Abstract
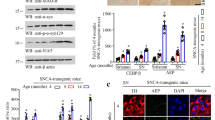
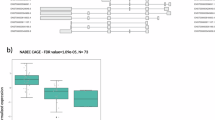
α-Synuclein is the main component of Lewy bodies, the intracellular protein aggregates representing the histological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease. Elevated α-synuclein levels and mutations in SNCA gene are associated with increased risk for Parkinson’s disease. Despite this, little is known about the molecular mechanisms regulating SNCA transcription. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) β and δ are b-zip transcription factors that play distinct roles in neurons and glial cells. C/EBPβ overexpression increases SNCA expression in neuroblastoma cells and putative C/EBPβ and δ binding sites are present in the SNCA genomic region suggesting that these proteins could regulate SNCA transcription. Based on these premises, the goal of this study was to determine if C/EBPβ and δ regulate the expression of SNCA. We first observed that α-synuclein CNS expression was not affected by C/EBPβ deficiency but it was markedly increased in C/EBPδ-deficient mice. This prompted us to characterize further the role of C/EBPδ in SNCA transcription. C/EBPδ absence led to the in vivo increase of α-synuclein in all brain regions analyzed, both at mRNA and protein level, and in primary neuronal cultures. In agreement with this, CEBPD overexpression in neuroblastoma cells and in primary neuronal cultures markedly reduced SNCA expression. ChIP experiments demonstrated C/EBPδ binding to the SNCA genomic region of mice and humans and luciferase experiments showed decreased expression of a reporter gene attributable to C/EBPδ binding to the SNCA promoter. Finally, decreased CEBPD expression was observed in the substantia nigra and in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons from Parkinson patients resulting in a significant negative correlation between SNCA and CEBPD levels. This study points to C/EBPδ as an important repressor of SNCA transcription and suggests that reduced C/EBPδ neuronal levels could be a pathogenic factor in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies and C/EBPδ activity a potential pharmacological target for these neurological disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–7.
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet. 1998;18:106–8.
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, et al. The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:164–73.
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science. 2003;302:841.
Ibanez P, Bonnet AM, Debarges B, Lohmann E, Tison F, Pollak P, et al. Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2004;364:1169–71.
Ibanez P, Lesage S, Janin S, Lohmann E, Durif F, Destee A, et al. Alpha-synuclein gene rearrangements in dominantly inherited parkinsonism: frequency, phenotype, and mechanisms. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:102–8.
Ahn TB, Kim SY, Kim JY, Park SS, Lee DS, Min HJ, et al. alpha-Synuclein gene duplication is present in sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2008;70:43–49.
Ross OA, Braithwaite AT, Skipper LM, Kachergus J, Hulihan MM, Middleton FA, et al. Genomic investigation of alpha-synuclein multiplication and parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 2008;63:743–50.
Kingsbury AE, Daniel SE, Sangha H, Eisen S, Lees AJ, Foster OJ. Alteration in alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2004;19:162–70.
Tan EK, Chandran VR, Fook-Chong S, Shen H, Yew K, Teoh ML, et al. Alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2005;20:620–3.
Chiba-Falek O, Nussbaum RL. Effect of allelic variation at the NACP-Rep1 repeat upstream of the alpha-synuclein gene (SNCA) on transcription in a cell culture luciferase reporter system. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:3101–9.
Touchman JW, Dehejia A, Chiba-Falek O, Cabin DE, Schwartz JR, Orrison BM, et al. Human and mouse alpha-synuclein genes: comparative genomic sequence analysis and identification of a novel gene regulatory element. Genome Res. 2001;11:78–86.
Maraganore DM, de Andrade M, Elbaz A, Farrer MJ, Ioannidis JP, Kruger R, et al. Collaborative analysis of alpha-synuclein gene promoter variability and Parkinson disease. JAMA. 2006;296:661–70.
Mata IF, Shi M, Agarwal P, Chung KA, Edwards KL, Factor SA, et al. SNCA variant associated with Parkinson disease and plasma alpha-synuclein level. Arch Neurol. 2010;67:1350–6.
Fernandez-Santiago R, Garrido A, Infante J, Gonzalez-Aramburu I, Sierra M, Fernandez M, et al. alpha-synuclein (SNCA) but not dynamin 3 (DNM3) influences age at onset of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) Parkinson’s disease in Spain. Mov Disord. 2018;33:637–41.
Kirik D, Annett LE, Burger C, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ, Bjorklund A. Nigrostriatal alpha-synucleinopathy induced by viral vector-mediated overexpression of human alpha-synuclein: a new primate model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:2884–9.
Kirik D, Rosenblad C, Burger C, Lundberg C, Johansen TE, Muzyczka N, et al. Parkinson-like neurodegeneration induced by targeted overexpression of alpha-synuclein in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurosci. 2002;22:2780–91.
Shimshek DR, Schweizer T, Schmid P, van der Putten PH. Excess alpha-synuclein worsens disease in mice lacking ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1. Sci Rep. 2012;2:262.
Recasens A, Dehay B, Bove J, Carballo-Carbajal I, Dovero S, Perez-Villalba A, et al. Lewy body extracts from Parkinson disease brains trigger alpha-synuclein pathology and neurodegeneration in mice and monkeys. Ann Neurol. 2014;75:351–62.
Devine MJ, Gwinn K, Singleton A, Hardy J. Parkinson’s disease and alpha-synuclein expression. Mov Disord. 2011;26:2160–8.
Piper DA, Sastre D, Schule B. Advancing Stem Cell Models of Alpha-Synuclein Gene Regulation in Neurodegenerative Disease. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:199.
Clough RL, Dermentzaki G, Stefanis L. Functional dissection of the alpha-synuclein promoter: transcriptional regulation by ZSCAN21 and ZNF219. J Neurochem. 2009;110:1479–90.
Brenner S, Wersinger C, Gasser T. Transcriptional regulation of the alpha-synuclein gene in human brain tissue. Neurosci Lett. 2015;599:140–5.
Dermentzaki G, Paschalidis N, Politis PK, Stefanis L. Complex Effects of the ZSCAN21 Transcription Factor on Transcriptional Regulation of alpha-Synuclein in Primary Neuronal Cultures and in Vivo. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:8756–72.
Scherzer CR, Grass JA, Liao Z, Pepivani I, Zheng B, Eklund AC, et al. GATA transcription factors directly regulate the Parkinson’s disease-linked gene alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:10907–12.
Duplan E, Giordano C, Checler F, Alves da Costa C. Direct alpha-synuclein promoter transactivation by the tumor suppressor p53. Mol Neurodegener. 2016;11:13.
Soldner F, Stelzer Y, Shivalila CS, Abraham BJ, Latourelle JC, Barrasa MI, et al. Parkinson-associated risk variant in distal enhancer of alpha-synuclein modulates target gene expression. Nature. 2016;533:95–9.
Chiba-Falek O, Kowalak JA, Smulson ME, Nussbaum RL. Regulation of alpha-synuclein expression by poly (ADP ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) binding to the NACP-Rep1 polymorphic site upstream of the SNCA gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;76:478–92.
Kfoury N, Kapatos G. Identification of neuronal target genes for CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2009;40:313–27.
Gomez-Santos C, Barrachina M, Gimenez-Xavier P, Dalfo E, Ferrer I, Ambrosio S. Induction of C/EBP beta and GADD153 expression by dopamine in human neuroblastoma cells. Relationship with alpha-synuclein increase and cell damage. Brain Res Bull. 2005;65:87–95.
Pulido-Salgado M, Vidal-Taboada JM, Saura J. C/EBPbeta and C/EBPdelta transcription factors: basic biology and roles in the CNS. Prog Neurobiol. 2015;132:1–33.
Straccia M, Gresa-Arribas N, Dentesano G, Ejarque-Ortiz A, Tusell JM, Serratosa J, et al. Pro-inflammatory gene expression and neurotoxic effects of activated microglia are attenuated by absence of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta. J Neuroinflamm. 2011;8:156.
Valente T, Straccia M, Gresa-Arribas N, Dentesano G, Tusell JM, Serratosa J, et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta regulates glial proinflammatory gene expression. Neurobiol Aging. 2013;34:2110–24.
Ejarque-Ortiz A, Medina MG, Tusell JM, Perez-Gonzalez AP, Serratosa J, Saura J. Upregulation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta in activated astrocytes and microglia. Glia. 2007;55:178–88.
Gresa-Arribas N, Serratosa J, Saura J, Sola C. Inhibition of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta expression by chrysin in microglial cells results in anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. J Neurochem. 2010;115:526–36.
Wang W, Stock RE, Gronostajski RM, Wong YW, Schachner M, Kilpatrick DL. A role for nuclear factor I in the intrinsic control of cerebellar granule neuron gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:53491–7.
Fernandez-Santiago R, Carballo-Carbajal I, Castellano G, Torrent R, Richaud Y, Sanchez-Danes A, et al. Aberrant epigenome in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons from Parkinson’s disease patients. EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7:1529–46.
Sanchez-Danes A, Richaud-Patin Y, Carballo-Carbajal I, Jimenez-Delgado S, Caig C, Mora S, et al. Disease-specific phenotypes in dopamine neurons from human iPS-based models of genetic and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4:380–95.
Sanchez-Danes A, Consiglio A, Richaud Y, Rodriguez-Piza I, Dehay B, Edel M, et al. Efficient generation of A9 midbrain dopaminergic neurons by lentiviral delivery of LMX1A in human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum Gene Ther. 2012;23:56–69.
Valente T, Mancera P, Tusell JM, Serratosa J, Saura J. C/EBPbeta expression in activated microglia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33:2186–99.
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24:197–211.
Compta Y, Valente T, Saura J, Segura B, Iranzo A, Serradell M, et al. Correlates of cerebrospinal fluid levels of oligomeric- and total-alpha-synuclein in premotor, motor and dementia stages of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2015;262:294–306.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Aguilera C, Hoya-Arias R, Haegeman G, Espinosa L, Bigas A. Recruitment of IkappaBalpha to the hes1 promoter is associated with transcriptional repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:16537–42.
Iwai A, Masliah E, Yoshimoto M, Ge N, Flanagan L, de Silva HA, et al. The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron. 1995;14:467–75.
Guhathakurta S, Bok E, Evangelista BA, Kim YS. Deregulation of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: Insight from epigenetic structure and transcriptional regulation of SNCA. Prog Neurobiol. 2017;154:21–36.
Ko CY, Chang WC, Wang JM. Biological roles of CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein delta during inflammation. J Biomed Sci. 2015;22:6.
Lutzenberger M, Burwinkel M, Riemer C, Bode V, Baier M. Ablation of CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein delta (C/EBPD): increased plaque burden in a murine Alzheimer’s disease model. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0134228.
Chu YY, Ko CY, Wang WJ, Wang SM, Gean PW, Kuo YM, et al. Astrocytic CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta regulates neuronal viability and spatial learning ability via miR-135a. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53:4173–88.
Tong Y, Zhou J, Mizutani J, Fukuoka H, Ren SG, Gutierrez-Hartmann A, et al. CEBPD suppresses prolactin expression and prolactinoma cell proliferation. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25:1880–91.
Lai HY, Hsu LW, Tsai HH, Lo YC, Yang SH, Liu PY, et al. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta promotes intracellular lipid accumulation in M1 macrophages of vascular lesions. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113:1376–88.
Turgeon N, Valiquette C, Blais M, Routhier S, Seidman EG, Asselin C. Regulation of C/EBPdelta-dependent transactivation by histone deacetylases in intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 2008;103:1573–83.
Laguna A, Schintu N, Nobre A, Alvarsson A, Volakakis N, Jacobsen JK, et al. Dopaminergic control of autophagic-lysosomal function implicates Lmx1b in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:826–35.
Ejarque-Ortiz A, Gresa-Arribas N, Straccia M, Mancera P, Sola C, Tusell JM, et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta in microglial activation. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88:1113–23.
Sterneck E, Paylor R, Jackson-Lewis V, Libbey M, Przedborski S, Tessarollo L, et al. Selectively enhanced contextual fear conditioning in mice lacking the transcriptional regulator CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:10908–13.
Arguello AA, Ye X, Bozdagi O, Pollonini G, Tronel S, Bambah-Mukku D, et al. CCAAT enhancer binding protein delta plays an essential role in memory consolidation and reconsolidation. J Neurosci. 2013;33:3646–58.
Winner B, Regensburger M, Schreglmann S, Boyer L, Prots I, Rockenstein E, et al. Role of alpha-synuclein in adult neurogenesis and neuronal maturation in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci. 2012;32:16906–16.
Taguchi K, Watanabe Y, Tsujimura A, Tatebe H, Miyata S, Tokuda T, et al. Differential expression of alpha-synuclein in hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e89327.
Cardinaux JR, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ. Pro-inflammatory cytokines induce the transcription factors C/EBPbeta and C/EBPdelta in astrocytes. Glia. 2000;29:91–7.
Taubenfeld SM, Wiig KA, Monti B, Dolan B, Pollonini G, Alberini CM. Fornix-dependent induction of hippocampal CCAAT enhancer-binding protein [beta] and [delta] co-localizes with phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein and accompanies long-term memory consolidation. J Neurosci. 2001;21:84–91.
Ramberg V, Tracy LM, Samuelsson M, Nilsson LN, Iverfeldt K. The CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) delta is differently regulated by fibrillar and oligomeric forms of the Alzheimer amyloid-beta peptide. J Neuroinflamm. 2011;8:34.
Akar CA, Feinstein DL. Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by sumoylation. J Neuroinflamm. 2009;6:12.
Tang Y, Pacary E, Freret T, Divoux D, Petit E, Schumann-Bard P, et al. Effect of hypoxic preconditioning on brain genomic response before and following ischemia in the adult mouse: identification of potential neuroprotective candidates for stroke. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;21:18–28.
Hirata T, Cui YJ, Funakoshi T, Mizukami Y, Ishikawa Y, Shibasaki F, et al. The temporal profile of genomic responses and protein synthesis in ischemic tolerance of the rat brain induced by repeated hyperbaric oxygen. Brain Res. 2007;1130:214–22.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Esta Sterneck (NCI, Maryland, USA) for generously providing C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ deficient mice, to Dr Knut Steffensen (Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden) for mouse C/EBPδ cDNA construct, to Drs. Karin Milde-Langosch and Birgit Gellersen (IHF, Hamburg) for human C/EBPδ cDNA construct and to Dr Ellen Gelpí (Neurological Tissue Bank of the Biobanc, Barcelona) for selection of human samples. This study was supported by grants PI10/378, PI12/709, and PI14/302 from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain, cofinanced with FEDER funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by L. Greene
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valente, T., Dentesano, G., Ezquerra, M. et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein δ is a transcriptional repressor of α-synuclein. Cell Death Differ 27, 509–524 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0368-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0368-8
This article is cited by
-
Basic biology and roles of CEBPD in cardiovascular disease
Cell Death Discovery (2025)
-
Altered expression of the immunoregulatory ligand-receptor pair CD200-CD200R1 in the brain of Parkinson’s disease patients
npj Parkinson's Disease (2022)