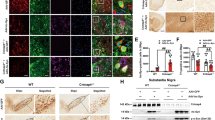
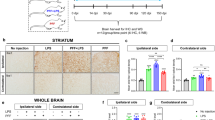
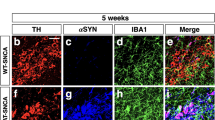
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized by the aggregation of misfolded α-synuclein (α-syn) and microglial activation. Galectin-9 (Gal-9) is an immunoregulatory mediator generated by microglia. Here, we found that α-syn fibrils are internalized by microglia and processed by microglial protease AEP, generating α-syn species with enhanced seeding activity and neurotoxicity. Notably, the uptake of α-syn fibrils by microglia leads to increased expression of Gal-9, which further promotes the production of toxic α-syn species via activation of the C/EBPβ/AEP axis. Knockout of Gal-9 attenuates α-syn pathology, dopaminergic neuronal loss, and motor impairments in a mouse model induced by intrastriatal injection of α-syn PFFs. Intrastriatal injection of Gal-9 promoted PD-like phenotypes induced by α-syn PFFs. Furthermore, the detrimental effect of Gal-9 was attenuated by the knockout of AEP. These observations illustrate the key role of Gal-9 in promoting α-syn pathology and neurodegeneration via the C/EBPβ/AEP axis in PD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Przedborski S. The two-century journey of Parkinson disease research. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18:251–9.
Luk KC, Song C, O’Brien P, Stieber A, Branch JR, Brunden KR, et al. Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:20051–6.
Cserép C, Pósfai B, Lénárt N, Fekete R, László ZI, Lele Z, et al. Microglia monitor and protect neuronal function through specialized somatic purinergic junctions. Science. 2020;367:528–37.
Gao C, Jiang J, Tan Y, Chen S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:359.
Xia Y, Zhang G, Kou L, Yin S, Han C, Hu J, et al. Reactive microglia enhance the transmission of exosomal α-synuclein via toll-like receptor 2. Brain. 2021;144:2024–37.
Bido S, Muggeo S, Massimino L, Marzi MJ, Giannelli SG, Melacini E, et al. Microglia-specific overexpression of α-synuclein leads to severe dopaminergic neurodegeneration by phagocytic exhaustion and oxidative toxicity. Nat Commun. 2021;12:6237.
Mariño KV, Cagnoni AJ, Croci DO, Rabinovich GA. Targeting galectin-driven regulatory circuits in cancer and fibrosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023;22:295–316.
Yang RY, Rabinovich GA, Liu FT. Galectins: structure, function and therapeutic potential. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008;10:e17.
John S, Mishra R. mRNA transcriptomics of galectins unveils heterogeneous organization in mouse and human brain. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016;9:139.
Jia J, Abudu YP, Claude-Taupin A, Gu Y, Kumar S, Choi SW, et al. Galectins control mTOR in response to endomembrane damage. Mol Cell. 2018;70:120–35.e128.
Jia J, Bissa B, Brecht L, Allers L, Choi SW, Gu Y, et al. AMPK, a regulator of metabolism and autophagy, is activated by lysosomal damage via a novel galectin-directed ubiquitin signal transduction system. Mol Cell. 2020;77:951–69.e959.
Liang T, Ma C, Wang T, Deng R, Ding J, Wang W, et al. Galectin-9 promotes neuronal restoration via binding TLR-4 in a rat intracerebral hemorrhage model. Neuromol Med. 2021;23:267–84.
Steelman AJ, Li J. Astrocyte galectin-9 potentiates microglial TNF secretion. J Neuroinflammation. 2014;11:144.
Duan H, Zhao S, Xiang J, Ju C, Chen X, Gramaglia I, et al. Targeting the CD146/Galectin-9 axis protects the integrity of the blood-brain barrier in experimental cerebral malaria. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:2443–54.
Wang X, Niu Y, Yue CX, Fu S, Wang RT. Increased ileal bile acid binding protein and galectin-9 are associated with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatr Res. 2019;119:102–6.
Zhang Z, Kang SS, Liu X, Ahn EH, Zhang Z, He L, et al. Asparagine endopeptidase cleaves α-synuclein and mediates pathologic activities in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017;24:632–42.
Fields J, Ghorpade A. C/EBPβ regulates multiple IL-1β-induced human astrocyte inflammatory genes. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:177.
Wang ZH, Gong K, Liu X, Zhang Z, Sun X, Wei ZZ, et al. C/EBPβ regulates delta-secretase expression and mediates pathogenesis in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1784.
Wu Z, Xia Y, Wang Z, Su Kang S, Lei K, Liu X, et al. C/EBPβ/δ-secretase signaling mediates Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis via regulating transcription and proteolytic cleavage of α-synuclein and MAOB. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:568–85.
Meng L, Zou L, Xiong M, Chen J, Zhang X, Yu T, et al. A synapsin Ⅰ cleavage fragment contributes to synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell. 2022;21:e13619.
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Lee VM. Addition of exogenous α-synuclein preformed fibrils to primary neuronal cultures to seed recruitment of endogenous α-synuclein to Lewy body and Lewy neurite-like aggregates. Nat Protoc. 2014;9:2135–46.
Pan L, Li C, Meng L, Tian Y, He M, Yuan X, et al. Tau accelerates α-synuclein aggregation and spreading in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2022;145:3454–71.
Peng C, Gathagan RJ, Covell DJ, Medellin C, Stieber A, Robinson JL, et al. Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological α-synuclein strains in α-synucleinopathies. Nature. 2018;557:558–63.
Abounit S, Delage E, Zurzolo C. Identification and characterization of tunneling nanotubes for intercellular trafficking. Current Protocols in Cell Biology. 2015;67:12.10.11–12.10.21.
Chakraborty R, Nonaka T, Hasegawa M, Zurzolo C. Tunnelling nanotubes between neuronal and microglial cells allow bi-directional transfer of α-Synuclein and mitochondria. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14:329.
Zhang Z, Song M, Liu X, Kang SS, Kwon IS, Duong DM, et al. Cleavage of tau by asparagine endopeptidase mediates the neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med. 2014;20:1254–62.
Liu Z, Sokratian A, Duda AM, Xu E, Stanhope C, Fu A, et al. Anionic nanoplastic contaminants promote Parkinson’s disease-associated α-synuclein aggregation. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eadi8716.
Mao X, Gu H, Kim D, Kimura Y, Wang N, Xu E, et al. Aplp1 interacts with Lag3 to facilitate transmission of pathologic α-synuclein. Nat Commun. 2024;15:4663.
Dorion MF, Yaqubi M, Senkevich K, Kieran NW, MacDonald A, Chen CXQ, et al. MerTK is a mediator of alpha-synuclein fibril uptake by human microglia. Brain. 2024;147:427–43.
Meng L, Liu C, Li Y, Chen G, Xiong M, Yu T, et al. The yeast prion protein Sup35 initiates α-synuclein pathology in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eadj1092.
Zhao L, Hua T, Crowley C, Ru H, Ni X, Shaw N, et al. Structural analysis of asparaginyl endopeptidase reveals the activation mechanism and a reversible intermediate maturation stage. Cell Res. 2014;24:344–58.
Siew JJ, Chern Y. Microglial lectins in health and neurological diseases. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:158.
Lee C, Yu D, Kim HS, Kim KS, Chang CY, Yoon HJ, et al. Galectin-9 mediates the functions of microglia in the hypoxic brain tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2024;84:3788–802.
Yang R, Sun L, Li CF, Wang YH, Yao J, Li H, et al. Galectin-9 interacts with PD-1 and TIM-3 to regulate T cell death and is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 2021;12:832.
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:388–405.
Boza-Serrano A, Ruiz R, Sanchez-Varo R, García-Revilla J, Yang Y, Jimenez-Ferrer I, et al. Galectin-3, a novel endogenous TREM2 ligand, detrimentally regulates inflammatory response in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138:251–73.
Panda SK, Facchinetti V, Voynova E, Hanabuchi S, Karnell JL, Hanna RN, et al. Galectin-9 inhibits TLR7-mediated autoimmunity in murine lupus models. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:1873–87.
Xu WD, Huang Q, Huang AF. Emerging role of galectin family in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20:102847.
Chen ZQ, Yu H, Li HY, Shen HT, Li X, Zhang JY, et al. Negative regulation of glial Tim-3 inhibits the secretion of inflammatory factors and modulates microglia to antiinflammatory phenotype after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25:674–84.
Lerman BJ, Hoffman EP, Sutherland ML, Bouri K, Hsu DK, Liu FT, et al. Deletion of galectin-3 exacerbates microglial activation and accelerates disease progression and demise in a SOD1(G93A) mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Behav. 2012;2:563–75.
Stancic M, van Horssen J, Thijssen VL, Gabius HJ, van der Valk P, Hoekstra D, et al. Increased expression of distinct galectins in multiple sclerosis lesions. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011;37:654–71.
Shahnawaz M, Mukherjee A, Pritzkow S, Mendez N, Rabadia P, Liu X, et al. Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Nature. 2020;578:273–7.
Wang J, Dai L, Chen S, Zhang Z, Fang X, Zhang Z. Protein-protein interactions regulating α-synuclein pathology. Trends Neurosci. 2024;47:209–26.
Choi I, Zhang Y, Seegobin SP, Pruvost M, Wang Q, Purtell K, et al. Microglia clear neuron-released α-synuclein via selective autophagy and prevent neurodegeneration. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1386.
George S, Rey NL, Tyson T, Esquibel C, Meyerdirk L, Schulz E, et al. Microglia affect α-synuclein cell-to-cell transfer in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2019;14:34.
Suthar SK, Lee SY. Truncation or proteolysis of α-synuclein in Parkinsonism. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;90:101978.
Dilsizoglu Senol A, Samarani M, Syan S, Guardia CM, Nonaka T, Liv N, et al. α-Synuclein fibrils subvert lysosome structure and function for the propagation of protein misfolding between cells through tunneling nanotubes. PLOS Biology. 2021;19:e3001287.
Grudina C, Kouroupi G, Nonaka T, Hasegawa M, Matsas R, Zurzolo C. Human NPCs can degrade α-syn fibrils and transfer them preferentially in a cell contact-dependent manner possibly through TNT-like structures. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;132:104609.
Scheiblich H, Dansokho C, Mercan D, Schmidt SV, Bousset L, Wischhof L, et al. Microglia jointly degrade fibrillar alpha-synuclein cargo by distribution through tunneling nanotubes. Cell. 2021;184:5089–106.e5021.
Chen K, Martens YA, Meneses A, Ryu DH, Lu W, Raulin AC, et al. LRP1 is a neuronal receptor for α-synuclein uptake and spread. Mol Neurodegener. 2022;17:57.
Choi YR, Park SJ, Park SM. Molecular events underlying the cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein. FEBS J. 2021;288:6593–602.
Kaur U, Lee JC. Membrane interactions of α-Synuclein Probed by Neutrons and Photons. Accounts Chem Res. 2021;54:302–10.
Stykel MG, Humphries KM, Kamski-Hennekam E, Buchner-Duby B, Porte-Trachsel N, Ryan T, et al. α-Synuclein mutation impairs processing of endomembrane compartments and promotes exocytosis and seeding of α-synuclein pathology. Cell Reports. 2021;35:109099.
Badimon A, Strasburger HJ, Ayata P, Chen X, Nair A, Ikegami A, et al. Negative feedback control of neuronal activity by microglia. Nature. 2020;586:417–23.
Bartels T, De Schepper S, Hong S. Microglia modulate neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Science (New York, NY). 2020;370:66–9.
Zhao S, Umpierre AD, Wu L-J. Tuning neural circuits and behaviors by microglia in the adult brain. Trends in Neurosciences. 2024;47:181–94.
Gresa-Arribas N, Serratosa J, Saura J, Solà C. Inhibition of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein δ expression by chrysin in microglial cells results in anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. J Neurochem. 2010;115:526–36.
Pulido-Salgado M, Vidal-Taboada JM, Saura J. C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ transcription factors: basic biology and roles in the CNS. Prog Neurobiol. 2015;132:1–33.
Qi H, Li Y, Liu X, Jiang Y, Li Z, Xu X, et al. Tim-3 regulates the immunosuppressive function of decidual MDSCs via the Fyn-STAT3-C/EBPβ pathway during Toxoplasma gondii infection. PLOS Pathogens. 2023;19:e1011329.
Zhang S, Liu YQ, Jia C, Lim YJ, Feng G, Xu E, et al. Mechanistic basis for receptor-mediated pathological α-synuclein fibril cell-to-cell transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2011196118.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82271447 and 81771382 to ZZ, No. 81901090 to LM, No. 82301598 to GZ), the Innovative Research Groups of Hubei Province (2022CFA026 to ZZ), Shenzhen Medical Research Fund (B2404001 to ZZ), and the New 20 Terms of Universities in Jinan grant (No. 202228022 to SL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZ conceived and supervised the project. QP performed the majority of experiments and data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. GZ conducted experiments involving primary neurons, developed methodology, and revised the paper. XG, YL, and LP performed the immunostaining of mouse brain sections. LM and JX helped with the cell culture and animal experiments. XX and SL helped in the analysis and interpretation of data. All authors critically read and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All of the animal experiments were performed by the relevant guidelines and regulations and were approved by the ethical committees of Renmin Hospital, Wuhan University.
Consent for publication
All authors have consented for the publication of manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Q., Zhang, G., Guo, X. et al. Galectin-9 activates microglial asparagine endopeptidase and promotes α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Differ (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-025-01640-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-025-01640-2