Abstract
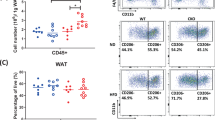
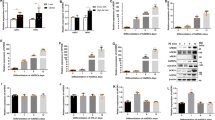
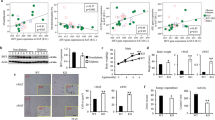
Obesity is defined as excessive white adipose tissue (WAT) expansion and adipose inflammation. HERP is a crucial member of the ERAD machine and plays a critical role in protein degradation. Nevertheless, its role in adipose tissue remains uncharacterized. Here we identify HERP as a nutrient-sensing factor. When fed a low-fat diet, both male and female HERP-KO mice exhibited adipose expansion and mild metabolic disturbances without altered body weight. Conversely, high-fat diet-fed HERP-KO mice developed exacerbated obesity, adipose expansion, and severe metabolic disorders. Further analysis revealed that HERP deficiency stimulated adipogenesis/lipogenesis and inflammation in WAT and primary adipocytes, driving the observed phenotypes. Intriguingly, chronic HFD exposure induced adipogenic/lipogenic resistance in HERP-deficient WAT. Mechanistically, HERP interacted with STEAP4 to prevent its ubiquitin-mediated degradation. HERP regulates adipogenesis through STEAP4 in a PPARγ-dependent manner. Enhancing STEAP4 expression ameliorated adipose expansion, obesity, and metabolic disorders in HERP-KO mice by suppressing adipogenesis/lipogenesis and inflammation in WAT. Clinically, HERP and STEAP4 expression inversely correlate with BMI, showing reduced levels in overweight individuals. Collectively, our study establishes HERP as a protective factor against adipose expansion and inflammation, revealing potential therapeutic strategies for obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Original uncropped western blot images have been included in the Supplementary Information.
References
Sakers A, De Siqueira MK, Seale P, Villanueva CJ. Adipose-tissue plasticity in health and disease. Cell. 2022;185:419–46.
Ghaben AL, Scherer PE. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:242–58.
Yau SW, Russo VC, Clarke IJ, Dunshea FR, Werther GA, MA Sabin. IGFBP-2 inhibits adipogenesis and lipogenesis in human visceral, but not subcutaneous, adipocytes. Int J Obes. 2015;39:770–81.
Wellen KE, Fucho R, Gregor MF, Furuhashi M, Morgan C, Lindstad T, et al. Coordinated regulation of nutrient and inflammatory responses by STAMP2 is essential for metabolic homeostasis. Cell. 2007;129:537–48.
Zhao W, Xu Q, Yang J, Xie X, Li C, Zhang W, et al. Murine double minute 2 aggravates adipose tissue dysfunction through ubiquitin-mediated six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 4 degradation. iScience. 2022;25:104544.
Kim HY, Park SY, Lee MH, Rho JH, Oh YJ, Jung HU, et al. Hepatic STAMP2 alleviates high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. J Hepatol. 2015;63:477–85.
Sikkeland J, Saatcioglu F. Differential expression and function of stamp family proteins in adipocyte differentiation. PLoS One. 2013;8:e68249.
Yan L, Liu W, Zhang H, Liu C, Shang Y, Ye Y, et al. Ube2g2-gp78-mediated HERP polyubiquitylation is involved in ER stress recovery. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:1417–27.
Schulze A, Standera S, Buerger E, Kikkert M, van Voorden S, Wiertz E, et al. The ubiquitin-domain protein HERP forms a complex with components of the endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation pathway. J Mol Biol. 2005;354:1021–7.
Leitman J, Shenkman M, Gofman Y, Shtern NO, Ben-Tal N, Hendershot LM, et al. Herp coordinates compartmentalization and recruitment of HRD1 and misfolded proteins for ERAD. Mol Biol Cell. 2014;25:1050–60.
Torrealba N, Navarro-Marquez M, Garrido V, Pedrozo Z, Romero D, Eura Y, et al. Herpud1 negatively regulates pathological cardiac hypertrophy by inducing IP3 receptor degradation. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13402.
Luo H, Cao L, Liang X, Du A, Peng T, Li H. Herp Promotes Degradation of Mutant Huntingtin: Involvement of the Proteasome and Molecular Chaperones. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55:7652–68.
Yang L, Mu Y, Cui H, Liang Y, Su X. MiR-9-3p augments apoptosis induced by H2O2 through down regulation of Herpud1 in glioma. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0174839.
Lin H, Ni T, Zhang J, Meng L, Gao F, Pan S, et al. Knockdown of Herp alleviates hyperhomocysteinemia mediated atherosclerosis through the inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype switching. Int J Cardiol. 2018;269:242–9.
Americo-Da-Silva L, Diaz J, Bustamante M, Mancilla G, Oyarzun I, Verdejo HE, et al. A new role for HERPUD1 and ERAD activation in osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. FASEB J. 2018;32:4681–95.
Eura Y, Yanamoto H, Arai Y, Okuda T, Miyata T, Kokame K. Derlin-1 deficiency is embryonic lethal, Derlin-3 deficiency appears normal, and Herp deficiency is intolerant to glucose load and ischemia in mice. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34298.
van der Laan SW, Harshfield EL, Hemerich D, Stacey D, Wood AM, Asselbergs FW. From lipid locus to drug target through human genomics. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114:1258–70.
Oh SW, Lee JE, Shin E, Kwon H, Choe EK, Choi SY, et al. Genome-wide association study of metabolic syndrome in Korean populations. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0227357.
Oh YJ, Kim HY, Lee MH, Suh SH, Choi Y, Nam TG, et al. Cilostazol Improves HFD-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Upregulating Hepatic STAMP2 Expression through AMPK. Mol Pharm. 2018;94:1401–11.
Consultation WHOE. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004;363:157–63.
An SM, Cho SH, Yoon JC. Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Health. Diab Metab J. 2023;47:595–611.
Li W, Wang Y, Zhu L, Du S, Mao J, Wang Y, et al. The P300/XBP1s/Herpud1 axis promotes macrophage M2 polarization and the development of choroidal neovascularization. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:6709–20.
Kawai T, Autieri MV, Scalia R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021;320:C375–91.
Hori O, Ichinoda F, Yamaguchi A, Tamatani T, Taniguchi M, Koyama Y, et al. Role of Herp in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Genes Cells. 2004;9:457–69.
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Petrov P, Serrano M, Ortega F, Garcia-Ruiz E, Oliver P, et al. Decreased RB1 mRNA, protein, and activity reflect obesity-induced altered adipogenic capacity in human adipose tissue. Diabetes. 2013;62:1923–31.
Mayas MD, Ortega FJ, Macias-Gonzalez M, Bernal R, Gomez-Huelgas R, Fernandez-Real JM, et al. Inverse relation between FASN expression in human adipose tissue and the insulin resistance level. Nutr Metab. 2010;7:3.
Ortega FJ, Mayas D, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Esteve E, et al. The gene expression of the main lipogenic enzymes is downregulated in visceral adipose tissue of obese subjects. Obesity. 2010;18:13–20.
Wang H, Zhang L, Chen X, Hong L, Zhao J, Qian W, et al. Adipocyte-specific Steap4 deficiency reduced thermogenesis and energy expenditure in mice. iScience. 2025;28:111903.
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Serrano M, Perez-Perez R, Sabater M, Ricart W, et al. Decreased STAMP2 expression in association with visceral adipose tissue dysfunction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:E1816–25.
ten Freyhaus H, Calay ES, Yalcin A, Vallerie SN, Yang L, Calay ZZ, et al. Stamp2 controls macrophage inflammation through nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate homeostasis and protects against atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2012;16:81–89.
Han L, Tang MX, Ti Y, Wang ZH, Wang J, Ding WY, et al. Overexpressing STAMP2 improves insulin resistance in diabetic ApoE(-)/(-)/LDLR(-)/(-) mice via macrophage polarization shift in adipose tissues. PLoS One. 2013;8:e78903.
Peng Y, Li N, Tang F, Qian C, Jia T, Liu J, et al. Corosolic acid sensitizes ferroptosis by upregulating HERPUD1 in liver cancer cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:376.
Jeon BH, Lee YH, Yun MR, Kim SH, Lee BW, Kang ES, et al. Increased expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) as a possible mechanism for the protective effect of cilostazol against hepatic steatosis. Metabolism. 2015;64:1444–53.
Min T, Qiu S, Bai Y, Cao H, Guo J, Su Z. Cilostazol Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis and Intestinal Disorders in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25:6280.
Hollander S, von Heesen M, Gabelein G, Mercier J, Laschke MW, Menger MD, et al. Perioperative treatment with cilostazol reverses steatosis and improves liver regeneration after major hepatectomy in a steatotic rat model. Sci Rep. 2025;15:2753.
Ozmen F, Ozmen MM, Gelecek S, Bilgic I, Moran M, Sahin TT. STEAP4 and HIF-1alpha gene expressions in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue of the morbidly obese patients. Mol Immunol. 2016;73:53–59.
Zhang CM, Chi X, Wang B, Zhang M, Ni YH, Chen RH, et al. Downregulation of STEAP4, a highly-expressed TNF-alpha-inducible gene in adipose tissue, is associated with obesity in humans. Acta Pharm Sin. 2008;29:587–92.
Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Rodriguez A, Ramirez B, Rotellar F, Valenti V, et al. Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 4 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin expression in visceral adipose tissue is related to iron status and inflammation in human obesity. Eur J Nutr. 2013;52:1587–95.
Arner P, Stenson BM, Dungner E, Naslund E, Hoffstedt J, Ryden M, et al. Expression of six transmembrane protein of prostate 2 in human adipose tissue associates with adiposity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2249–54.
Chen YC, Zeng XY, He Y, Liu H, Wang B, Zhou H, et al. Rutaecarpine Analogues Reduce Lipid Accumulation in Adipocytes via Inhibiting Adipogenesis/Lipogenesis with AMPK Activation and UPR Suppression. ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8:2301–11.
Chen Y, He R, Han Z, Wu Y, Wang Q, Zhu X, et al. Cooperation of ATF4 and CTCF promotes adipogenesis through transcriptional regulation. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022;38:741–63.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82000830 and 82341066); Excellent Young Researchers Program of the 5th Affiliated Hospital of SYSU (WYYXQN-2021007); the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao University Joint Laboratory of Interventional Medicine Foundation of Guangdong Province (2023LSYS001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FX, YC and QW conceived the project and designed the experiments. YC performed the experiments, processed the data, and wrote the manuscript. YW, HQ and YT assisted the animal experiments. ZH collected human subcutaneous adipose tissues.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wu, Y., Qin, H. et al. HERP constrains white adipose expansion and inflammation by STEAP4 stabilization. Cell Death Differ (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-025-01608-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-025-01608-2