Abstract
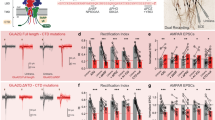
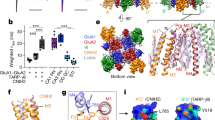
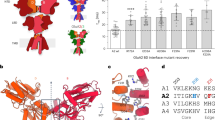
In response to stimuli, the immediate early gene product Arc can acutely down-regulate synaptic strength by removing AMPA receptors (AMPARs) from synapses and thus regulate synaptic plasticity. How Arc, a scaffold protein, can specifically facilitate synaptic removal of AMPARs is unknown. We found that Arc directly antagonizes with PSD-95 in binding to TARPs, which are the auxiliary subunits of AMPARs. Arc, in a highly concentration-sensitive manner, acutely disperses TARPs from the postsynaptic density (PSD) condensate formed via phase separation. TARPs with the Ser residue in the “P-S-Y”-motif of its tail phosphorylated are completely refractory from being dispersed by Arc, suggesting that Arc cannot displace AMPARs from PSDs in active synapses. Conversely, strengthening the interaction between Arc and TARPs enhances Arc’s capacity in weakening synapses. Thus, Arc can specifically and effectively modulate synaptic AMPAR clustering via modulating PSD phase separation. Our study further suggests that activity-dependent, bi-directional modulation of PSD condensate formation/dispersion represents a general regulatory mechanism for synaptic plasticity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Lyford, G. L. et al. Arc, a growth factor and activity-regulated gene, encodes a novel cytoskeleton-associated protein that is enriched in neuronal dendrites. Neuron 14, 433–445 (1995).
Moga, D. E. et al. Activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein is localized to recently activated excitatory synapses. Neuroscience 125, 7–11 (2004).
Steward, O., Wallace, C. S., Lyford, G. L. & Worley, P. F. Synaptic activation causes the mRNA for the IEG Arc to localize selectively near activated postsynaptic sites on dendrites. Neuron 21, 741–751 (1998).
Steward, O. & Worley, P. F. Selective targeting of newly synthesized Arc mRNA to active synapses requires NMDA receptor activation. Neuron 30, 227–240 (2001).
Link, W. et al. Somatodendritic expression of an immediate early gene is regulated by synaptic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5734–5738 (1995).
Waung, M. W., Pfeiffer, B. E., Nosyreva, E. D., Ronesi, J. A. & Huber, K. M. Rapid translation of Arc/Arg3.1 selectively mediates mGluR-dependent LTD through persistent increases in AMPAR endocytosis rate. Neuron 59, 84–97 (2008).
Maier, B., Medrano, S., Sleight, S. B., Visconti, P. E. & Scrable, H. Developmental association of the synaptic activity-regulated protein arc with the mouse acrosomal organelle and the sperm tail. Biol. Reprod. 68, 67–76 (2003).
Vazdarjanova, A. et al. Spatial exploration induces ARC, a plasticity-related immediate-early gene, only in calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-positive principal excitatory and inhibitory neurons of the rat forebrain. J. Comp. Neurol. 498, 317–329 (2006).
Okuno, H. et al. Inverse synaptic tagging of inactive synapses via dynamic interaction of Arc/Arg3.1 with CaMKIIbeta. Cell 149, 886–898 (2012).
Steward, O., Farris, S., Pirbhoy, P. S., Darnell, J. & Driesche, S. J. Localization and local translation of Arc/Arg3.1 mRNA at synapses: some observations and paradoxes. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 7, 101 (2014).
Dynes, J. L. & Steward, O. Arc mRNA docks precisely at the base of individual dendritic spines indicating the existence of a specialized microdomain for synapse-specific mRNA translation. J. Comp. Neurol. 520, 3105–3119 (2012).
Rao, V. R. et al. AMPA receptors regulate transcription of the plasticity-related immediate-early gene Arc. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 887–895 (2006).
Giorgi, C. et al. The EJC factor eIF4AIII modulates synaptic strength and neuronal protein expression. Cell 130, 179–191 (2007).
Greer, P. L. et al. The Angelman Syndrome protein Ube3A regulates synapse development by ubiquitinating arc. Cell 140, 704–716 (2010).
Chowdhury, S. et al. Arc/Arg3.1 interacts with the endocytic machinery to regulate AMPA receptor trafficking. Neuron 52, 445–459 (2006).
Rial Verde, E. M., Lee-Osbourne, J., Worley, P. F., Malinow, R. & Cline, H. T. Increased expression of the immediate-early gene arc/arg3.1 reduces AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission. Neuron 52, 461–474 (2006).
Shepherd, J. D. et al. Arc/Arg3.1 mediates homeostatic synaptic scaling of AMPA receptors. Neuron 52, 475–484 (2006).
Beique, J. C., Na, Y., Kuhl, D., Worley, P. F. & Huganir, R. L. Arc-dependent synapse-specific homeostatic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 816–821 (2011).
Guzowski, J. F. et al. Inhibition of activity-dependent arc protein expression in the rat hippocampus impairs the maintenance of long-term potentiation and the consolidation of long-term memory. J. Neurosci. 20, 3993–4001 (2000).
Park, S. et al. Elongation factor 2 and fragile X mental retardation protein control the dynamic translation of Arc/Arg3.1 essential for mGluR-LTD. Neuron 59, 70–83 (2008).
Plath, N. et al. Arc/Arg3.1 is essential for the consolidation of synaptic plasticity and memories. Neuron 52, 437–444 (2006).
Wall, M. J. et al. The temporal dynamics of Arc expression regulate cognitive flexibility. Neuron 98, 1124–1132 (2018).
Manago, F. et al. Genetic disruption of Arc/Arg3.1 in mice causes alterations in dopamine and neurobehavioral phenotypes related to schizophrenia. Cell Rep. 16, 2116–2128 (2016).
Wu, J. et al. Arc/Arg3.1 regulates an endosomal pathway essential for activity-dependent beta-amyloid generation. Cell 147, 615–628 (2011).
Peebles, C. L. et al. Arc regulates spine morphology and maintains network stability in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 18173–18178 (2010).
El-Boustani, S. et al. Locally coordinated synaptic plasticity of visual cortex neurons in vivo. Science 360, 1349–1354 (2018).
DaSilva L. L. et al. Activity-Regulated Cytoskeleton-Associated Protein Controls AMPAR Endocytosis through a Direct Interaction with Clathrin-Adaptor Protein 2. eNeuro 3, 0144–15 (2016).
Blanpied, T. A., Scott, D. B. & Ehlers, M. D. Dynamics and regulation of clathrin coats at specialized endocytic zones of dendrites and spines. Neuron 36, 435–449 (2002).
Racz, B., Blanpied, T. A., Ehlers, M. D. & Weinberg, R. J. Lateral organization of endocytic machinery in dendritic spines. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 917–918 (2004).
Zhang, W. et al. Structural basis of arc binding to synaptic proteins: implications for cognitive disease. Neuron 86, 490–500 (2015).
Zeng, M. et al. Reconstituted postsynaptic density as a molecular platform for understanding synapse formation and plasticity. Cell 174, 1172–1187 (2018).
Zeng, M. et al. Phase separation-mediated TARP/MAGUK complex condensation and AMPA receptor synaptic transmission. Neuron 104, 529–543 (2019).
Zeng, M. et al. Phase transition in postsynaptic densities underlies formation of synaptic complexes and synaptic plasticity. Cell 166, 1163–1175 (2016).
Chen, X., Wu, X., Wu, H. & Zhang, M. Phase separation at the synapse. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 301–310 (2020).
Diering, G. H. et al. Homer1a drives homeostatic scaling-down of excitatory synapses during sleep. Science 355, 511–515 (2017).
Feng, Z., Wu, X. & Zhang, M. Presynaptic bouton compartmentalization and postsynaptic density-mediated glutamate receptor clustering via phase separation. Neuropharmacology 193, 108622 (2021).
Hosokawa, T. et al. CaMKII activation persistently segregates postsynaptic proteins via liquid phase separation. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 777–785 (2021).
Nielsen, L. D., Pedersen, C. P., Erlendsson, S. & Teilum, K. The capsid domain of Arc changes its oligomerization propensity through direct interaction with the NMDA receptor. Structure 27, 1071–1081 (2019).
Opazo, P. et al. CaMKII triggers the diffusional trapping of surface AMPARs through phosphorylation of stargazin. Neuron 67, 239–252 (2010).
Park, J. et al. CaMKII phosphorylation of TARPgamma-8 is a mediator of LTP and learning and memory. Neuron 92, 75–83 (2016).
Sumioka, A., Yan, D. & Tomita, S. TARP phosphorylation regulates synaptic AMPA receptors through lipid bilayers. Neuron 66, 755–767 (2010).
Tomita, S., Stein, V., Stocker, T. J., Nicoll, R. A. & Bredt, D. S. Bidirectional synaptic plasticity regulated by phosphorylation of stargazin-like TARPs. Neuron 45, 269–277 (2005).
Hafner, A. S. et al. Lengthening of the Stargazin Cytoplasmic Tail Increases Synaptic Transmission by Promoting Interaction to Deeper Domains of PSD-95. Neuron 86, 475–489 (2015).
Inamura, M. et al. Differential localization and regulation of stargazin-like protein, gamma-8 and stargazin in the plasma membrane of hippocampal and cortical neurons. Neurosci. Res. 55, 45–53 (2006).
Tomita, S. et al. Functional studies and distribution define a family of transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins. J. Cell Biol. 161, 805–816 (2003).
Fukaya, M., Yamazaki, M., Sakimura, K. & Watanabe, M. Spatial diversity in gene expression for VDCCgamma subunit family in developing and adult mouse brains. Neurosci. Res. 53, 376–383 (2005).
Guzowski, J. F., McNaughton, B. L., Barnes, C. A. & Worley, P. F. Environment-specific expression of the immediate-early gene Arc in hippocampal neuronal ensembles. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 1120–1124 (1999).
Wallace, C. S., Lyford, G. L., Worley, P. F. & Steward, O. Differential intracellular sorting of immediate early gene mRNAs depends on signals in the mRNA sequence. J. Neurosci. 18, 26–35 (1998).
Cheng, D. et al. Relative and absolute quantification of postsynaptic density proteome isolated from rat forebrain and cerebellum. Mol. Cell Proteom. 5, 1158–1170 (2006).
Li, T. P., Song, Y., MacGillavry, H. D., Blanpied, T. A. & Raghavachari, S. Protein crowding within the postsynaptic density can impede the escape of membrane proteins. J. Neurosci. 36, 4276–4295 (2016).
Berry, K. P. & Nedivi, E. Spine dynamics: are they all the same? Neuron 96, 43–55 (2017).
Shin, S. M. et al. GKAP orchestrates activity-dependent postsynaptic protein remodeling and homeostatic scaling. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 1655–1666 (2012).
Zhu, J. et al. Synaptic targeting and function of SAPAPs mediated by phosphorylation-dependent binding to PSD-95 MAGUKs. Cell Rep. 21, 3781–3793 (2017).
Cai, Q. et al. CaMKIIalpha-driven, phosphatase-checked postsynaptic plasticity via phase separation. Cell Res. 31, 37–51 (2021).
Ashley, J. et al. Retrovirus-like Gag protein Arc1 binds RNA and traffics across synaptic boutons. Cell 172, 262–274 (2018).
Pastuzyn, E. D. et al. The neuronal gene Arc encodes a repurposed retrotransposon Gag protein that mediates intercellular RNA transfer. Cell 173, 275 (2018).
Erlendsson, S. et al. Structures of virus-like capsids formed by the Drosophila neuronal Arc proteins. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 172–175 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Minister of Science and Technology of China (2019YFA0508402), a grant from the National Science Foundation of China (82188101), grants from Research Grant Council of Hong Kong (AoE-M09-12, 16104518 and 16101419), a HFSP Research Grant (RGP0020/2019) to M.Z. and a grant from National Institute of Health (RO1 NS036715) to R.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.C., B.J., Y.A., B.L., and F.Y. performed experiments; X.C., B.J., Y.A., B.L., F.Y., R.H., and M.Z. analyzed data; X.C., B.J., Y.A., M.Z. designed the research; X.C., B.J., M.Z. drafted, all authors commented on the paper; M.Z. coordinated the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Jia, B., Araki, Y. et al. Arc weakens synapses by dispersing AMPA receptors from postsynaptic density via modulating PSD phase separation. Cell Res 32, 914–930 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-022-00697-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-022-00697-9
This article is cited by
-
Emergent mechanics of a networked multivalent protein condensate
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Phase separation-mediated biomolecular condensates and their relationship to tumor
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
BCI Improves Alcohol-Induced Cognitive and Emotional Impairments by Restoring pERK-BDNF
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2024)
-
Captive ERVWE1 triggers impairment of 5-HT neuronal plasticity in the first-episode schizophrenia by post-transcriptional activation of HTR1B in ALKBH5-m6A dependent epigenetic mechanisms
Cell & Bioscience (2023)
-
Mechanisms and Functions of Activity-Regulated Cytoskeleton-Associated Protein in Synaptic Plasticity
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)