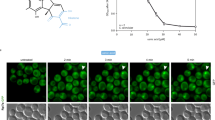
Abstract
Ribosome biogenesis is an essential, energy demanding process whose deregulation has been implicated in cancer, aging, and neurodegeneration. Ribosome biogenesis is therefore under surveillance of pathways including the p53 tumor suppressor. Here, we first performed a high-content siRNA-based screen of 175 human ribosome biogenesis factors, searching for impact on p53. Knock-down of 4 and 35 of these proteins in U2OS cells reduced and increased p53 abundance, respectively, including p53 accumulation after depletion of BYSL, DDX56, and WDR75, the effects of which were validated in several models. Using complementary approaches including subcellular fractionation, we demonstrate that endogenous human WDR75 is a nucleolar protein and immunofluorescence analysis of ectopic GFP-tagged WDR75 shows relocation to nucleolar caps under chemically induced nucleolar stress, along with several canonical nucleolar proteins. Mechanistically, we show that WDR75 is required for pre-rRNA transcription, through supporting the maintenance of physiological levels of RPA194, a key subunit of the RNA polymerase I. Furthermore, WDR75 depletion activated the RPL5/RPL11-dependent p53 stabilization checkpoint, ultimately leading to impaired proliferation and cellular senescence. These findings reveal a crucial positive role of WDR75 in ribosome biogenesis and provide a resource of human ribosomal factors the malfunction of which affects p53.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Bohnsack KE, Bohnsack MT. Uncovering the assembly pathway of human ribosomes and its emerging links to disease. EMBO J. 2019;38:e100278.
Pelletier J, Thomas G, Volarevic S. Ribosome biogenesis in cancer: new players and therapeutic avenues. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18:51–63.
Noller HF. Evolution of protein synthesis from an RNA world. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4:a003681.
Gentilella A, Kozma SC, Thomas G. A liaison between mTOR signaling, ribosome biogenesis and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1849:812–20.
Goodfellow SJ, Zomerdijk JC. Basic mechanisms in RNA polymerase I transcription of the ribosomal RNA genes. Subcell Biochem. 2013;61:211–36.
Woolford JL Jr., Baserga SJ. Ribosome biogenesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2013;195:643–81.
Ban N, Beckmann R, Cate JH, Dinman JD, Dragon F, Ellis SR, et al. A new system for naming ribosomal proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2014;24:165–169.
Zhang J, Harnpicharnchai P, Jakovljevic J, Tang L, Guo Y, Oeffinger M, et al. Assembly factors Rpf2 and Rrs1 recruit 5S rRNA and ribosomal proteins rpL5 and rpL11 into nascent ribosomes. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2580–92.
Nicolas E, Parisot P, Pinto-Monteiro C, de Walque R, De Vleeschouwer C, Lafontaine DL. Involvement of human ribosomal proteins in nucleolar structure and p53-dependent nucleolar stress. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11390.
Badertscher L, Wild T, Montellese C, Alexander LT, Bammert L, Sarazova M, et al. Genome-wide RNAi screening identifies protein modules required for 40S subunit synthesis in human cells. Cell Rep. 2015;13:2879–91.
Wild T, Horvath P, Wyler E, Widmann B, Badertscher L, Zemp I, et al. A protein inventory of human ribosome biogenesis reveals an essential function of exportin 5 in 60S subunit export. PLoS Biol. 2010;8:e1000522.
Tafforeau L, Zorbas C, Langhendries JL, Mullineux ST, Stamatopoulou V, Mullier R, et al. The complexity of human ribosome biogenesis revealed by systematic nucleolar screening of Pre-rRNA processing factors. Mol Cell. 2013;51:539–51.
Orsolic I, Jurada D, Pullen N, Oren M, Eliopoulos AG, Volarevic S. The relationship between the nucleolus and cancer: current evidence and emerging paradigms. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016;37-38:36–50.
Draptchinskaia N, Gustavsson P, Andersson B, Pettersson M, Willig TN, Dianzani I, et al. The gene encoding ribosomal protein S19 is mutated in Diamond-Blackfan anaemia. Nat Genet. 1999;21:169–75.
Volarevic S, Stewart MJ, Ledermann B, Zilberman F, Terracciano L, Montini E, et al. Proliferation, but not growth, blocked by conditional deletion of 40S ribosomal protein S6. Science. 2000;288:2045–7.
Aspesi A, Ellis SR. Rare ribosomopathies: insights into mechanisms of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19:228–38.
Lindstrom MS, Jurada D, Bursac S, Orsolic I, Bartek J, Volarevic S. Nucleolus as an emerging hub in maintenance of genome stability and cancer pathogenesis. Oncogene. 2018;37:2351–66.
Pestov DG, Strezoska Z, Lau LF. Evidence of p53-dependent cross-talk between ribosome biogenesis and the cell cycle: effects of nucleolar protein Bop1 on G(1)/S transition. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:4246–55.
Bursac S, Brdovcak MC, Pfannkuchen M, Orsolic I, Golomb L, Zhu Y, et al. Mutual protection of ribosomal proteins L5 and L11 from degradation is essential for p53 activation upon ribosomal biogenesis stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:20467–72.
Fumagalli S, Ivanenkov VV, Teng T, Thomas G. Suprainduction of p53 by disruption of 40S and 60S ribosome biogenesis leads to the activation of a novel G2/M checkpoint. Genes Dev. 2012;26:1028–40.
Panic L, Tamarut S, Sticker-Jantscheff M, Barkic M, Solter D, Uzelac M, et al. Ribosomal protein S6 gene haploinsufficiency is associated with activation of a p53-dependent checkpoint during gastrulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:8880–91.
Barkic M, Crnomarkovic S, Grabusic K, Bogetic I, Panic L, Tamarut S, et al. The p53 tumor suppressor causes congenital malformations in Rpl24-deficient mice and promotes their survival. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:2489–504.
Jones NC, Lynn ML, Gaudenz K, Sakai D, Aoto K, Rey JP, et al. Prevention of the neurocristopathy Treacher Collins syndrome through inhibition of p53 function. Nat Med. 2008;14:125–33.
Lohrum MAE, Ludwig RL, Kubbutat MHG, Hanlon M, Vousden KH. Regulation of HDM2 activity by the ribosomal protein L11. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:577–87.
Zhang Y, Wolf GW, Bhat K, Jin A, Allio T, Burkhart WA, et al. Ribosomal protein L11 negatively regulates oncoprotein MDM2 and mediates a p53-dependent ribosomal-stress checkpoint pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:8902–12.
Bhat KP, Itahana K, Jin A, Zhang Y. Essential role of ribosomal protein L11 in mediating growth inhibition-induced p53 activation. EMBO J. 2004;23:2402–12.
Dai MS, Lu H. Inhibition of MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation by ribosomal protein L5. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:44475–82.
Donati G, Peddigari S, Mercer CA, Thomas G. 5S ribosomal RNA is an essential component of a nascent ribosomal precursor complex that regulates the Hdm2-p53 checkpoint. Cell Rep. 2013;4:87–98.
Sloan KE, Bohnsack MT, Watkins NJ. The 5S RNP couples p53 homeostasis to ribosome biogenesis and nucleolar stress. Cell Rep. 2013;5:237–47.
Orsolic I, Bursac S, Jurada D, Drmic Hofman I, Dembic Z, Bartek J, et al. Cancer-associated mutations in the ribosomal protein L5 gene dysregulate the HDM2/p53-mediated ribosome biogenesis checkpoint. Oncogene 2020;39:3443–57.
Bursac S, Prodan Y, Pullen N, Bartek J, Volarevic S. Dysregulated ribosome biogenesis reveals therapeutic liabilities in cancer. Trends Cancer. 2021;7:57–76.
Bywater MJ, Poortinga G, Sanij E, Hein N, Peck A, Cullinane C, et al. Inhibition of RNA polymerase I as a therapeutic strategy to promote cancer-specific activation of p53. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:51–65.
Espinoza JA, Zisi A, Kanellis DC, Carreras-Puigvert J, Henriksson M, Huhn D, et al. The antimalarial drug amodiaquine stabilizes p53 through ribosome biogenesis stress, independently of its autophagy-inhibitory activity. Cell Death Differ. 2019;27:773–89.
Farley-Barnes KI, McCann KL, Ogawa LM, Merkel J, Surovtseva YV, Baserga SJ. Diverse regulators of human ribosome biogenesis discovered by changes in nucleolar number. Cell Rep. 2018;22:1923–34.
Bernstein KA, Baserga SJ. The small subunit processome is required for cell cycle progression at G1. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:5038–46.
Sulic S, Panic L, Barkic M, Mercep M, Uzelac M, Volarevic S. Inactivation of S6 ribosomal protein gene in T lymphocytes activates a p53-dependent checkpoint response. Genes Dev. 2005;19:3070–3082.
Frankum J, Moudry P, Brough R, Hodny Z, Ashworth A, Bartek J, et al. Complementary genetic screens identify the E3 ubiquitin ligase CBLC, as a modifier of PARP inhibitor sensitivity. Oncotarget. 2015;6:10746–58.
Ozdian T, Holub D, Maceckova Z, Varanasi L, Rylova G, Rehulka J, et al. Proteomic profiling reveals DNA damage, nucleolar and ribosomal stress are the main responses to oxaliplatin treatment in cancer cells. J Proteomics. 2017;162:73–85.
Evangelou K, Bartkova J, Kotsinas A, Pateras IS, Liontos M, Velimezi G, et al. The DNA damage checkpoint precedes activation of ARF in response to escalating oncogenic stress during tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:1485–1497.
Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H, et al. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1–11.
Zhou Q, Hou Z, Zuo S, Zhou X, Feng Y, Sun Y, et al. LUCAT1 promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis by targeting the ribosomal protein L40-MDM2-p53 pathway through binding with UBA52. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:1194–1207.
Lee AS, Kranzusch PJ, Cate JH. eIF3 targets cell-proliferation messenger RNAs for translational activation or repression. Nature. 2015;522:111–114.
Miyoshi M, Okajima T, Matsuda T, Fukuda MN, Nadano D. Bystin in human cancer cells: intracellular localization and function in ribosome biogenesis. Biochem J. 2007;404:373–381.
Zirwes RF, Eilbracht J, Kneissel S, Schmidt-Zachmann MS. A novel helicase-type protein in the nucleolus: protein NOH61. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:1153–1167.
Zhang F, Hamanaka RB, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Gordan JD, Dai MS, Lu H, et al. Ribosomal stress couples the unfolded protein response to p53-dependent cell cycle arrest. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:30036–30045.
Sato M, Araki N, Kumeta M, Takeyasu K, Taguchi Y, Asai T, et al. Interaction, mobility, and phosphorylation of human orthologues of WD repeat-containing components of the yeast SSU processome t-UTP sub-complex. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;91:466–475.
Wada K, Sato M, Araki N, Kumeta M, Hirai Y, Takeyasu K, et al. Dynamics of WD-repeat containing proteins in SSU processome components. Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;92:191–199.
Zhang H, Wu Z, Lu JY, Huang B, Zhou H, Xie W, et al. DEAD-Box Helicase 18 Counteracts PRC2 to Safeguard Ribosomal DNA in Pluripotency Regulation. Cell Rep. 2020;30:81–97 e87.
Prieto JL, McStay B. Recruitment of factors linking transcription and processing of pre-rRNA to NOR chromatin is UBF-dependent and occurs independent of transcription in human cells. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2041–2054.
Peltonen K, Colis L, Liu H, Trivedi R, Moubarek MS, Moore HM, et al. A targeting modality for destruction of RNA polymerase I that possesses anticancer activity. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:77–90.
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ, Howley PM. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus type-16 and type-18 promotes the degradation of P53. Cell. 1990;63:1129–1136.
Werness BA, Levine AJ, Howley PM. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990;248:76–79.
Kwon I, Xiang S, Kato M, Wu L, Theodoropoulos P, Wang T, et al. Poly-dipeptides encoded by the C9orf72 repeats bind nucleoli, impede RNA biogenesis, and kill cells. Science. 2014;345:1139–1145.
Zhou B, Wu Q, Chen G, Zhang TP, Zhao YP. NOP14 promotes proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2012;322:195–203.
Payne EM, Bolli N, Rhodes J, Abdel-Wahab OI, Levine R, Hedvat CV, et al. Ddx18 is essential for cell-cycle progression in zebrafish hematopoietic cells and is mutated in human AML. Blood. 2011;118:903–915.
Kouyama Y, Masuda T, Fujii A, Ogawa Y, Sato K, Tobo T, et al. Oncogenic splicing abnormalities induced by DEAD-Box Helicase 56 amplification in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:3132–3144.
Qiu YB, Liao LY, Jiang R, Xu M, Xu LW, Chen GG, et al. PES1 promotes the occurrence and development of papillary thyroid cancer by upregulating the ERalpha/ERbeta protein ratio. Sci Rep. 2019;9:1032.
Zheng X, Huang M, Xing L, Yang R, Wang X, Jiang R, et al. The circRNA circSEPT9 mediated by E2F1 and EIF4A3 facilitates the carcinogenesis and development of triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:73.
Schapira M, Tyers M, Torrent M, Arrowsmith CH. WD40 repeat domain proteins: a novel target class? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:773–786.
Dragon F, Gallagher JE, Compagnone-Post PA, Mitchell BM, Porwancher KA, Wehner KA, et al. A large nucleolar U3 ribonucleoprotein required for 18S ribosomal RNA biogenesis. Nature. 2002;417:967–970.
Maya-Mendoza A, Moudry P, Merchut-Maya JM, Lee M, Strauss R, Bartek J. High speed of fork progression induces DNA replication stress and genomic instability. Nature 2018;559:279–84.
Merchut-Maya JM, Bartek J, Maya-Mendoza A. Regulation of replication fork speed: Mechanisms and impact on genomic stability. DNA Repair. 2019;81:102654.
Bursac S, Brdovcak MC, Donati G, Volarevic S. Activation of the tumor suppressor p53 upon impairment of ribosome biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1842:817–830.
Uhlen M, Zhang C, Lee S, Sjostedt E, Fagerberg L, Bidkhori G, et al. A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science. 2017;357.
Funding
This project was supported by the Czech Science Foundation (grant no. 20-03457Y), the European Regional Development Fund—Project ENOCH (No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000868), the MEYS CR (Large RI Project LM2018129 - Czech-BioImaging), the Danish Cancer Society (R204-A12617-B153), the Novo Nordisk Foundation (0060590), the Danish Council for Independent Research (DFF-7016-00313), the Lundbeck Foundation (R266-2017-4289), the Swedish Research Council (VR-MH 2014-46602-117891-30), the Swedish Cancer Society (Cancerfonden): #170176, the Croatian Science Foundation (no. 2079) and the Croatian Scientific Center of Excellence for Reproductive and Regenerative Medicine (KK.01.1.1.01.0008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PM, SV, and JB designed experiments, which were performed mostly by PM. KC performed western blot analysis. SB performed cell fractionation experiments. PM, SV, and JB discussed and interpreted the results. PM, SV, and JB wrote the manuscript, which was approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by M. Oren
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moudry, P., Chroma, K., Bursac, S. et al. RNA-interference screen for p53 regulators unveils a role of WDR75 in ribosome biogenesis. Cell Death Differ 29, 687–696 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00882-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00882-0
This article is cited by
-
Cardiac repair using regenerating neonatal heart tissue-derived extracellular vesicles
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Docetaxel treatment together with CTLA-4 knockdown enhances reduction of cell viability and amplifies apoptosis stimulation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
Cytotechnology (2025)
-
Genome-wide association analysis provides genetic insights into variation of nutritional quality traits in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus
Journal of Oceanology and Limnology (2025)
-
DCAF13-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination of RNA polymerase I promotes uncontrolled proliferation in Breast Cancer
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Screening of hub genes for sepsis-induced myopathy by weighted gene co-expression network analysis and protein-protein interaction network construction
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2024)