinction recall) [20,21,22].
Accordingly, neuroimaging research has identified patterns of heightened BNST activity among individuals who have PTSD. Findings from task-based fMRI studies show individuals with PTSD display greater BNST activity when they are awaiting a future threat (i.e., hypervigilant threat monitoring) [8] and when they are exposed to trauma-related stimuli compared to healthy controls [7]. Notably, similar patterns of BNST activity are observed when individuals with PTSD are at rest (i.e., not engaged in a task). Relative to healthy controls, individuals with PTSD exhibit greater BNST resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) with regions of the brain that are implicated in arousal and vigilance, which is theorized to underlie chronic anticipatory anxiety and hyperarousal symptoms of PTSD [9]. Considering a diminished ability to inhibit one's fear response in the absence of a threat is a hallmark trait of PTSD [21, 23], BNST rsFC may be a particularly salient neural marker of risk for future PTSD development.
The effects of racial discrimination and trauma exposure on BNST functioning
Black Americans continue to experience race-related stressors, including racial discrimination, across a variety of settings, which can elicit psychological symptoms and neurobiological alterations that mirror PTSD [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. For instance, greater exposure to racial discrimination is associated with heightened functional connectivity between threat processing regions of the brain [28,29,30] as well as persistent states of arousal and vigilance [25, 26, 31]. Notably, repeated exposure to DSM-5 defined traumatic events (i.e., exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence) can also elicit similar changes in threat neurocircuitry and threat monitoring behavior [32, 33]. Elevated BNST resting-state activity may contribute to these posttraumatic alterations in neuropsychological functioning, as the BNST appears to be sensitive to the effects of chronic stressors[14, 34].
In general, repeated stressor exposure can upregulate and alter a variety of neurobiological functions related to threat monitoring and the fear response in humans [32]. Preclinical models show chronic stress increases the expression of neurochemicals within the BNST that modulate the stress response and upregulate BNST activity [14, 34]. Increasing BNST activity is also associated with an increase in anxiety-related behaviors. Thus, in the acute aftermath of a traumatic event, BNST connectivity may be an early marker of risk for PTSD, particularly among individuals who have a greater history of stress and trauma exposure (e.g., racial discrimination, “criterion A” stressors).
Previous research conducted by Webb et al. (2022), Harb et al. (2023), and Bird et al. (2021) identified racial discrimination as a unique predictor of PTSD symptoms [4], tested potential mediators of the relationship [35], and investigated the relationship between discrimination and activity in threat-processing regions [30] in the same sample as the present study. Considering greater lifetime exposure to DSM-5 “criterion A” stressors and racial discrimination are associated with an increased risk for PTSD following subsequent trauma exposure [36], and both experiences elicit similar neural and psychological alterations, it is possible racial discrimination and “criterion A” stressor exposure similarly impact BNST connectivity as a biomarker of PTSD.
Current study
The present study builds upon previous findings from our group [4, 30, 35] by using a prospective longitudinal design to investigate two-week post-trauma (T1) BNST rsFC as a predictor of future PTSD symptoms (six-months post-trauma; T2) among Black trauma survivors. We also examined whether lifetime exposure to racial discrimination and “criterion A” stressors moderated the relationship between acute BNST rsFC and future PTSD symptoms. Considering previous research implicates greater BNST activity with PTSD symptomatology [7,8,9], we hypothesized heightened T1 BNST rsFC would predict T2 PTSD symptoms. Additionally, given the effects of chronic stress on BNST functioning and risk for PTSD [14, 15], we hypothesized racial discrimination and prior trauma exposure would independently moderate the relationship between T1 BNST connectivity and T2 PTSD symptoms.
Methods and materials
Participants
Two-hundred and fifteen adults (Black/African American, n = 124) were recruited from an emergency department (ED) in the Midwest. Because the present study investigated BNST rsFC as a biomarker for PTSD among Black trauma survivors and the moderating effects of racial discrimination and exposure to “criterion A” stressors, only individuals who identified as Black or African American were included in the analyses. Individuals were either screened directly in the ED or via telephone shortly after discharge. Individuals were eligible for study participation if they met the following criteria: were seen in the ED due to a traumatic injury (as defined by the DSM-52), right-handed, spoke English, between the ages of 18–65, and were able to schedule their first study visit within two weeks of the trauma. Individuals were excluded for contraindications of MRI scanning (e.g. metal objects in body, current or planned pregnancy in the next 6 months), if they suffered a head injury more severe than a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) as measured by the Glasgow Coma Scale [37], or if the injury resulted in a loss of consciousness. Additional exclusion criteria included injuries resulting from self-inflicted harm, individuals with severe vision or hearing impairments, a history of psychotic or manic symptoms, antipsychotic medication prescription, or if they were on police hold.
Eligible participants provided written informed consent prior to the study and were financially compensated for each visit. The study involving human subjects was approved by the Medical College of Wisconsin Institutional Review Board and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
PTSD symptom assessment
The self-report PTSD Checklist for the DSM-5 (PCL-5) [38] was administered to assess PTSD symptoms at T1. The PCL-5 is a 20-item self-report questionnaire (current sample Cronbach α = 0.94) that assesses the frequency and severity of PTSD symptoms one has experienced within the past month, rated on a 5-point Likert scale from 0 (not at all) to 4 (extremely). All questions referred to the index trauma responsible for the ED visit, and scores ranged from 0–80, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity.
At T2, PTSD symptoms were assessed by a team member trained to administer the Clinician Administered PTSD scale for the DSM-5 (CAPS-5) [39]. The CAPS-5 is a 20-item structured interview (current sample Cronbach α = 0.92) that measures the frequency and severity of PTSD symptoms one has experienced within the past month. All questions referred to the same index trauma related to the ED visit, and the interviewer scored each item on the questionnaire from 0 (never/no effort to avoid) to 4 (daily or almost daily/extreme efforts to avoid) based on the information provided by the participant. Total scores ranged from 0 to 80, with higher scores indicating greater symptom severity. Both the PCL-5 and CAPS-5 are well-established, empirically validated methods of PTSD assessment [40, 41].
Racial discrimination
The Perceived Ethnic Discrimination Questionnaire – Community Version (PEDQ-CV) [42] was administered to evaluate lifetime exposure to racial discrimination. The PEDQ-CV consists of 17 items (current sample Cronbach α = .93) that assess participants’ prior experiences with racial discrimination across various settings. Participants respond on a scale from 1 (never) to 5 (very often). The scores across all items are averaged to create a total score, with higher scores indicating greater discrimination.
Lifetime trauma exposure
The Life Events Checklist for the DSM-5 (LEC-5) [43] was administered to evaluate lifetime exposure to traumatic events, a known risk factor for PTSD following subsequent trauma exposure. Participants rated their experience (i.e., 0 = does not apply, 1 = happened to them, 2 = witnessed the event, 3 = learned about the event) with 17 different traumatic events (current sample Cronbach α = 0.83). The scoring method developed by Weis et al. (2022) [44] was implemented. Total scores were weighted according to one’s proximity to the traumatic event (e.g., happened to them vs learned about the event). Total scores range from 0–102.
Imaging Acquisition
Images were collected on a Discovery MR750 3.0 Tesla scanner, using a GE 32-channel head-coil. High resolution T1-weighted images were acquired with the following parameters: field of view (FOV), 240 mm; matrix, 256 × 224; slice thickness, 1 mm; 150 slices; repetition time (TR)/echo time (TE), 8.2/3.2 s, flip angle, 12°; voxel size, 1 × 0.938 × 0.938 mm. At T1, participants underwent an eight-minute resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) scan where they were instructed to stare at a fixation cross on a black screen; 240 volumes were acquired using the following parameters: FOV, 22.4 mm; matrix, 64 × 64; slice thickness, 3.5 mm; 41 sagittal slices; TR/TE, 2000/25 milliseconds; flip angle, 77°; voxel size, 3.5 × 3.5 × 3.5 mm.
fMRI preprocessing
Structural and resting-state images were preprocessed using the default pipeline in the CONN Toolbox 20, with SPM 12 and MatLab 2019b [45]. Of the 124 Black Americans in the sample, 111 completed a baseline resting-state scan (no scan, n = 13). The first 3 TRs were discarded to account for initial instability of MR environment. All remaining images were motion-corrected using a 6-parameter linear transformation, normalized to Montreal Neurological Institute template (MNI 152), and then spatially smoothed using a 4-mm full-width-at-half-maximum kernel. BNST seed activity was extracted before smoothing. During the first-level analyses, head motion parameters (along with their first-order derivatives), white matter signal, and cerebrospinal fluid signal were regressed out. Volumes with framewise displacement > 0.3 mm were removed from analyses (“scrubbed). There was no relationship between the number of discarded volumes and PTSD symptom severity, r(93) = 0.04, p = 0.713. If more than 20% of the resting-state volumes were scrubbed or the scan quality was deemed poor after visual inspection, the participant was excluded from the analysis. Of the 111 Black Americans who underwent rs-fMRI, 4 were removed from the analysis (n = 2 removed after visual quality checks and n = 2 exceeding 20% of volumes discarded) based on these criteria. An additional 12 participants were removed from the analyses because they either did not complete a baseline PCL-5 (n = 2), or the six-month CAPS-5 (n = 10), leaving an n = 95 for the current analysis.
Data analysis
A seed-to-voxel whole brain analysis, correlating the mean BOLD signal from the BNST with all other voxels in the brain, was conducted in CONN [46]. An established BNST seed for 3T fMRI images [47] was used, and each participant was visually inspected to ensure proper placement of the BNST seed. In CONN, a group-level analysis examined T1 BNST connectivity as a predictor of T2 PTSD symptoms after adjusting for other known self-report predictors of PTSD, including sex, age, education, and T1 PTSD symptoms (i.e., PCL-5 total scores) [48]. The threshold for statistical significance was set at two-tailed p < 0.05, with a height threshold of p < 0.001 uncorrected, and a cluster-size threshold of an adjusted p < 0.05 false discovery rate (FDR)-corrected.
Fisher’s Z-scores representing the strength of rsFC between the BNST and identified regions were extracted for each participant and analyzed in SPSS version 28.0. The PROCESS macro for SPSS (version 4.1) [49] was used to examine whether the PEDQ and LEC-5 moderated the relationship between BNST connectivity patterns and six-month CAPS-5 scores after adjusting for covariates. Bonferroni’s correction for multiple comparisons was used to calculate an α = 0.0125 for moderation analyses.
Results
Demographics
Among the 95 participants included in the analyses (mean age = 34.04, SD = 10.48), 54.7% (n = 52) identified as female, and 72.6% presented to the ED due to a motor vehicle accident (see Table 1). At 6-months post-trauma, 18 participants (18.95%) met DSM-5 criteria for PTSD.
PTSD, racial discrimination, and lifetime trauma
Results from the self-report measures are included in Table 2. T1 PCL-5 scores (M = 26.16, SD = 18.03) prospectively predicted T2 CAPS-5 scores (M = 13.04, SD = 12.52; r = 0.47, p < 0.001; R2 = 0.22, F(1,93) = 25.74, p < 0.001). T1 PCL-5 scores were also positively correlated with the PEDQ (r(93) = 0.49, p < 0.001) and the weighted LEC-5 (r(93) = 0.47, p < 0.001) (also demonstrated in Bird et al. 2021) [4]. Both the PEDQ (F(1,89) = 5.42, p = 0.022) and weighted LEC-5 (F(1,93) = 11.05, p = 0.001) predicted T2 CAPS-5 scores, which replicated findings from Bird et al. (2021).
BNST resting-state connectivity
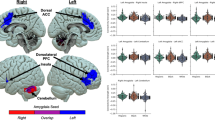
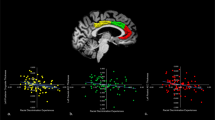
Greater rsFC between the BNST and four regions predicted T2 CAPS-5 scores: a cluster spanning the precuneus and posterior cingulate cortex (PRE/PCC; Fig. 1A; peak voxel: −10, −48, +22; size = 90 voxels; p-FDR = 0.018), and clusters located on the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC; Fig. 1B; peak: −08, −36, +36; size = 75; p-FDR = 0.02), left angular gyrus (LAG; Fig. 1C; peak: −46, −64, +20; size = 70; p-FDR = .02), and hippocampus (Fig. 1D; peak: −18, −38, +02; size = 56; p-FDR = 0.037).
A Cluster spanning the PCC and Precuneus; corresponding graph of T1 BNST–Pre/PCC rsFC predicting T2 CAPS-5 scores. B Cluster located on the PCC; corresponding graph of T1 BNST–PCC rsFC predicting T2 CAPS-5 scores. C Cluster located on the LAG; corresponding graph of T1 BNST–LAG rsFC predicting T2 CAPS-5 scores. D Cluster located on the hippocampus; corresponding graph of T1 BNST–hippocampus rsFC predicting T2 CAPS-5 scores.
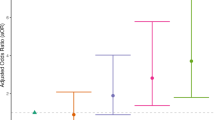
Racial discrimination significantly moderated the relationship between T1 BNST rsFC and T2 CAPS-5 scores. As exposure to racial discrimination increased, BNST connectivity with all 4 regions strengthened as a predictor of T2 PTSD symptoms: PRE/PCC (b = 26.46, t(87) = 2.29, p = 0.025), PCC (b = 30.99, t(87) = 2.55, p = 0.013), LAG (b = 25.33, t(87) = 2.36, p = 0.021), hippocampus (b = 26.08, t(87) = 2.81, p = 0.01). However, only BNST-PCC and BNST-hippocampus rsFC remained significant after Bonferroni’s correction for multiple comparisons (α = 0.0125). When controlling for the weighted LEC-5, the PEDQ still moderated the strength of BNST-PCC (b = 23.80, t(86) = 2.01, p = 0.047) and BNST-hippocampus (b = 20.81, t(86) = 2.29, p = 0.024) rsFC as predictors of T2 PTSD symptoms, but neither were significant after correcting for multiple comparisons (α = 0.0125). Table 3 presents conditional effects at low (1 SD below the mean), average (mean), and high (1 SD above the mean) rates of exposure to racial discrimination.
Lifetime exposure to traumatic events also moderated the relationship between T1 BNST rsFC and T2 PTSD symptoms. As LEC-5 scores increased, T1 BNST-LAG (b = 1.38, t(91) = 2.47, p = 0.01) and BNST-hippocampus (b = 1.16, t(91) = 1.97, p = 0.05) rsFC strengthened as predictors of T2 PTSD symptoms. However, only BNST-LAG rsFC remained significant after Bonferroni’s correction for multiple comparisons (α = 0.0125). LEC-5 scores still moderated the strength of BNST-LAG (b = 1.18, t(86) = 2.45, p = 0.016) and BNST-hippocampus (b = 1.45, t(86) = 2.84, p = 0.006) rsFC as predictors of T2 PTSD symptoms after covarying for PEDQ scores and correcting for multiple comparisons (α = 0.0125). Table 4 presents conditional effects at low, average, and high lifetime exposure to traumatic events.
Discussion
The present study evaluated whether BNST rsFC in the acute aftermath of a psychological trauma predicted future PTSD symptoms in Black Americans, as well as if racial discrimination and lifetime trauma exposure moderated the relationship. As hypothesized, participants who exhibited greater BNST rsFC with regions involved in threat processing and arousal two-weeks post-injury were more likely to experience more severe PTSD symptoms at the six-month follow-up. Furthermore, this risk was moderated by participants’ history of racial discrimination and traumatic exposure, where acute BNST rsFC was a stronger predictor of future PTSD symptoms for participants who experienced more lifetime racial discrimination or had a greater history of traumatic exposure.
BNST and hyperarousal
Research on the role of the BNST in the etiology of PTSD is lacking despite its well-known implications in threat detection and anxious arousal [16]. To our knowledge, only one other study has investigated the relationship between BNST rsFC and PTSD [9], and the present study is the first to identify the BNST as a potential marker of risk for future PTSD development. We posit altered BNST rsFC may confer risk for PTSD due to its role in promoting prolonged states of heightened arousal and threat vigilance, which are known risk factors of PTSD [20].
Rabellino et al. (2018) found individuals with PTSD tend to exhibit heightened BNST activity at rest, which is associated with hyperarousal and hypervigilant threat monitoring [17, 19]. Similarly, participants from the current study with more severe PTSD symptoms at the six-month follow-up tended to exhibit greater BNST rsFC with the PCC, hippocampus, precuneus, and the LAG, which are all nodes of the default mode network (DMN). The DMN is primarily active during states of wakeful rest [50], and research suggests rsFC within the DMN is crucial for fear extinction recall as well as other processes that promote post-traumatic growth [22, 51]. However, a meta-analysis found individuals with PTSD consistently exhibit lower rsFC within the DMN and greater rsFC between the DMN and threat-processing regions of the brain compared to healthy controls [51]. Considering the opposing functions of the BNST (i.e., arousal and vigilance) and the DMN (i.e. wakeful rest), it is possible greater BNST rsFC diminishes intrinsic DMN rsFC. Thus, greater BNST rsFC may increase risk for PTSD by impairing fear extinction recall and other DMN-related processes that support post-traumatic growth.
In the acute aftermath of a traumatic event, heightened rsFC between the BNST and nodes of default mode network (DMN) may reflect a shift in focus from internally directed processes to externally oriented threat monitoring (underlying hyperarousal/hypervigilance). Although the DMN as a whole is primarily implicated in non-goal-oriented, self-referential tasks (e.g., daydreaming), the individual structures that compose the DMN also support processes related to threat monitoring. For instance, the hippocampus, PCC, and precuneus are implicated in hypervigilant threat appraisal and fear expression [52, 53], while the angular gyrus is involved in sensory processing and modulating attention during goal-oriented tasks [54]. Individuals at risk for PTSD may struggle to inhibit their fear response in contextually safe situations following a traumatic event, which can lead to prolonged states of hyperarousal and hypervigilant threat monitoring, [21, 23, 55] and greater BNST rsFC with nodes of the DMN may underlie these perpetual states of arousal and vigilance. However, further research is needed to delineate the neurobiological and psychological mechanisms that link acute BNST-DMN rsFC with future PTSD symptoms. Nevertheless, considering chronic hyperarousal is a risk factor for PTSD, and the identified nodes of the DMN (PCC, precuneus, hippocampus, LAG) are implicated in a variety of hyperarousal/hypervigilance related functions, there is evidence to suggest greater BNST-DMN rsFC contributes to chronic states of hyperarousal, which in turn, increases risk for PTSD.
Kindling
The current study is the first to investigate the effects of racial discrimination and previous trauma exposure (i.e., “criterion A” stressors defined within the DSM-5) on acute BNST functioning as a predictor of PTSD in Black trauma survivors. Among individuals who experienced more racial discrimination or reported a greater lifetime history of traumatic exposure, BNST rsFC was a stronger predictor of PTSD symptoms. These findings add to the growing body of research that has identified neuropsychological similarities between racial discrimination and DSM-5 defined trauma exposure in Black individuals [4, 25, 28,29,30, 35]. Both racial discrimination and prior trauma exposure may confer risk for PTSD due to a theorized “kindling effect” that increases one’s vulnerability to PTSD following subsequent trauma exposure [32, 55]. The kindling hypothesis refers to stress-induced alterations of neurobiological functioning (see Smid et al. 2022) that heighten the sensitivity of one’s threat detection system in response to repeated stressor exposure. As a result, individuals may be more likely to exhibit altered activation in threat neurocircuitry and hyperarousal symptoms following a future traumatic event.
Given the BNST’s sensitivity to chronic stressors [14, 34], kindling may help explain why BNST rsFC was a stronger predictor of PTSD symptoms for individuals who experienced more racial discrimination or had a greater history of trauma exposure. Indeed, studies show racial discrimination and trauma exposure are associated with alterations in resting-state activity in regions related to threat detection and arousal [28, 30, 56]. Furthermore, a scoping review of the literature found that kindling can lead to persistent states of hyperarousal and other prodromal symptoms of PTSD that are associated with the BNST [32]. Thus, recurrent experiences of racial discrimination or “criterion A” events may “prime” the BNST to be in a heightened state following subsequent trauma exposure.
Limitations
The current study has a couple noteworthy limitations. First, most participants experienced a motor vehicle accident, which usually result in less severe outcomes compared to interpersonal traumas [57, 58]. Accordingly, less than 20% of the sample had clinically significant levels of PTSD at the six-month follow-up (i.e., met CAPS-5 criteria for current PTSD diagnosis). While it is expected to observe natural resilience/recovery [58], the low average CAPS-5 scores may limit the generalizability of these findings to individuals with more severe PTSD symptoms. However, considering the role of the BNST in arousal and vigilance [16], as well as previous research implicating the BNST in the etiology of PTSD [7,8,9], we hypothesize the results would be more robust in samples that consist of individuals who only had clinically significant levels of PTSD six-months post-trauma. Additionally, the PEDQ and LEC-5 are retrospective measures, which makes them susceptible to bias in the respondents’ memory [59]. Nevertheless, current findings are consistent with the literature on the relationship between racial discrimination and PTSD symptoms, as well as prior work within this sample [4, 30, 35]. Furthermore, the reliability is substantiated by the use of the CAPS-5, which is the “gold standard” measurement for PTSD [41]. Lastly, BNST functioning was only assessed post-trauma. Considering the proposed kindling effect of racism-related stress, as well as the known impact of stress on BNST activity, it is unclear to what extent the alterations in BNST rsFC would be visible prior to the index trauma. Therefore, future directions include disentangling the effects of racialized stress on BNST function in typical controls.
Conclusion
Our results suggest the BNST may be a compelling biomarker that can predict the onset and severity of PTSD. The present study extends previous research by highlighting the potential role of the BNST in the etiology of PTSD, as well as its sensitivity to lived experiences. In the immediate aftermath of a traumatic event, the BNST appears to be a salient marker of risk for PTSD in Black Americans, particularly for individuals with a greater history of racial discrimination or previous traumatic exposure (i.e., to DSM-5 “criterion A” stressors). Given the role of the BNST in modulating arousal and threat monitoring, greater BNST rsFC could underlie chronic symptoms of hyperarousal and hypervigilance, which are known to play a prominent role in the etiology of PTSD. Alterations in BNST functioning may also explain why Black Americans who experience more racial discrimination are at an increased risk for more severe PTSD symptoms [26].
More broadly, lifetime exposure to racial discrimination and DSM-5 defined trauma exposure may similarly moderate neural markers of risk for PTSD in Black Americans. Our findings highlight the importance of incorporating racial discrimination, and more generally racialized stress, into trauma neuroscience research. Future research should continue to explore the relationship between BNST functioning, racial discrimination, and PTSD, as well as any potential kindling effects in the BNST that are caused by racial discrimination. Despite the limited research in humans, the BNST appears to be a promising marker of risk for PTSD, and it is important that future research continues to explore its utility.
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Jones AL, Rafferty J, Cochran SD, Abelson J, Hanna MR, Mays VM. Prevalence, Severity and Burden of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Black Men and Women Across the Adult Life span. J Aging Health. 2022;34:401–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/08982643221086071
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596
Colvonen PJ, Glassman LH, Crocker LD, Buttner MM, Orff H, Schiehser D, et al. Pretreatment biomarkers predicting PTSD psychotherapy outcomes: A systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017;75:140–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.01.027
Bird CM, Webb EK, Schramm AT, Torres L, Larson C, deRoon‐Cassini TA. Racial Discrimination is Associated with Acute Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms and Predicts Future Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptom Severity in Trauma‐Exposed Black Adults in the United States. J Trauma Stress. 2021;34:995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.22670
Schultebraucks K, Qian M, Abu-Amara D, Dean K, Laska E, Siegel C, et al. Pre-deployment risk factors for PTSD in active-duty personnel deployed to Afghanistan: a machine-learning approach for analyzing multivariate predictors. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:5011–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0789-2
Hughes KC, Shin LM. Functional neuroimaging studies of post-traumatic stress disorder. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011;11:275–85. https://doi.org/10.1586/ern.10.198
Awasthi S, Pan H, LeDoux JE, Cloitre M, Altemus M, McEwen B, et al. The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and functionally linked neurocircuitry modulate emotion processing and HPA axis dysfunction in posttraumatic stress disorder. NeuroImage Clin. 2020;28:102442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102442
Brinkmann L, Buff C, Neumeister P, Tupak SV, Becker MP, Herrmann MJ, et al. Dissociation between amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis during threat anticipation in female post-traumatic stress disorder patients: Threat Anticipation in PTSD. Hum Brain Mapp. 2017;38:2190–205. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23513
Rabellino D, Densmore M, Harricharan S, Jean T, McKinnon MC, Lanius RA. Resting-state functional connectivity of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in post-traumatic stress disorder and its dissociative subtype. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018;39:1367–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23925
Forray MI, Gysling K. Role of noradrenergic projections to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. Brain Res Rev. 2004;47:145–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.07.011
Weis CN, Huggins AA, Bennett KP, Parisi EA, Larson CL. High-Resolution Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Extended Amygdala. Brain Connect. 2019;9:627–37. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2019.0688
Dong HW, Swanson LW. Projections from bed nuclei of the stria terminalis, dorsomedial nucleus: Implications for cerebral hemisphere integration of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and drinking responses. J Comp Neurol. 2006;494:75–107. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20790
Goode TD, Maren S. Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in aversive learning and memory. Learn Mem. 2017;24:480–91. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.044206.116
Hammack SE, Roman CW, Lezak KR, Kocho-Shellenberg M, Grimmig B, Falls WA, et al. Roles for Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Peptide (PACAP) Expression and Signaling in the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) in Mediating the Behavioral Consequences of Chronic Stress. J Mol Neurosci. 2010;42:327–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9364-7
Miles OW, Maren S. Role of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis in PTSD: Insights From Preclinical Models. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019;13:68. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00068
Lebow MA, Chen A. Overshadowed by the amygdala: the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis emerges as key to psychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21:450–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.1
Avery SN, Clauss JA, Blackford JU. The Human BNST: Functional Role in Anxiety and Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016;41:126–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.185
Somerville LH, Whalen PJ, Kelley WM. Human Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis Indexes Hypervigilant Threat Monitoring. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;68:416–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.04.002
Knight LK, Depue BE. New Frontiers in Anxiety Research: The Translational Potential of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:510. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00510
Schell TL, Marshall GN, Jaycox LH. All Symptoms Are Not Created Equal: The Prominent Role of Hyperarousal in the Natural Course of Posttraumatic Psychological Distress. J Abnorm Psychol. 2004;113:189–97. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.113.2.189
Christianson JP, Fernando ABP, Kazama AM, Jovanovic T, Ostroff LE, Sangha S. Inhibition of Fear by Learned Safety Signals: A Mini-Symposium Review. J Neurosci. 2012;32:14118–24. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3340-12.2012
Miller DR, Hayes SM, Hayes JP, Spielberg JM, Lafleche G, Verfaellie M. Default Mode Network Subsystems Are Differentially Disrupted in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2017;2:363–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2016.12.006
Jovanovic T, Norrholm SD Neural Mechanisms of Impaired Fear Inhibition in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Front Behav Neurosci. 2011;5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00044
Joseph NT, Peterson LM, Gordon H, Kamarck TW. The double burden of racial discrimination in daily-life moments: Increases in negative emotions and depletion of psychosocial resources among emerging adult African Americans. Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. 2021;27:234–44. https://doi.org/10.1037/cdp0000337
Carter RT, Kirkinis K, Johnson VE. Relationships between trauma symptoms and race-based traumatic stress. Traumatology. 2020;26:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/trm0000217
Carter RT. Racism and Psychological and Emotional Injury: Recognizing and Assessing Race-Based Traumatic Stress. Couns Psychol. 2007;35:13–105. https://doi.org/10.1177/0011000006292033
Webb EK, Carter SE, Ressler KJ, Fani N, Harnett NG. The neurophysiological consequences of racism-related stressors in Black Americans. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024;161:105638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105638
Clark US, Miller ER, Hegde RR. Experiences of Discrimination Are Associated With Greater Resting Amygdala Activity and Functional Connectivity. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2018;3:367–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2017.11.011
Fani N, Carter SE, Harnett NG, Ressler KJ, Bradley B. Association of Racial Discrimination With Neural Response to Threat in Black Women in the US Exposed to Trauma. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:1005. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.1480
Webb EK, Bird CM, deRoon-Cassini TA, Weis CN, Huggins AA, Fitzgerald JM, et al. Racial Discrimination and Resting-State Functional Connectivity of Salience Network Nodes in Trauma-Exposed Black Adults in the United States. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2144759 https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.44759
Hicken MT, Lee H, Ailshire J, Burgard SA, Williams DR. “Every Shut Eye, Ain’t Sleep”: The Role of Racism-Related Vigilance in Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Sleep Difficulty. Race Soc Probl. 2013;5:100–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12552-013-9095-9
Smid GE, Lind J, Bonde JP. Neurobiological mechanisms underlying delayed expression of posttraumatic stress disorder: A scoping review. World J Psychiatry. 2022;12:151–68. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.151
Jang KL, Taylor S, Stein MB, Yamagata S. Trauma Exposure and Stress Response: Exploration of Mechanisms of Cause and Effect. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2007;10:564–72. https://doi.org/10.1375/twin.10.4.564
Roman CW, Lezak KR, Hartsock MJ, Falls WA, Braas KM, Howard AB, et al. PAC1 receptor antagonism in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) attenuates the endocrine and behavioral consequences of chronic stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014;47:151–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.05.014
Harb F, Bird CM, Webb EK, Torres L, deRoon-Cassini TA, Larson CL. Experiencing racial discrimination increases vulnerability to PTSD after trauma via peritraumatic dissociation. Eur J Psychotraumatology. 2023;14:2211486. https://doi.org/10.1080/20008066.2023.2211486
Dorrington S, Zavos H, Ball H, McGuffin P, Rijsdijk F, Siribaddana S, et al. Trauma, post-traumatic stress disorder and psychiatric disorders in a middle-income setting: prevalence and comorbidity. Br J Psychiatry. 2014;205:383–9. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.113.141796
Sternbach GL. The Glasgow Coma Scale. J Emerg Med. 2000;19:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0736-4679(00)00182-7
Blevins CA, Weathers FW, Davis MT, Witte TK, Domino JL. The Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5): Development and Initial Psychometric Evaluation: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28:489–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.22059
Weathers FW, Bovin MJ, Lee DJ, Sloan D, Schnurr PP, Kaloupek DG, et al. The Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM–5 (CAPS-5): Development and initial psychometric evaluation in military veterans. Psychol Assess. 2018;30:383–95. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000486
Bovin MJ, Marx BP, Weathers FW, Gallagher MW, Rodriguez P, Schnurr PP, et al. Psychometric properties of the PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders–Fifth Edition (PCL-5) in veterans. Psychol Assess. 2016;28:1379–91. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000254
Pupo MC, Jorge MR, Schoedl AF, Bressan RA, Andreoli SB, Mello MF, et al. The accuracy of the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) to identify PTSD cases in victims of urban violence. Psychiatry Res. 2011;185:157–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2009.11.006
Brondolo E, Kelly KP, Coakley V, Gordon T, Thompson S, Levy E, et al. The Perceived Ethnic Discrimination Questionnaire: Development and Preliminary Validation of a Community Version1. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2005;35:335–65. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2005.tb02124.x
Gray MJ, Litz BT, Hsu JL, Lombardo TW. Psychometric Properties of the Life Events Checklist. Assessment. 2004;11:330–41. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191104269954
Weis CN, Webb EK, Stevens SK, Larson CL, deRoon-Cassini TA. Scoring the Life Events Checklist: Comparison of three scoring methods. Psychol Trauma Theory Res Pract Policy. 2022;14:714–20. https://doi.org/10.1037/tra0001049
MathWorks. MATLAB.
Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Nieto-Castanon A. Conn: A Functional Connectivity Toolbox for Correlated and Anticorrelated Brain Networks. Brain Connect. 2012;2:125–41. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2012.0073
Theiss JD, Ridgewell C, McHugo M, Heckers S, Blackford JU. Manual segmentation of the human bed nucleus of the stria terminalis using 3 T MRI. NeuroImage. 2017;146:288–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.11.047
Brewin CR, Andrews B, Valentine JD. Meta-analysis of risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder in trauma-exposed adults. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2000;68:748–66. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.68.5.748
Hayes AF Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach. Third edition. The Guilford Press; 2022.
Raichle ME. The Brain’s Default Mode Network. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2015;38:433–47. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-071013-014030
Koch SBJ, Van Zuiden M, Nawijn L, Frijling JL, Veltman DJ, Olff M. ABERRANT RESTING-STATE BRAIN ACTIVITY IN POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER: A META-ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMATIC REVIEW: Theoretical Review: Brain Activity in PTSD during Rest. Depress Anxiety. 2016;33:592–605. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22478
Bremner JD, Staib LH, Kaloupek D, Southwick SM, Soufer R, Charney DS. Neural correlates of exposure to traumatic pictures and sound in Vietnam combat veterans with and without posttraumatic stress disorder: a positron emission tomography study. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;45:806–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(98)00297-2
Rougemont-Bücking A, Linnman C, Zeffiro TA, Zeidan M, Lebron-Milad K, Rodriguez-Romaguera J, et al. Altered Processing of Contextual Information during Fear Extinction in PTSD: An fMRI Study: Altered Processing of Contextual Information during Fear Extinction in PTSD. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2011;17:227–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00152.x
Zwosta K, Ruge H, Wolfensteller U. Neural mechanisms of goal-directed behavior: outcome-based response selection is associated with increased functional coupling of the angular gyrus. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015;9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00180
Waller RJ. Application of the Kindling Hypothesis to the Long-Term Effects of Racism. Soc Work Ment Health. 2003;1:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1300/J200v01n03_06
Akiki TJ, Averill CL, Abdallah CG. A Network-Based Neurobiological Model of PTSD: Evidence From Structural and Functional Neuroimaging Studies. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2017;19:81 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-017-0840-4
Thomas EA, Owens GP, Keller EM. Relationships among non‐interpersonal and interpersonal trauma types, posttraumatic stress, and posttraumatic growth. J Clin Psychol. 2021;77:2592–608. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.23190
Goldstein RB, Smith SM, Chou SP, Jung TD. et al. The epidemiology of DSM-5 posttraumatic stress disorder in the United States: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions-III. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2016;51:1137–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-016-1208-5.
Lalande KM, Bonanno GA. Retrospective memory bias for the frequency of potentially traumatic events: A prospective study. Psychol Trauma Theory Res Pract Policy. 2011;3:165–70. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020847
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH; R01MH106574), the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Faculty Research and Creative Activities Support Awards, the Clinical and Translational Science Institute, Medical College of Wisconsin, and the Injury Research Center 53at the Medical College of Wisconsin (awarded to T.A.D. R49/CE001175).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EKW, CW, and KP conducted the analyses. KP, EKW, and FH interpreted the results. KP and EKW drafted and revised the manuscript. CLL conceptualized, designed, and managed all aspects of the grant that produced the data for this manuscript. TAD and LT contributed to the study design. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript and approved of the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Petranu, K., Webb, E.K., Tomas, C.W. et al. Investigating the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis as a predictor of posttraumatic stress disorder in Black Americans and the moderating effects of racial discrimination. Transl Psychiatry 14, 337 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-024-03050-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-024-03050-3