Abstract
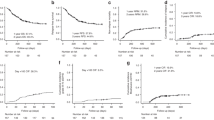
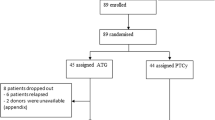
Since 2021 the use of G-CSF was implemented in allo-HCT with PTCY-based prophylaxis with the aim of shortening the aplastic phase and reducing infectious complications. This study investigates the effectiveness of this change in protocol performed at our institution. One-hundred forty-six adults undergoing allo-HCT with PTCY-based prophylaxis were included, and among them, 58 (40%) received G-CSF. The median of days to neutrophil engraftment was shorter in the G-CSF group (15 vs. 20 days, p < 0.001). Patients receiving G-CSF had a lower incidence of day +30 bacterial bloodstream infections (BSI) than the rest (20.7% vs. 47.7%, p < 0.001). GVHD, SOS, and TA-TMA incidences were comparable between groups, and using G-CSF did not impact on survival. Endothelial activation was investigated using EASIX and by the measurement of soluble biomarkers in cryopreserved plasma samples obtained on days 0, +7, +14 and +21 of 39 consecutive patients (10 received G-CSF) included in the study. EASIX, VWF:Ag, sVCAM-1, sTNFRI, ST2, REG3α, TM and NETs medians values were comparable in patients receiving G-CSF and those who did not. Compared with allo-HCT performed without G-CSF, the addition of G-CSF to PTCY-based allo-HCT accelerated neutrophil engraftment contributing on decreasing BSI incidence, and without inducing additional endothelial activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing would be only considered after specific request.
References
Pedraza A, Jorge S, Suárez-Lledó M, Pereira A, Gutiérrez-García G, Fernández-Avilés F, et al. High-dose cyclophosphamide and tacrolimus as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis for matched and mismatched unrelated donor transplantation. Transpl Cell Ther. 2021;27:619.e1–619.e8.
Salas MQ, Pedraza A, Charry P, Suárez-Lledó M, Rodríguez-Lobato LG, Brusosa M, et al. Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide and tacrolimus for graft-versus-host disease prevention after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation from HLA-matched donors has more advantages than limitations. Transpl Cell Ther. 2024;30:213.e1–213.e12.
Salas MQ, Charry P, Pedraza A, Martínez-Cibrian N, Solano MT, Domènech A, et al. PTCY and tacrolimus for GVHD prevention for older adults undergoing HLA-matched sibling and unrelated donor AlloHCT. Transpl Cell Ther. 2022;28:489.e1–489.e9.
Luznik L, O’Donnell PV, Symons HJ, Chen AR, Leffell MS, Zahurak M, et al. HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2008;14:641–50.
Nakamae H. Systematic overview of HLA-matched allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide. Int J Hematol. 2022;116:465–81.
Esquirol A, Cadenas IG, Novelli S, Garrido A, Caballero AC, Oñate G, et al. Outcome improvement over time in reduced intensity conditioning hematopoietic transplantation: a 20-year experience. Ann Hematol. 2024;103:321–34.
O’Donnell PV, Jones RJ. The development of post-transplant cyclophosphamide: Half a century of translational team science. Blood Rev. 2023;62:101034.
Salas MQ, Charry P, Puerta-Alcalde P, Martínez-Cibrian N, Solano MT, Serrahima A, et al. Bacterial bloodstream infections in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide. Transpl Cell Ther. 2022;28:850.e1–850.e10.
Little JS, Dulery R, Shapiro RM, Aleissa MM, Prockop SE, Koreth J, et al. Opportunistic infections in patients receiving post-transplantation cyclophosphamide: impact of haploidentical versus unrelated donor allograft. Transpl Cell Ther. 2023;30:233.e1–233.e14.
Fusté B, Mazzara R, Escolar G, Merino A, Ordinas A, Díaz-Ricart M. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor increases expression of adhesion receptors on endothelial cells through activation of p38 MAPK. Haematologica. 2004;89:578–85.
Fuste B, Escolar G, Marin P, Mazzara R, Ordinas A, Diaz-Ricart M. G-CSF increases the expression of VCAM-1 on stromal cells promoting the adhesion of CD34ϩ hematopoietic cells: Studies under flow conditions. Exp Hematol. 2004;32:765–72.
Link H. Current state and future opportunities in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). Support Care Cancer. 2022;30:7067–77.
Palomo M, Diaz-Ricart M, Carbo C, Rovira M, Fernandez-Aviles F, Escolar G, et al. The release of soluble factors contributing to endothelial activation and damage after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is not limited to the allogeneic setting and involves several pathogenic mechanisms. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2009;15:537–46.
Milone G, Bellofiore C, Leotta S, Milone GA, Cupri A, Duminuco A, et al. Endothelial dysfunction after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a review based on physiopathology. J Clin Med. 2022;11:623.
Carmona A, Díaz-Ricart M, Palomo M, Molina P, Pino M, Rovira M, et al. Distinct deleterious effects of cyclosporine and tacrolimus and combined tacrolimus–sirolimus on endothelial cells: protective effect of defibrotide. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013;19:1439–45.
Mercanoglu F, Turkmen A, Kocaman O, Pinarbasi B, Dursun M, Selcukbiricik F, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in renal transplant patients is closely related to serum cyclosporine levels. Transpl Proc. 2004;36:1357–60.
Eissner G, Kohlhuber F, Grell M, Ueffing M, Scheurich P, Hieke A, et al. Critical involvement of transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-cu in endothelial programmed cell death mediated by ionizing radiation and bacterial endotoxin. Blood. 1995;86:4184–93.
Ringdén O, Labopin M, Gorin NC, Le Blanc K, Rocha V, Gluckman E, et al. Treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute leukemia increases the risk of graft-versus-host disease and death: a study from the acute leukemia working party of the european group for blood and marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:416–23.
Dekker A, Bulley S, Beyene J, Dupuis LL, Doyle JJ, Sung L. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor after autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5207–15.
Palomo M, Diaz-Ricart M, Carbo C, Rovira M, Fernandez-Aviles F, Martine C, et al. Endothelial dysfunction after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: role of the conditioning regimen and the type of transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2010;16:985–93.
Palomo M, Diaz-Ricart M, Carreras E. Endothelial dysfunction in hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin Hematol Int. 2019;1:45.
Rodríguez-Lobato LG, Martínez-Roca A, Castaño-Díez S, Palomino-Mosquera A, Gutiérrez-García G, Pedraza A, et al. The avoidance of G-CSF and the addition of prophylactic corticosteroids after autologous stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients appeal for the at-home setting to reduce readmission for neutropenic fever. Palaniyandi S, editor. PLOS ONE. 2020;15:e0241778.
Gupta AK, Meena JP, Haldar P, Tanwar P, Seth R. Impact of G-CSF administration post-allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation on outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Blood Res. 2021;11:544–63.
Luft T, Dreger P, Radujkovic A. Endothelial cell dysfunction: a key determinant for the outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021;56:2326–35.
Moreno-Castaño AB, Salas MQ, Palomo M, Martinez-Sanchez J, Rovira M, Fernández-Avilés F, et al. Early vascular endothelial complications after hematopoietic cell transplantation: Role of the endotheliopathy in biomarkers and target therapies development. Front Immunol. 2022;13(Nov):1050994.
Luft T, Benner A, Jodele S, Dandoy CE, Storb R, Gooley T, et al. EASIX in patients with acute graft-versus-host disease: a retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4:e414–23.
Lia G, Giaccone L, Leone S, Bruno B. Biomarkers for early complications of endothelial origin after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: do they have a potential clinical role? Front Immunol. 2021;12:641427.
Pedraza A, Salas MQ, Rodríguez-Lobato LG, Escribano-Serrat S, Suárez-Lledo M, Martínez-Cebrian N, et al. Easix score correlates with endothelial dysfunction biomarkers and predicts risk of acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic transplantation. Transpl Cell Ther. 2024;30:187.e1–187.e12.
Kordelas L, Terzer T, Gooley T, Davis C, Sandmaier BM, Sorror M, et al. EASIX-1year and late mortality after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2023;7:5374–81.
Shouval R, Fein JA, Shouval A, Danylesko I, Shem-Tov N, Zlotnik M, et al. External validation and comparison of multiple prognostic scores in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2019;3:1881–90.
Esquirol A, Pascual MJ, Kwon M, Pérez A, Parody R, Ferra C, et al. Severe infections and infection-related mortality in a large series of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021;56:2432–44.
Carreira AS, Salas MQ, Remberger M, Basso IN, Law AD, Lam W, et al. Bloodstream infections and outcomes following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a single-center study. Transpl Cell Ther. 2022;28:50.e1–50.e8.
Remberger M, Naseh N, Aschan J, Barkholt L, LeBlanc K, Svennberg P, et al. G-CSF given after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation using HLA-identical sibling donors is associated to a higher incidence of acute GVHD II–IV. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2003;32:217–23.
Eapen M, Horowitz MM, Klein JP, Champlin RE, Loberiza FR, Ringdén O, et al. Higher mortality after allogeneic peripheral-blood transplantation compared with bone marrow in children and adolescents: the histocompatibility and alternate stem cell source working committee of the international bone marrow transplant registry. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4872–80.
Nomura S, Konishi A, Tsubokura Y, Azuma Y, Hotta M, Yoshimura H, et al. Effects of recombinant thrombomodulin on long-term prognosis after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl Immunol. 2019;57:101247.
Kashyap R, Anwer F, Areeb Iqbal M, Khalid F, Khan A, Ashar Ali M, et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant thrombomodulin for the prophylaxis of veno-occlusive complication in allogeneiccit hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2023;16:93–101.
Martinez-Sanchez J, Pascual-Diaz R, Palomo M, Moreno-Castaño AB, Ventosa H, Salas MQ, et al. Mafosfamide, a cyclophosphamide analog, causes a proinflammatory response and increased permeability on endothelial cells in vitro. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2023;58:407–13.
Arai Y, Yamashita K, Mizugishi K, Watanabe T, Sakamoto S, Kitano T, et al. Serum neutrophil extracellular trap levels predict thrombotic microangiopathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013;19:1683–9.
Nawas MT, Sanchez-Escamilla M, Devlin SM, Maloy MA, Ruiz JD, Sauter CS, Giralt SA, et al. Dynamic EASIX scores closely predict nonrelapse mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2022;6:5898–907.
Sanchez-Escamilla M, Flynn J, Devlin S, Maloy M, Fatmi SA, Tomas AA, et al. EASIX score predicts inferior survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2023;58:498–505.
Escribano-Serrat S, Rodríguez-Lobato LG, Charry P, Martínez-Cibrian N, Suárez-Lledó M, Rivero A, et al. Endothelial activation and stress index in adults undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide-based prophylaxis. Cytotherapy. 2024;26:73–80.
Acknowledgements
We thank our patients and the nursing and support staff in the Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Program and Laboratory of Hemostasis at Hospital Clinic de Barcelona.
Funding
This study was supported by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (projects: PI19/00888 and FIS PI22/00367; co-funded by the Euopean Union), Agencia de Gestión de Ayudas Universitarias y de Investigación (AGAUR 2021-SGR-01118), Deutsche José Carreras Leukämie-Stiftung (23 R/2021), and Fundació Marató de TV3 (202026-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MQS, MDR and SES designed the study, analyzed, interpreted the results and wrote the paper. SES updated the data base. BDM, JMS, AR, HVC, PG, EG and LM conducted the experimental analysis. AP, MSL, PC, BDM, JMS, AR, HVC, CM, LG, IM, GR, EC, JC, ML, EC, FFA, CM, and MR provided valuable input into the study, interpretation of the results, and statement of the conclusions. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Escribano-Serrat, S., Pedraza, A., Suárez-Lledó, M. et al. Safety and efficacy of G-CSF after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation using post-transplant cyclophosphamide: clinical and in vitro examination of endothelial activation. Bone Marrow Transplant 59, 1466–1476 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-024-02388-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-024-02388-y