Abstract
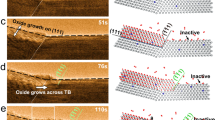
Although a multilayered metallic coatings on epoxy surfaces can enhance material performance, under acidic and salty conditions, such as sweat, the coatings usually delaminate from polymer surfaces. Therefore, we investigated the interfacial failure of a Ni/Ag/Ni coating on an epoxy surface after long-term exposure to salt spray air or artificial sweat containing abundant Cl− ions. Cross-sectional atomic force microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were used to probe the changes in the interfacial morphologies and depth profiles of the chemical composition, respectively, to elucidate the mechanism by which Ni/Ag/Ni trilayered coatings delaminate from epoxy substrates in Cl−-containing atmospheres. The results revealed that Cl− ions penetrated through the epoxy, diffused into the metal–polymer interface, and dissolved the Ni layer at the epoxy surface, detaching the metallic layer from the polymer surface. In response to the failure mechanism mentioned above, we propose that by partially replacing the Ni primer layer with Ni2O3, which is inert in acidic Cl− atmospheres, the Ni2O3/Ni/Ag/Ni coating strongly resists corrosion in salt spray air and possesses good long-term interfacial bonding under acidic Cl− atmospheres.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Lin G, Vaidya U, Wang H. Past, present and future prospective of global carbon fibre composite developments and applications. Composites Part B Eng. 2022;250:1–19.
Meng Y, Gao J, Jiang C. Component of middle frame, its preparation method and the electronic device. CN Patent. Honor Terminal Co. Ltd. 2022.
Zhang YZ, Qian, Pan Z. Hinge structure for folding model and device of foldable screen. CN Patent. Guangdong OPPO Mobile Telecommunication Corp. Ltd. 2021.
Gong H, Zhang Y. Support sheet, flexible display screen and electronic device. CN Patent. Guangdong OPPO Mobile Telecommunication Corp. Ltd. 2022.
Zhao Q, Zhang K, Zhu S, Xu H, Cao D, Zhao L, et al. Review on the electrical resistance/conductivity of carbon fiber reinforced polymer. Applied Sci. 2019;9:1–25.
Xu X, Fang J. An assembly process for copper foil on conductive tape multi-layer material. CN Patent. Kunshan Beisong Precision Electronics Co. Ltd. 2020.
Lewin RW, Spencer AG, Howson RP. A control process for stable operation of a high rate dc reactive planar magnetron sputtering system. Vacuum. 1988;38:8–10.
Sun J, Li H, Zhong Q, Huang Z, Li Y. Preparation and corrosion resistance of Ni/Cu/Zn multilayer coating. Corrosion Prot. 2017;38:928–32.
Yavuz A, Yilmaz NF, Kalkan MF. Enhancement in the corrosion resistance of nickel metal via a straightforward thermal oxidation method. J Bio Tribo Corros. 2023;9:1–10.
Harasim P, Filipek T. Nickel in the environment. J Elementol. 2014;20:525–34.
Li G, He W, Cheng Y, Li J, Zhu P. Effect of composition and concentration of artificial sweat on nickel release. Gold. 2015;10:9–12.
Zhang Y. Composite materials science. Chemical Industry Press, China; 2022.
Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Physical Rev Lett. 1986;56:930–3.
Huang H. Surface chemical analysis. East China University of Science and Technology Press, China; 2007.
Graedel TE. Corrosion mechanisms for silver exposed to the atmosphere. J Electrochem Soc. 1992;139:1963–70.
Zhou J, Lucas JP. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part I: the nature of water in epoxy. Polymer. 1999;40:5505–12.
Zhou J, Lucas JP. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part II: variations of glass transition temperature. Polymer. 1999;40:5513–22.
Jean YC. Positron annihilation spectroscopy for chemical analysis: a novel probe for microstructural analysis of polymers. Microchemical J. 1990;42:72–102.
Dang LX, Smith DE. Molecular dynamics simulations of aqueous ionic clusters using polarizable water. J Chem Phys. 1993;99:6950–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. LZ25E030001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Ding, Y., Chen, Z. et al. Quantitative characterization of the interfacial failure of metallic coatings on epoxy substrates in salty atmospheres. Polym J 57, 1015–1023 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-025-01062-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-025-01062-4